Software testing is essential to development. It saves you time and money in production mode.
But software testing is a complex topic and can be a bit difficult to understand.
In this article, I'll explain the major topics in software testing and how this practice can help you.
Table of Contents:
- What is Software Testing?
- Types of Software Testing
- Different Types of Functional Software Testing
- Software Testing Principles
- Why is Software Testing needed?
- Conclusion
What is Software Testing?
Software testing is the process of making sure your software/app works as it should. There are various methods you can use to test your code, and each testing method has different requirements.
For instance, unit testing involves writing test cases to ensure the code works as it should, and Beta testing consists of testing the preview version of the software or app to make sure users can use the product.
Software testing is integral to the process of building good software that works as it should. It also helps improve productivity and performance. Testing is an important part of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
Other benefits of testing your code include preventing bugs, reducing cost, and reducing time of development.
Types of Software Testing
There are two general types of software testing:
Functional Testing:
Functional Testing is a software testing method that validates the system against the customer's requirements or specifications.
This type of testing aims to test each function of the software by providing the correct input and ensuring the output is right.
For examples, let's say you write a test case to test creating a user. The test case provides the correct input (email, first name, last name and password) and ensures the output (success message) is accurate, as well.
Functional testing checks that everything is functioning properly by emulating business scenarios based on applicable requirements.
Non-functional Testing:
Non-functional testing is a software testing method that tests for end-user experiences, such as performance and reliability under load. This could either make or break a user experience.
When your code fails at non-functional testing, it may not cause an issue that user would note but it can flag a problem in the system.
Non-functional testing is just about testing the software to know how it responds to load on the system.
In this guide, we will focus on Functional Software Testing.
Different Types of Functional Software Testing
There are different types of software testing, and each has a specific aim. We'll look at each one quickly now.
Unit Testing:
Unit testing is a type of software testing that validates how each software unit performs and whether that specific piece of code does what it should. A unit is the smallest testable component of an application.
The aim is to confirm that each unit of software code works as expected. You do unit testing during the coding (development) stage or phase. Developers write these tests as they go.
Unit tests isolate possible bugs in your code and help you correct them. A unit could be a single function, method, procedure, module, or object.
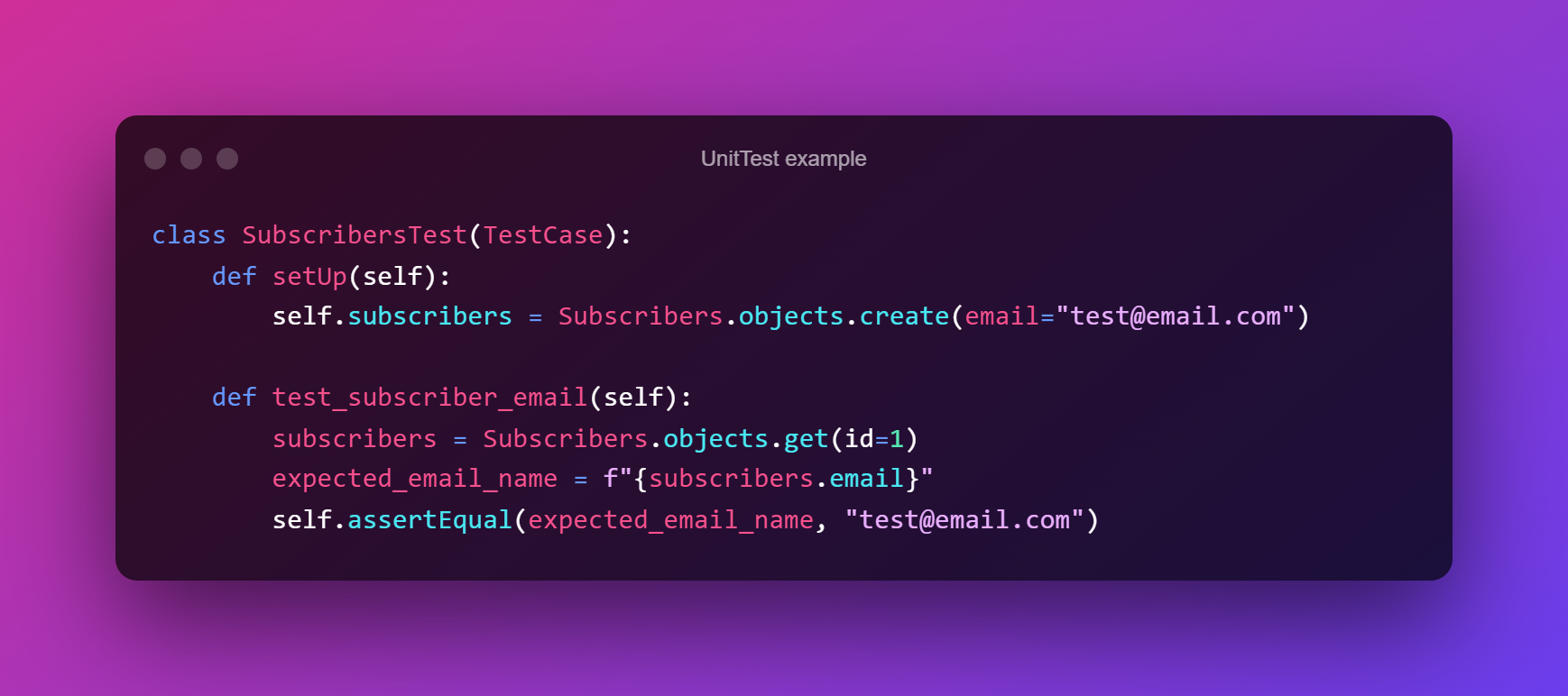
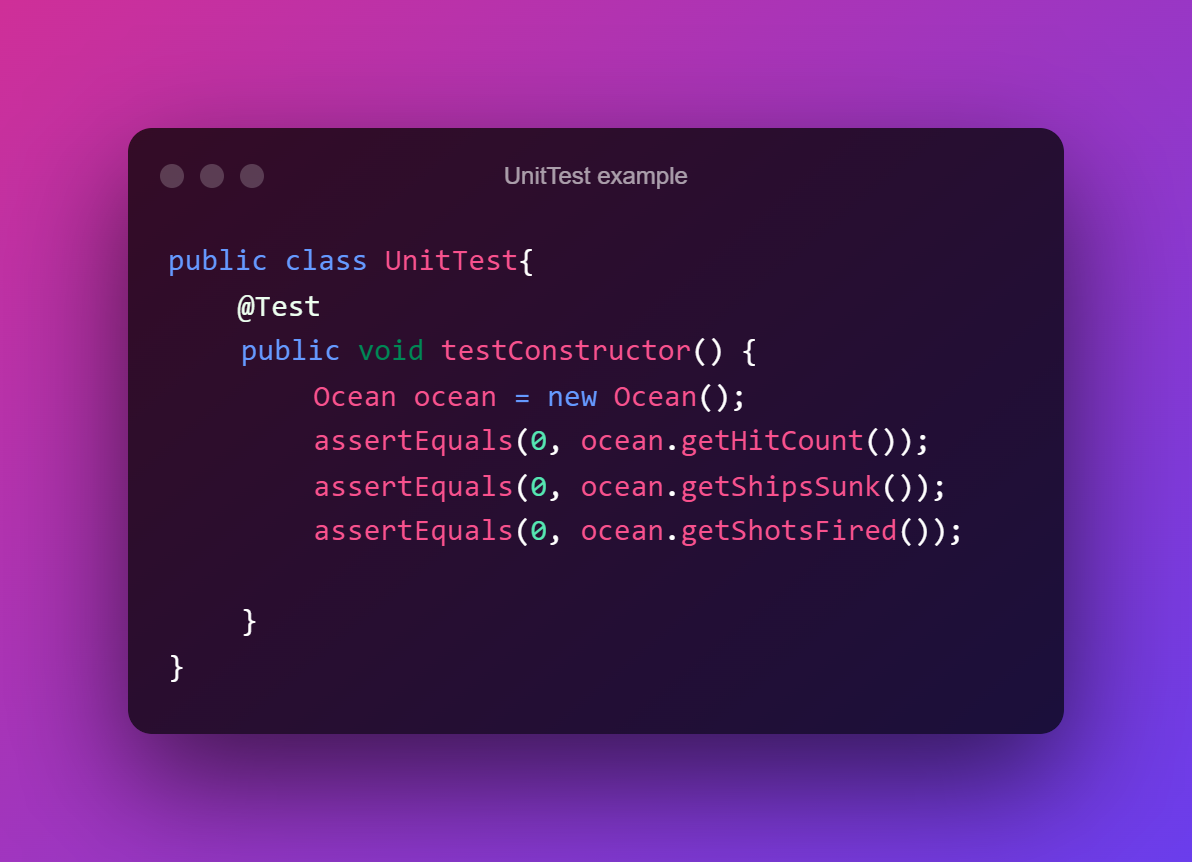
Integration Testing:
Integration Testing is software testing which helps ensure that software components or functions work together properly. This is the second phase of the software testing process that comes after unit testing.
In this type of testing, units or individual software components are tested in groups. This testing method mainly focuses on exposing defects in interactions between integrated components and units.
System Testing:
System testing involves the process of testing integrated software. The aim is to evaluate the system's compliance with specify requirements.
In system testing, the quality assurance team evaluates how each component of the application or software work together in a full, integrated environment.
Acceptance Testing:
Acceptance testing is a software testing method where a system is tested or checked for acceptability. It evaluates the system's compatibility with the business requirements and assesses whether it is acceptable for delivery.
It is also known as formal testing performed to fit user needs, requirements, and business processes. It determines if a system satisfies the standard business criteria and if users or customers will be able to accept it.
Acceptance testing is the last stage of software testing done after system testing and before making the system available for public use.
Regression Testing:
Regression testing ensures that a component continues working as it should, after including additional components in the program. You perform regression testing when something changes, such as adding a new module to the program.
This type of testing represents the complete testing of executed test cases that are re-executed to ensure the current functionalities still work just fine.
Alpha Testing and Beta Testing:
Alpha testing is also known as initial validation testing. It is an aspect of acceptance testing done before the product is given to the consumers or users. QA (Quality Assurance) testers usually do this. Alpha testing is done internally by the QA team.
Beta testing is also known as second phase of validation testing. But this type of testing is done externally, which means the public does it.
The version of the code/software for this phase of testing is released to a limited number of users for testing in a real-time scenario. For instance, freeCodeCamp's math curriculum is available for beta testing here.
Software Testing Principles
Everything in tech has principles. These are guidelines to help you build better software and avoid errors.
Here are some software testing principles you should follow when writing tests for your code:
Testing aims to show the presence of defects, not the absence:
Software testing aims to spot software failures. This reduces the presence of faults and errors.
Software testing ensures defects are visible to the developer but doesn't guarantee defect-free software. Multiple types of testing can't even ensure error-free software. Testing can only decrease the number of errors.
Exhaustive testing is not possible:
Exhaustive Testing is the process of testing software for all valid and invalid inputs and pre-conditions.
This method of testing is not realistic because test cases presume that the software is correct and it produces the correct output in every test case. If you truly try to test every aspect and test case in your software, it will take too much time and effort, and it's not practical.
Perform early testing:
Testing your software at an early phase helps avoid minor bugs or errors. When you can spot errors at an early stage of the Software Development Life Cycle(SDLC), it's always less expensive. It is best to start software testing from the beginning of the project.
Defect clustering:
Defect clustering refers to when most of the problems you find occur in just a few parts of the application or software. If you can identify the modules or areas where these defects occur, you can focus most of your testing efforts on them.
Keep the Pareto Principle in mind when testing your code: 80% of software defects tend to come from 20% of the modules.
Beware of the Pesticide paradox:
This principle is based on a theory – "the more you use pesticide on a crop, the more immune the crop will eventually grow, and the pesticide will not be effective."
When you repeat particular test cases over and over, you will see fewer and fewer new bugs. So to find new bugs, update your test cases and run them once you add new test cases.
Testing is context-dependent:
Testing is context-dependent, which means that you should test your software based on its needs, functionalities, and requirements.
Your test approach should depend on what your software does. Not every software needs the same type/method of testing because every application has its unique functionalities.
For instance, when testing an eCommerce web app, you will focus on its functionality to display products, so you will test how it shows products to end-users. When dealing with an API, you will focus on the response the API returns when an endpoint is called.
You wouldn't necessarily use the same test cases for both – that is what it means that testing is context-dependent.
The absence of errors is a fallacy:
If you build software that is 99% bug-free, but it doesn't follow user requirements, it is not usable for end-users.
Know that it is very much necessary that your 99% bug-free software still meets or fulfills your user requirements. It is important to write test cases to find errors in the code, but you also need to test your software for your end-users (with them and how they'll use it in mind). The best way to do this is to carry out beta testing.
Why is Software Testing Needed?
Besides making sure your software is bug-free and meets user requirements, software testing has other advantages.
Software testing improves security:
When building software, security is a crucial part of your planning. This is because vulnerable software could jeopardize you users and their information, as hackers can use stolen info for malicious purposes.
As a product undergoes testing, the end-user can count on the fact that they will be getting a reliable product and their details will be secured and safe. So users are more likely to get a product that is free from vulnerabilities with the help of software testing.
Software testing improves product quality:
You want your software or product to be bug-free, low-risk, and effective at what it should do. And you can achieve this by including test cases and other testing methods when building out the code.
In addition, you won't know how good your product is until you test it. This helps you provide the best product version before it gets released (and discover any inconsistencies or pain points along the way – so you can improve them).
Software testing improves customer satisfaction:
For instance, let's say you download a new app and try to use some of its functionality – but it shows an error. This will probably frustrate you, and you might not want to use the app again, right?
This is exactly why software testing is important. It can help you discover such errors and detect them before you release the product to the user, and gives the developers a chance to prevent the error.
By investing in software testing early in the development stage, you are letting the users know that you care about their experience. It could also help you create a solid long-term customer relationship.
Software testing saves money:
Software testing can save you a lot of money – but how?
Each stage of development involves many things, such as clear communication and coordination between multiple teams, and each step has a laundry list of things that could go awry.
Catching those errors when the product is live is a horrible experience because you may have to handle PR, retasking fixes, and trying to sort the problem in real time.
In addition, your users won't be able to access the app while you're fixing it, which defeats the app's purpose and provides a bad user experience in the meantime. Software testing helps resolve this stress, and once live, your user can enjoy your app/product to the fullest.
Conclusion
In conclusion, software testing is a crucial part of development. It can help save your team a lot of trouble, and it feels great to create a usable, bug-free product that users enjoy and recommend.
If software testing interests you, you can check freeCodeCamp's QA certificate course here to learn more about QA testing. QA testers are techies that focus on testing softwares and apps for errors.

