What is Euler’s Method?
The Euler’s method is a first-order numerical procedure for solving ordinary differential equations (ODE) with a given initial value.
The General Initial Value Problem
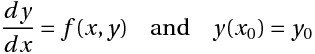
Methodology
Euler’s method uses the simple formula,
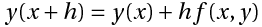
to construct the tangent at the point x and obtain the value of y(x+h), whose slope is,
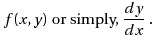
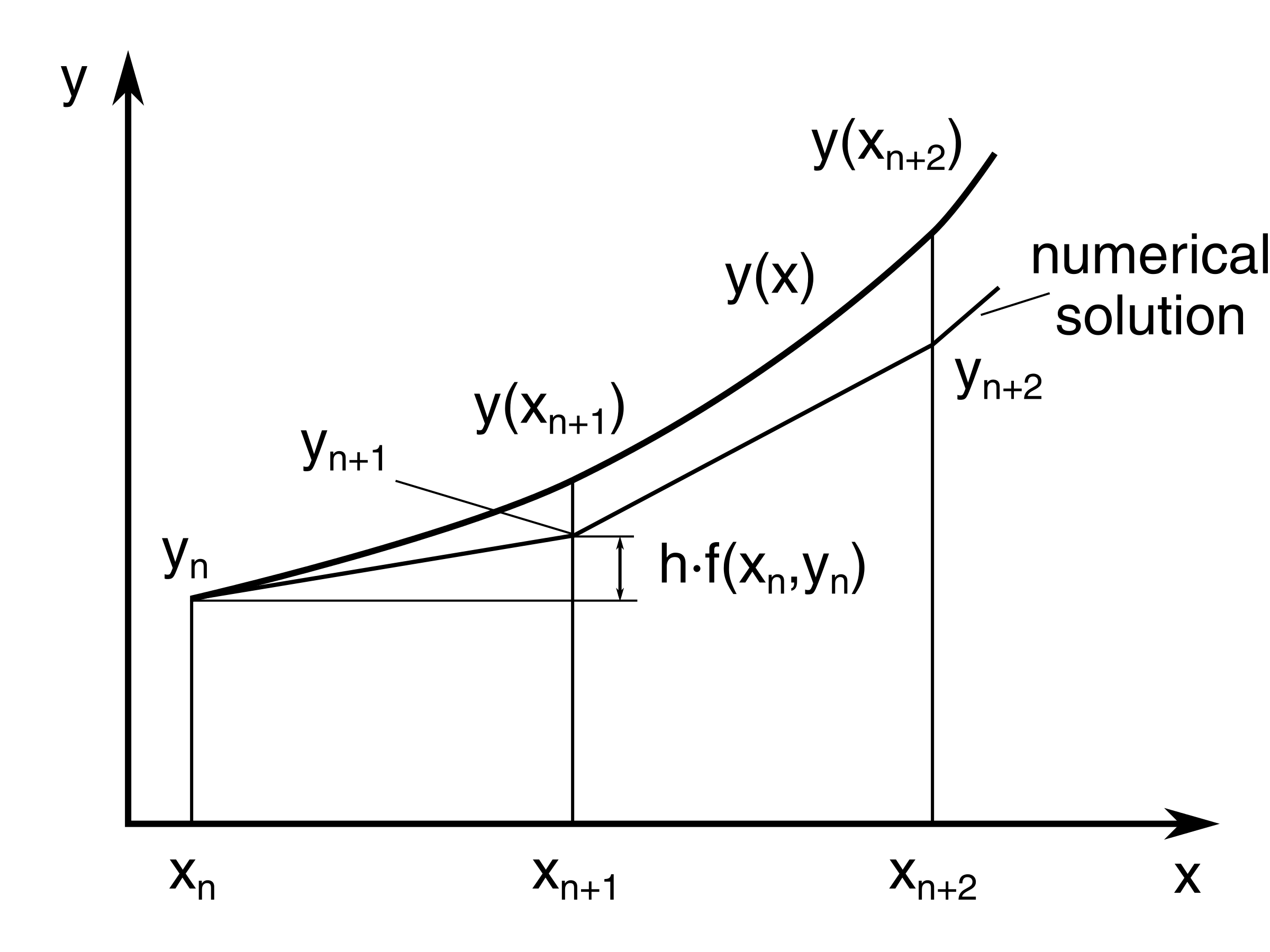
In Euler’s method, you can approximate the curve of the solution by the tangent in each interval (that is, by a sequence of short line segments), at steps of h.
In general, if you use small step size, the accuracy of approximation increases.
General Formula
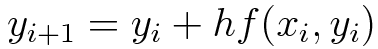

Functional value at any point b, given by y(b)
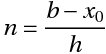
where,
- n = number of steps
- h = interval width (size of each step)
Pseudocode

Example
Find y(1), given
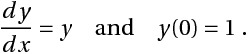
Solving analytically, the solution is y = ex and y(1)= 2.71828. (Note: This analytic solution is just for comparing the accuracy.)
Using Euler’s method, considering h = 0.2, 0.1, 0.01, you can see the results in the diagram below.
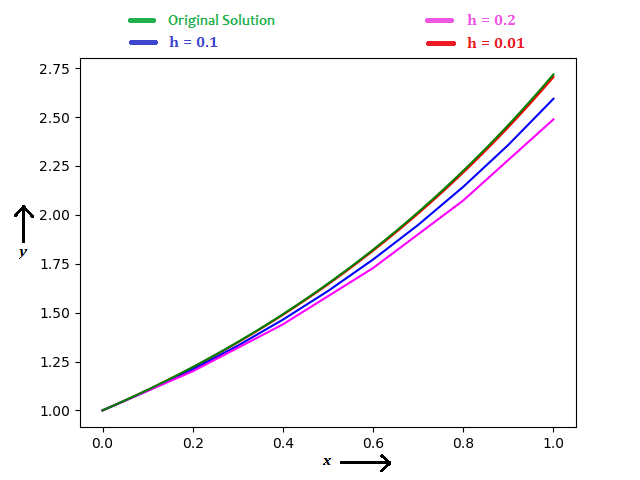
When h = 0.2, y(1) = 2.48832 (error = 8.46 %)
When h = 0.1, y(1) = 2.59374 (error = 4.58 %)
When h = 0.01, y(1) = 2.70481 (error = 0.50 %)
You can notice, how accuracy improves when steps are small.
