HTML(Hyper Text Markup Language) is one of the languages we use to create web applications. It adds structure to your web pages.
HTML has various tags we use to create elements. And multiple elements come together to create meaningful web pages and applications.
The anchor tag is one of the most used and well-known tags in HTML. In this article, we will learn about the anchor tag (<a>) and its main uses with many examples.
But why talk about the anchor tag if it is already well-known? There are a few essential details of this tag that many devs don't know - but they should. So let's learn them.
I have created an app to demonstrate different behaviors of the anchor tag. You can check it out and use it as you read this article.
If you like to learn from video content as well, this article is also available as a video tutorial here: 🙂
What is the Anchor Tag in HTML?
The primary purpose of an anchor tag is to link one page to another page or to a section of the same page. The anchor tag is also known as a HyperLink. Like any other HTML tags, you use the following construct to create an anchor tag:
<a>My Website</a>The above anchor tag is a valid HTML tag, but it doesn't do much other than act as a placeholder. Let's use this anchor tag to link to a web page. You need to use the href attribute to link to another page.
<a href="https://tapasadhikary.com">My Website</a>The value of the href attribute is usually a URL pointing to a web page (like the one above). You can also link another HTML element or a protocol (for example, sending email), and you can execute JavaScript using the href attribute. We will see the examples of how to do all this below.
Anchor Tag Uses with Examples
Along with href, there are other vital attributes that make the anchor tag useful. Let's learn about them with examples.
How to link to a section of the page
We have seen how to link to an external web page (website). But you can also link to a section of the same page by linking to an element using its id. Assume our page has a div section with the id news.
<div id="news">
<h2>News</h2>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Sed non risus. Suspendisse lectus tortor, dignissim sit amet,
adipiscing nec, ultricies sed, dolor. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit.
</p>
</div>You can now link to this section (div) using the anchor tag. To do that, just use the id of the section with a # as the prefix for the href value.
<a href="#news">Go</a>So, when you click on the Go link, you will scroll to the news section of the page.

How to link to an email client
You may need to open the default email client with the email address when users click on a link. You can do this by using the mailto protocol as the href attribute's value. The syntax of the value should be in the form of mailto:<email address>.
<a href="mailto:me@example.com">Send email</a>Now clicking on the Send email link will open up the default email client on your operating system with the email address (me@example.com) specified in the TO field.
Similarly, you can use the tel:<Phone Number> construct to open up the default phone app with the phone number when someone clicks on the link.
<a href="tel:+914123456765">Call +914123456765</a>How to link to a script and execute it
You can link to JavaScript code and execute it when someone clicks on the link. You shouldn't do this often, as it is always a better practice to rely on event handlers to execute actions rather than linking them. But let's learn this method too.
<a href="javascript:alert('Hello World!')">Click me</a>Now if you click on the Click me link, you will see a browser alert with the text, Hello World! in it.
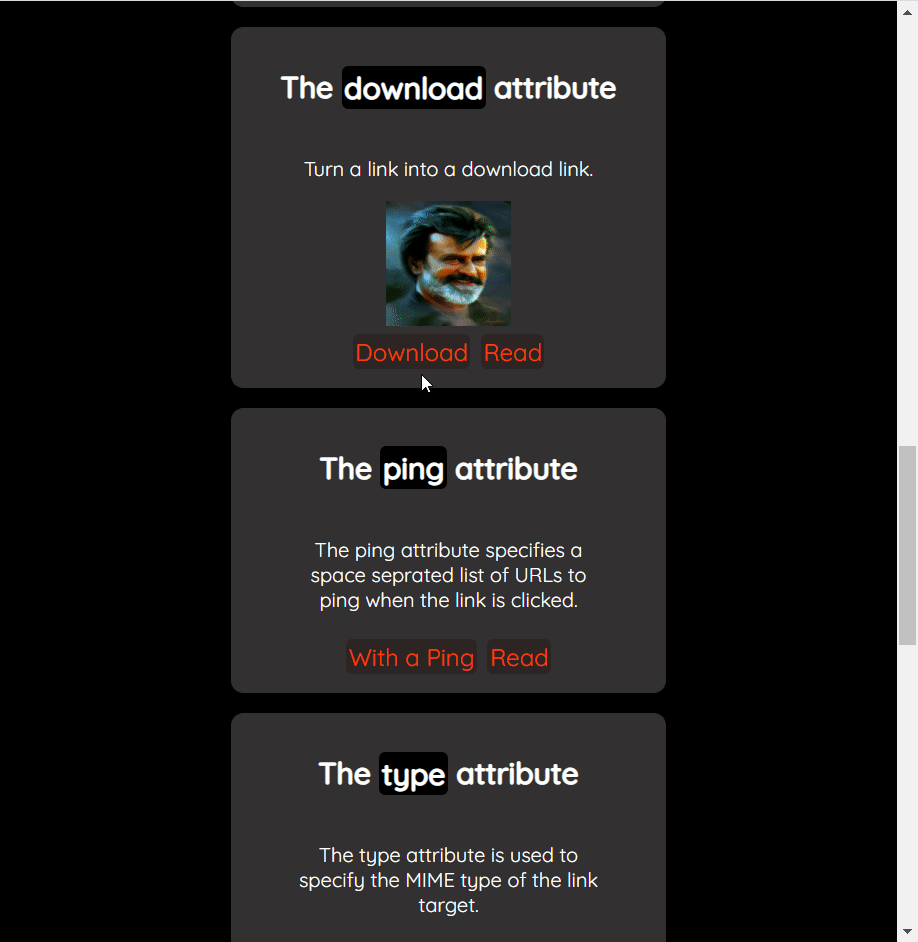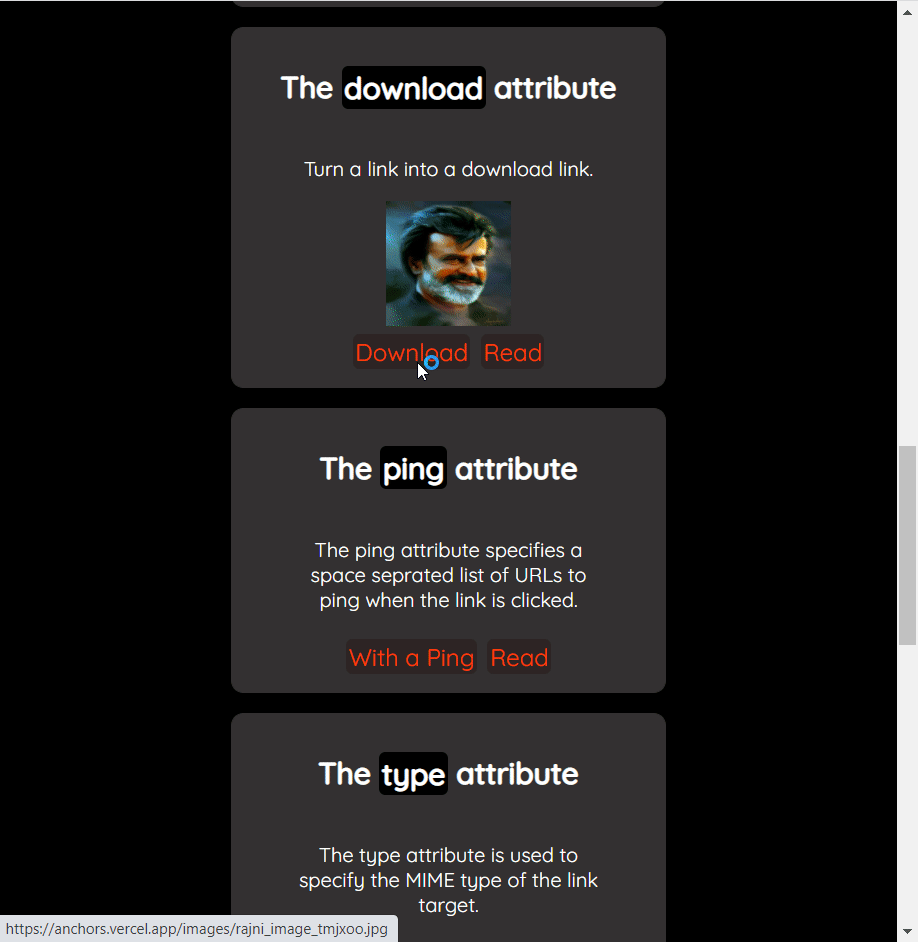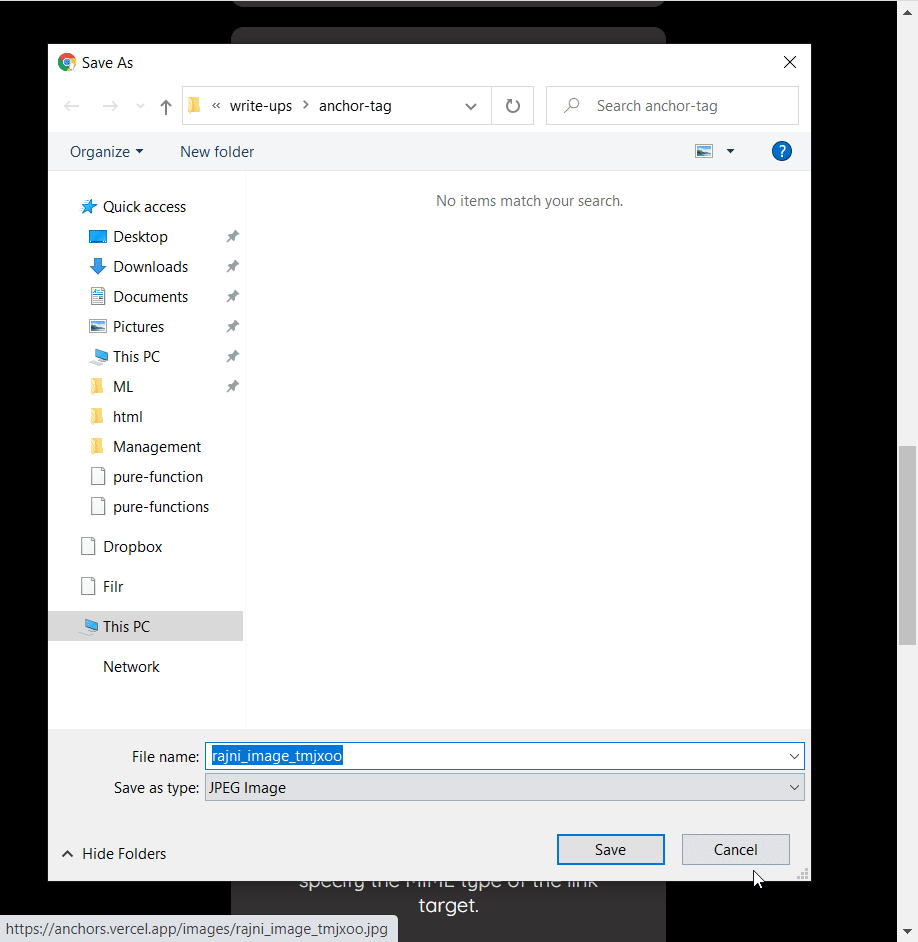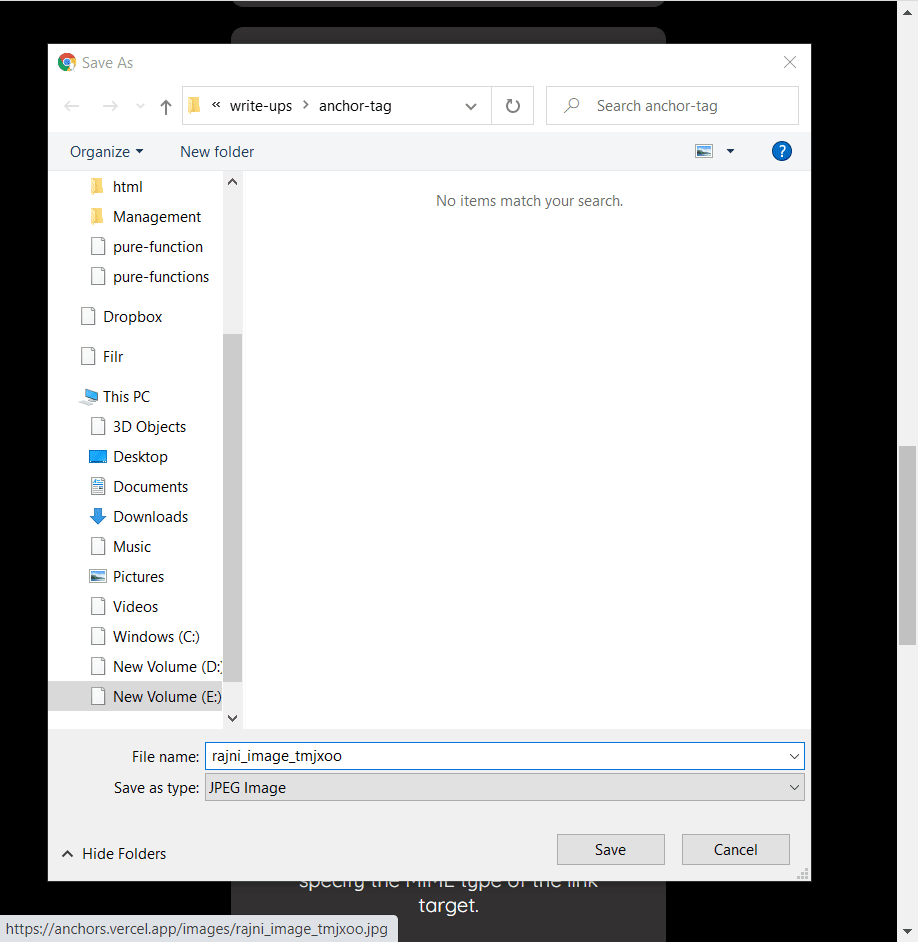
How to download a file
The anchor tag has the download attribute that turns a regular link into a download link. You can download a file by clicking the link. It opens up the download popup to save the file on the device.
<a href="./images/rajni.jpg" download="Thalaiva">Download</a>
You can optionally specify a custom file name by assigning the name to the download attribute. There is no need to specify the file extension while specifying the custom name. It will be added automatically depending on the file extension you are trying to download.
Note that this functionality works only if the file is of the same origin. The file you are downloading must be located under the same site where the link is added.
Check out this tweet,
The HTML anchor tag has a "download" attribute to turn a link into a download link.
— Tapas Adhikary (@tapasadhikary) December 13, 2021
- You can optionally set the download file name.
- Click on it will show the download popup to save the file on the device.
- It only works for the same-origin file URLs(from the same site) pic.twitter.com/SVfakpbsp7
How to open a page in a new window/tab
You may not want your users to get distracted too much from what they are doing when clicking on a link. You may want to open the page in a new browser window/tab when the user clicks on the link on a current page. We can use the target attribute for this purpose.
<a href="https://example.com" target="_blank">Click Me</a>The target attribute can have the following values,
_blank: this is the most used option. You can open the linked page on a new window/tab by setting the target attribute value as _blank._self: this is the default value. It helps open the linked page in the same window frame._top: this opens the linked page in the top window._parent: this opens the linked page in the parent frame.
We will see how to use the last two values when we discuss the link with frames in a while.
Anchor Link and Tabnabbing
Tabnabbing is a type of Cybersecurity attack where the attacker takes advantage of the user moving away from the current page and introduces a Phishing attack.
Assume you are browsing a website and click on a link to open the page in a new tab/window (remember target=_blank?). Now the attacker gets ahold of the window object of the browser and manipulates (redirects) the source page to a look-alike website with a few changes to trap you.
Those few changes could be a login form where you accidentally provide your credentials, and the attacker wins. This is called Tabnabbing.
To protect users from an attack like Tabnabbing, you need to pass a couple of values to an anchor tag's rel attribute:
noopener: makes the opening browser context unknown by setting thewindow.openerobject asnull. This means that the attacker doesn't have any way to redirect the source page.noreferrer: this makes sure thatreferrerheader will not be included when the link is clicked. You must set this value for older browsers.
So, the more secure way to use the target=_blank value is with the rel attribute, like this:
<a href="https://example.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">How to link with frames and child pages
You can include another HTML document on the current page using the <iframe> tag.
<iframe src="./child-frame.html" frameborder="0"></iframe>Then the chlid-frame.html may have another iframe to include another HTML document.
<div class="child-frame">
I am the Child frame.
<iframe src="./grand-child-frame.html" frameborder="0"></iframe>
</div>Now how do you link to the parent frame from the grand-child.html page? Also, how do you link to the top-most window frame?
<li>
<a href="https://example.com" target="_parent">Opens in the parent frame(target: _parent)</a>
<a href="https://example.com" target="_top ">Opens in full body of the window(target: _top)</a>
</li>
As the code above shows, we use the target as _parent to link to the parent frame. The target value _top links to the window frame.

How to ping in the background
You may want to track how many clicks a particular link is getting on your website. To do that, you can use the ping attribute of the anchor tag.
A ping attribute accepts one or more URLs as values. When someone clicks on the link, it makes a tiny POST request on those URLs. If there are multiple URLs, they must be comma-separated.
<a href="https://example.com" ping="https://example.com/tracking">With a Ping</a>
How to Style an Anchor Tag
The anchor tag has states. The default state is called link. The other three states are:
hover: An anchor has this state when a user mouses over it.active: An anchor has this state when a user clicks on the link.visited: A visited state means a user has already clicked the anchor link.
You may get confused with the differences between the active and visited states at times. The active state is brief. It activates just when the user clicks on a link, and then the state changes to the visited state.
CSS has pseudo-classes to apply styles for a specific state. The pseudo-classes are preceded by a colon (:) symbol and added after a selector. So, for the anchor tag(), we can style it for all the states we have seen above.
a:link: the same as applying styles to theatag directly.a:hover: applies styles when the user mouses over the anchor.a:active: applies styles when a user activates the link by clicking on it.a:visited: apples styles when the state changes tovisited.
Below is an example of applying different colors for every state of the anchor tag:
a:link {
color: #ff3e00;
}
a:hover {
color: #ffee00;
}
a:active {
color: #d900ff;
}
a:visited {
color: #51ff00;
}
You can apply any style of your choice based on these state changes.
Don't Confuse the Anchor Tag with the Link Tag
You may sometimes confuse the anchor tag with the link (<link>) tag. We use the link tag to link to external resources like stylesheets, favicon, fonts, and so on.
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Quicksand:wght@300;400;500&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="main.css">
<link rel="icon" href="./images/fav.ico">We have already learned that the primary purpose of the anchor (<a>) tag is to link one HTML page to another. Moreover, it is a hyperlink that you can click on to get to the target document.
Before We Go
That's all for now. I hope you found the article insightful and informative. My DMs are open on Twitter if you want to discuss further.
Let's connect. I share my learnings on JavaScript, Web Development, and Blogging on these platforms as well:
Before we end, here is the GitHub project link of the Anchors app we have used in this article. Please feel free to use/fork/improve.
See you soon with my next article. Until then, please take care of yourself, and stay happy.

