By Sebastian Sigl
Containers make software engineering easier and more efficient, and Docker containers are popular and easy to use.
Containers are essential for local development. They let you test-run your applications in local environments and start building out the required infrastructure.
Docker containers are immutable by nature. This means that restarting a container erases all your stored data in the container. But Docker provides volumes and bind mounts, which are two mechanisms for persisting data in your Docker container.
This tutorial will teach you how to bind local directories to your Docker container and use docker-managed volumes alternatively. Knowing both enables you to use Docker containers for many more use cases that can boost your productivity.
How to Mount Local Directories using docker run -v
The
docker runcommand first creates a writeable container layer over the specified image and then starts using the specified command. (Source docker.com)
Using the parameter -v allows you to bind a local directory.
-v or --volume allows you to mount local directories and files to your container. For example, you can start a MySQL database and mount the data directory to store the actual data in your mounted directory.
# run mysql container in the background
$ docker run --name mysql-db -v $(pwd)/datadir:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql:8.0.28-debian
# show content of data directory
$ ls -la datadir
total 383848
-rw-r----- 1 sebarthel staff 196608 Mar 26 22:47 #ib_16384_0.dblwr
-rw-r----- 1 sebarthel staff 8585216 Mar 26 22:47 #ib_16384_1.dblwr
drwxr-x--- 12 sebarthel staff 384 Mar 26 22:47 #innodb_temp
drwxr-xr-x@ 27 sebarthel staff 864 Mar 26 22:47 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 sebarthel staff 96 Mar 26 22:47 ..
-rw-r----- 1 sebarthel staff 56 Mar 26 22:47 auto.cnf
-rw-r----- 1 sebarthel staff 913 Mar 26 22:47 binlog.000001
(more directories)
# stop mysql container
docker rm -f mysql-db
Binding a directory is a 2-way sync. Every file you change on the host is changed in the container, and every file that is changed in the container is changed on the host. So if you stop and start the database, you can mount the same directory, and your configuration and stored data will be available.
The advantages of this method are that it’s straightforward to use and easy to access. You should use binding local directories for files you want to change or observe on the host, like configuration files and log files.
How to Use Docker Volumes to Persist Changes
Instead of binding your local directory, you can use Docker volumes. A Docker volume is a directory somewhere in your Docker storage directory and can be mounted to one or many containers. They are fully managed and do not depend on certain operating system specifics.
Let’s create a Docker volume and mount it to persist MySQL data:
# create volume
docker volume create mysql-data
# run mysql container in the background
$ docker run --name mysql-db -v mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql:latest
# stop mysql container
docker rm -f mysql-db
# remove volume
docker volume remove mysql-data
Before removing the Docker volume, you can open your Docker GUI and inspect the volume by clicking on the data tab.
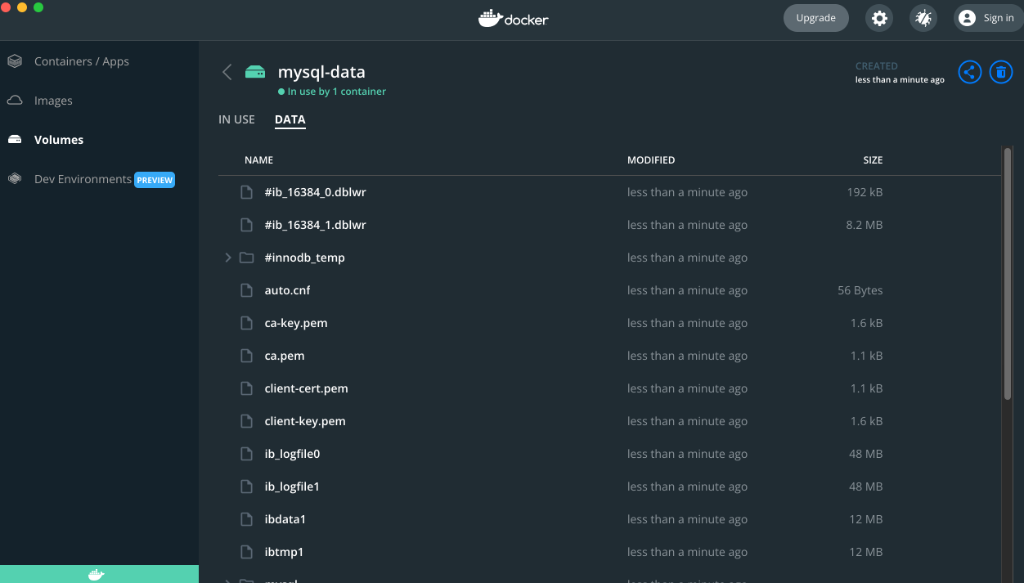
You see the files, but they're isolated in a Docker volume. It’s recommended to use them for persisting files that you don’t need to observe or change from your host system. This method is known to have better performance than local directory bindings.
Summary
Docker containers get more powerful when you know how to persist your data and not to lose them when stopping a container.
You bind local directories and volumes to a container by providing the Docker run -v parameter. You need to give the absolute local path or a volume name and map it to a directory within the container -v <source>:<target>.
I hope you enjoyed the article.
If you liked it and felt the need to give me a round of applause or just want to get in touch, follow me on Twitter.
I work at eBay Kleinanzeigen, one of the world’s biggest classified companies. By the way, we are hiring!
References
- How to mount a directory inside a Docker container
- Docker image for MySql
- Docker-Compose syntax volume or bind mount
- How to pause and resume Docker containers
- Docker volumes vs bind mounts
- Docker Documentation: command volume create
- Docker Documentation: Volumes backup and restore
- Docker containers on the desktop
