原文: How to code the Caesar Cipher: an introduction to basic encryption
恺撒密码是早期加密的一个著名实践。它会根据字母表上设定的密钥对句子进行重组加密。举个例子,密钥为3,取一个句子“I like to wear hats.”。
当这个句子使用密钥3加密后,它变成了:
L olnh wr zhdu kdwv.
这让它很难阅读并且不被查觉地传递。
虽然这是一个非常简单的加密案例,但对于学习编码的人来说,它是一个完美的练习项目。
理解加密
为了实现这个代码,至少在JAVA里,你需要思考实际要做些什么。所以,让我们看看必要的编码步骤。
步骤 1:识别句子中的字符
步骤 2:找到字符在字母表中的位置
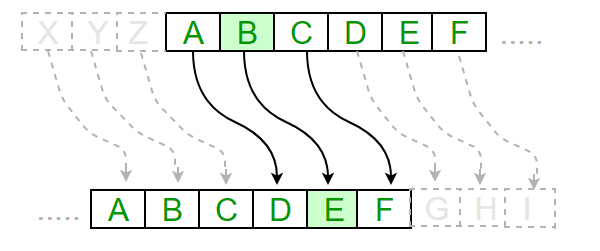
步骤 3:识别字符位置+密钥key后的位置
注意* 如果字符位置 + key > 26, 那么要从字母表的第1个字符继续循环。
步骤 4:用新字符代替原来的字符,生成一个新句子
步骤 5:重复直到达到句子原来的长度(for 循环)
步骤 6:返回结果
编码加密
当我们清楚要遵循哪些绝佳的步骤后,我们应该想一想编码时要做什么。
步骤 0:建立一个可以读取信息和密钥的函数
就像这样:
public String Encrypt(String message, int key) {
}
步骤 1:识别句子中的字符
为此,我们需要建立一张字母表用来查找字符。
创建一个包含26个字母的变量“alphabet”。
String alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
String alphabet2 = alphabet.toLowerCase();
步骤 2:找到字符在字母表中的位置
创建一个for循环来遍历消息中的每个字符。创建一个StringBuilder可以更便于我们来做这件事。
StringBuilder encrypted = new StringBuilder(message);
for (int q = 0; q < encrypted.length(); q++) {
char currchar = encrypted.charAt(q);
int index = alphabet.indexOf(currchar);
}
与此同时,我们要确保每个位置是一个字母。
if (index != -1) {
}
步骤 3:识别字符位置+密钥key后的位置
如果识别出字符是一个字母,那么我们要在修改后的字母表中找到它的位置。因此,我们需要建立一个修改后的字母表。
步骤 4:用新字符代替原来的字符,生成一个新句子
一旦我们在修改后的字母中找到了相应的值,我们应该将它设置到我们创建的StringBuilder中的相同位置。
public String Encryption(String input, int key){
StringBuilder encrypted = new StringBuilder(input);
String alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
String alphabet2 = alphabet.toLowerCase();
String keyedalphabet = alphabet.substring(key) + alphabet.substring(0, key);
for (int q = 0; q < encrypted.length(); q++) {
char currChar = encrypted.charAt(q);
int index = alphabet.indexOf(currChar);
if (index != -1) {
char newChar = keyedalphabet.charAt(index);
encrypted.setCharAt(q, newChar);
}
}
}
步骤 5:重复直到达到句子原来的长度(for 循环)
现在,我们已经检查了字符是否为大写,但我们还需要检查字符是否为小写。为此,我们需要访问之前建立的alphabet2。
index = alphabet2.indexOf(currChar);
if (index != -1) {
String keyedalphabet2 = keyedalphabet.toLowerCase();
char newChar = keyedalphabet2.charAt(index);
encrypted.setCharAt(q, newChar);
}
步骤 6:返回结果
现在,我们已经完成了For循环。剩下的就是退出循环并返回String。
public String Encryption(String input, int key){
StringBuilder encrypted = new StringBuilder(input);
String alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
String alphabet2 = alphabet.toLowerCase();
String keyedalphabet = alphabet.substring(key) + alphabet.substring(0, key);
for (int q = 0; q < encrypted.length(); q++) {
char currChar = encrypted.charAt(q);
int index = alphabet.indexOf(currChar);
if (index != -1) {
char newChar = keyedalphabet.charAt(index);
encrypted.setCharAt(q, newChar);
}
index = alphabet2.indexOf(currChar);
if (index != -1) {
String keyedalphabet2 = keyedalphabet.toLowerCase();
char newChar = keyedalphabet2.charAt(index);
encrypted.setCharAt(q, newChar);
}
}
return encrypted
}
步骤 7:调试
但是等等,不对!encrypted不是一个字符串,它是一个StringBuilder,这个函数特别要求返回一个字符串!
幸运的是,有一个非常简单的函数可以纠正这种疏忽。
public String Encryption(String input, int key){
StringBuilder encrypted = new StringBuilder(input);
String alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
String alphabet2 = alphabet.toLowerCase();
String keyedalphabet = alphabet.substring(key) + alphabet.substring(0, key);
for (int q = 0; q < encrypted.length(); q++) {
char currChar = encrypted.charAt(q);
int index = alphabet.indexOf(currChar);
if (index != -1) {
char newChar = keyedalphabet.charAt(index);
encrypted.setCharAt(q, newChar);
}
index = alphabet2.indexOf(currChar);
if (index != -1) {
String keyedalphabet2 = keyedalphabet.toLowerCase();
char newChar = keyedalphabet2.charAt(index);
encrypted.setCharAt(q, newChar);
}
}
return encrypted.toString();
}
这就是你如何得到原始句子的加密版本的方法。自己试试吧!
感谢你阅读本文!