A URL is an address for a website. Just like postal addresses have to follow a specific format to be understood by the postman, URLS have to follow a format to be understood and get you to the right location.
There are only certain characters that are allowed in the URL string, alphabetic characters, numerals, and a few characters ; , / ? : @ & = + $ - _ . ! ~ * ' ( ) # that can have special meanings.
Reserved Characters
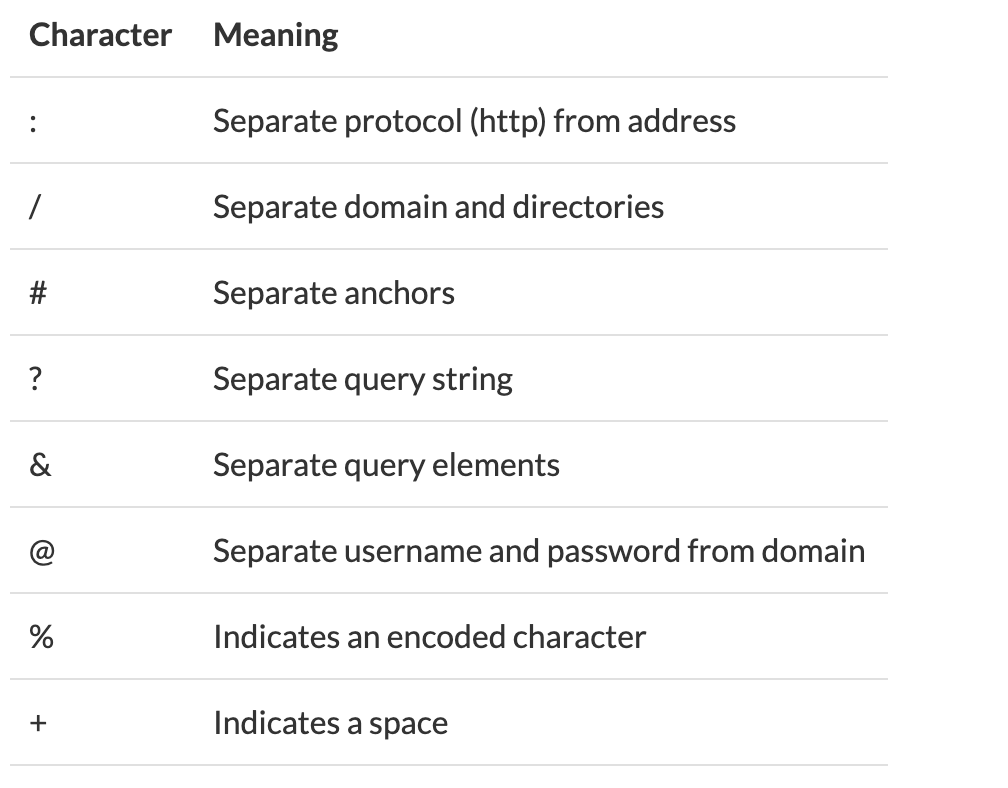
Encoding
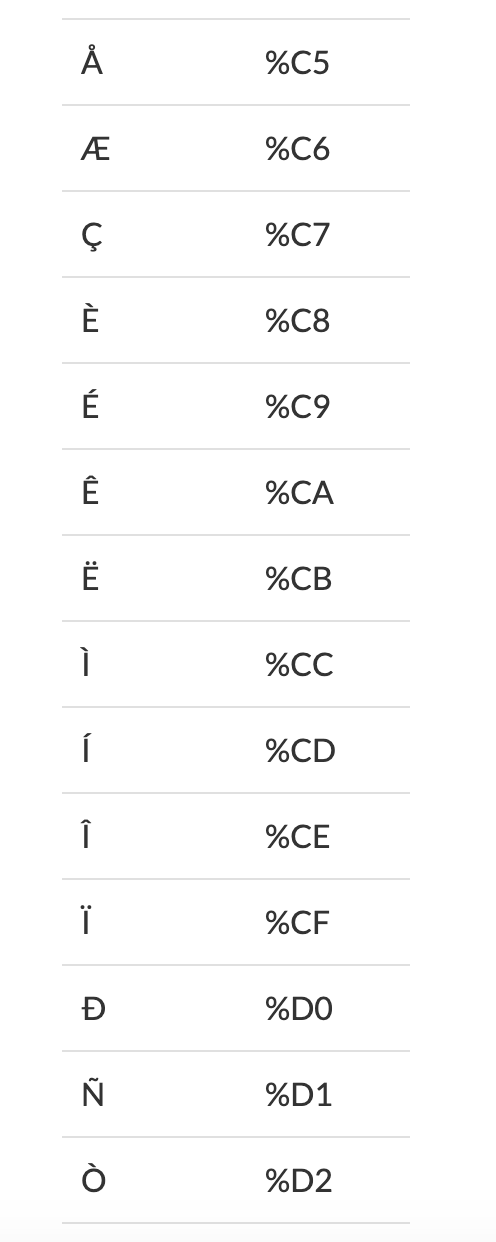
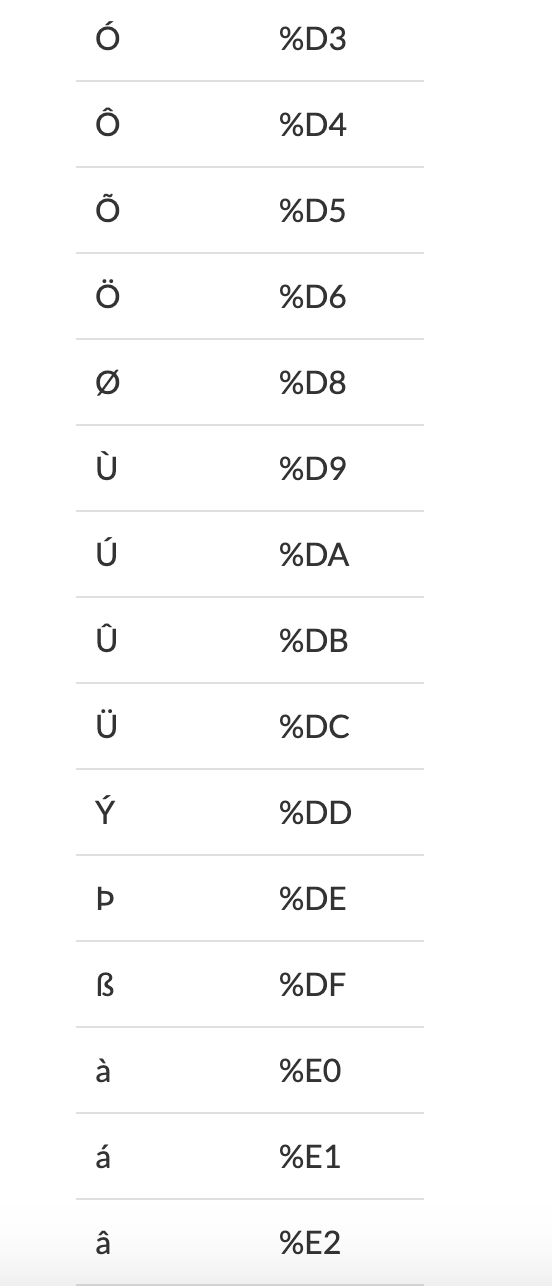
Any character that is not an alphabetic character, a number, or a reserved character being used needs to be encoded.
URLs use the ASCII (“American Standard Code for Information Interchange”) character-set and so encoding must be to a valid ASCII format.
There are functions in most web languages to do this encoding for you, for example in JavaScript encodeURI() and in PHP rawurlencode().



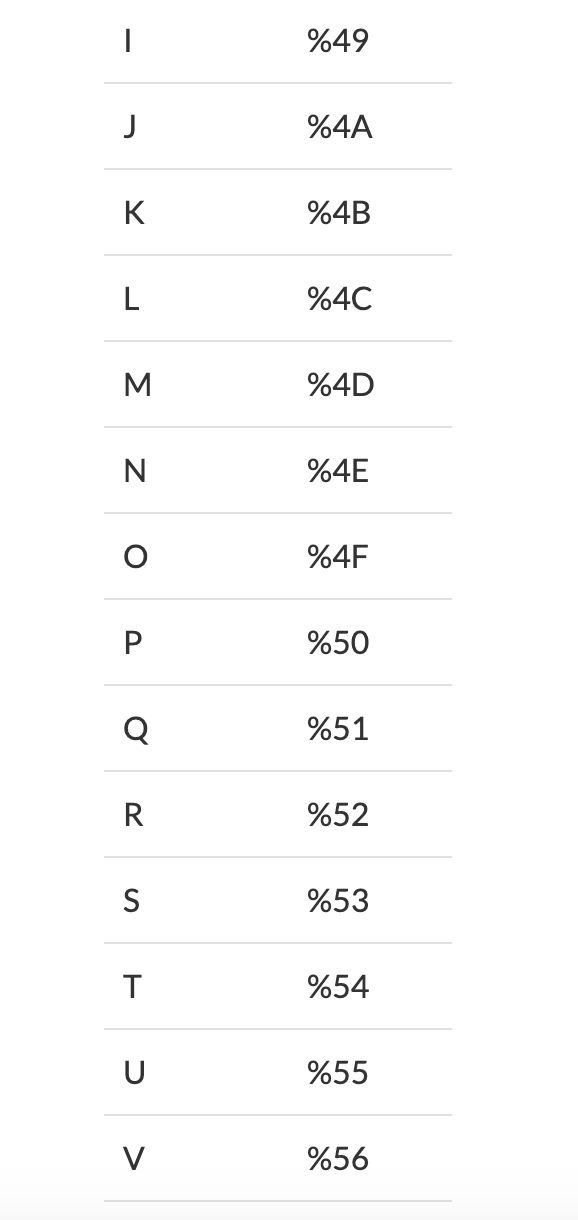
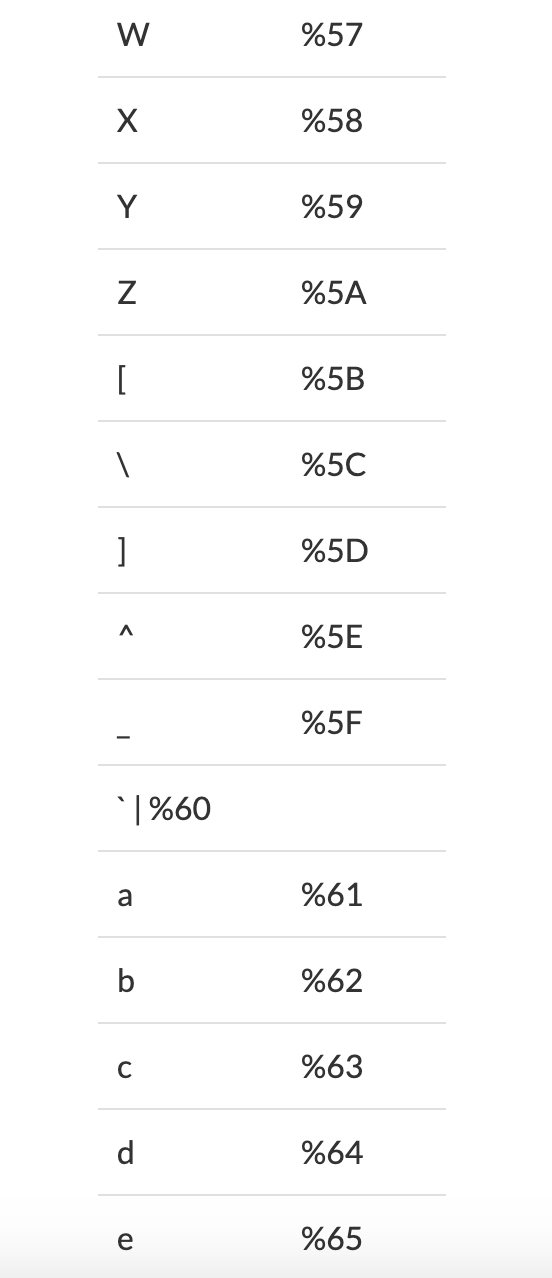
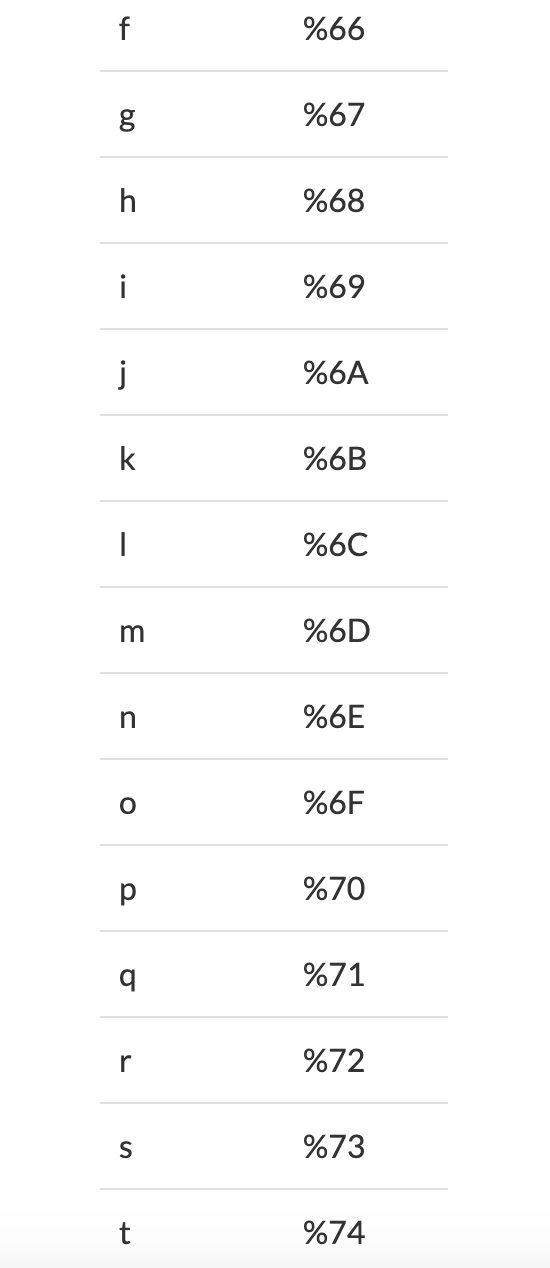




Example:
encodeURI(Free Code Camp);
// Free%20Code%20Camp
