By Pier Paolo Ippolito
Introduction
During the last few years, Internet of Things (IoT) devices have started becoming a more and more important component in our daily lives. Some common applications for IoT devices are:
- Smart Home (eg. smart lamps)
- Wearables (eg. smart-watches)
- Autonomous vehicles
- Smart cities
- Smart Retail
According to Wikipedia, IoT devices are defined as:
"The Internet of things (IoT) is the extension of Internet connectivity into physical devices and everyday objects. Embedded with electronics, Internet connectivity, and other forms of hardware (such as sensors), these devices can communicate and interact with others over the Internet, and they can be remotely monitored and controlled " – Wikipedia [1]
One of the most interesting characteristics of IoT devices is that they are able to produce large amounts of data. This can be particularly used in applications such as Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Most of IoT devices can produce in fact a great variety of Time Series data which are of huge interest in Artificial Intelligence.
According to a study carried out by Global Data, the IoT market is projected to reach $318bn new worth by 2023 (in constantly rise compared to the previous years).
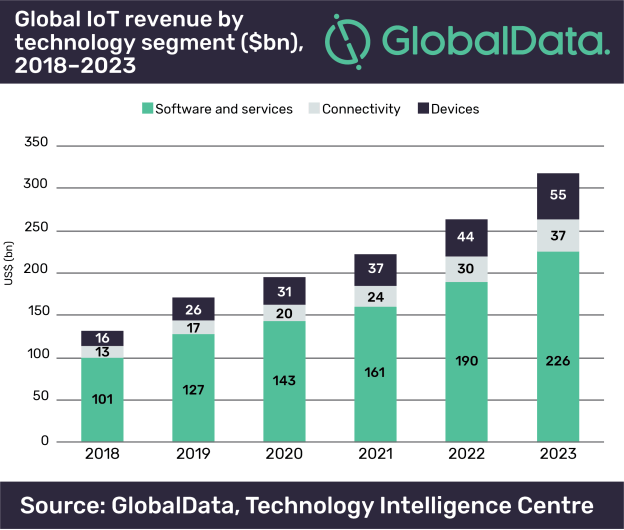 Figure 1: IoT markets projections [2].
Figure 1: IoT markets projections [2].
These projections are confirmed by the increased interest of companies such as Google and Microsoft to invest in IoT cloud platforms.
How do IoT devices work?
An IoT system is compromised of four main components:
- Sensors: enables the devices to collect data from the environment surrounding the device (eg. velocity, GPS coordinates, temperature, etc...).
- Connectivity: successively the data collected is sent to the cloud (through either WiFi or Bluetooth connection).
- Data Processing: once the data is received by the cloud infrastructure, it can then be processed (eg. check if the data received adhere to the requirements and if its not alert the user).
- User Interface: Once the data is processed, the results are then given to the and user.
As a simple workflow example, let's consider a security system in a house.
Our IoT device will check if there are any intruders in our house using a Computer Vision system (Sensors). The video recordings of the house are then sent to the cloud to see if there are any intruders or not (Connectivity). Successively, the data is processed in the cloud (Data Processing) and if some intruders are detected we get alerted (User Interface).
An IoT system could be able to alert us in many different ways (eg. phone call/message or App notification) and in some cases we could be able to control remotely the system itself (eg. lock the house doors).
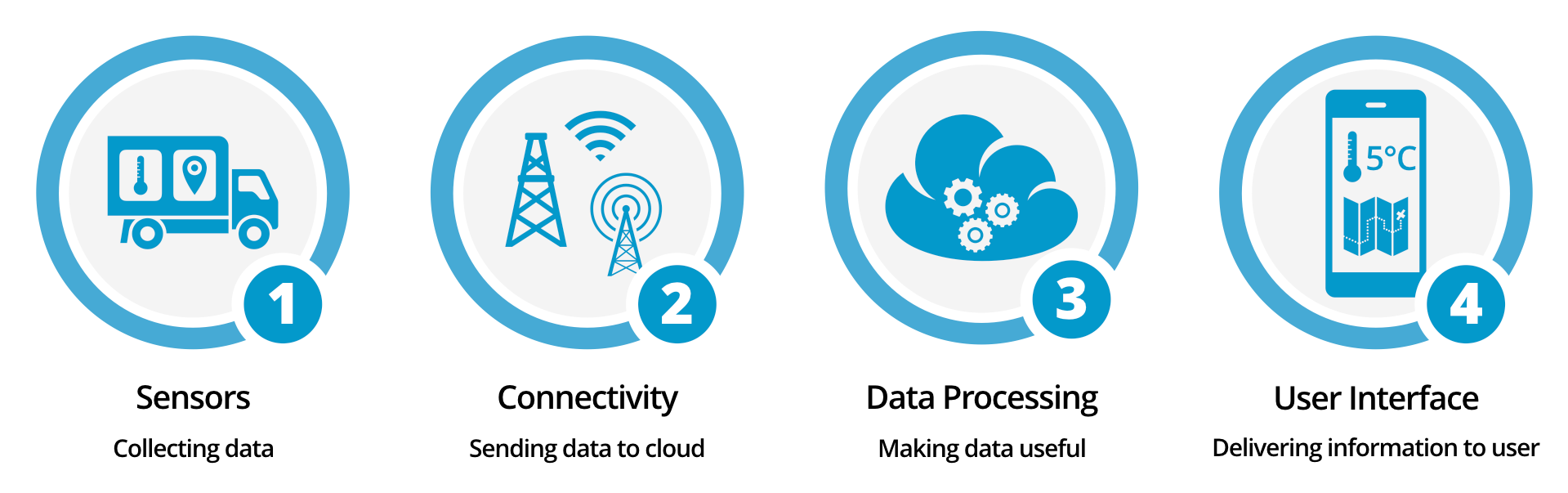 Figure 2: Main Components of an IoT System [3]
Figure 2: Main Components of an IoT System [3]
Internet of Things cloud platforms
I will now introduce you to some of the most interesting IoT cloud platforms which can be used for analysing and controlling IoT devices.
 Figure 3: IoT Cloud Platforms [4]
Figure 3: IoT Cloud Platforms [4]
Google Cloud Internet of Things
Google Cloud is currently one of the main Cloud solutions provider on the market. Some of the packages offered by Google Cloud for IoT implementations are:
- Cloud IoT Core: is used to set up the device(s) and establish a secure connection between them.
- Cloud Machine Learning Engine: it allows users to create Machine Learning models from the data gathered by the IoT devices in order to increase and monitor performances.
- Cloud Pub/Sub: provides real time analytics of the IoT devices.
Azure Internet of Things
Microsoft Azure is another really important cloud services provider. Azure is able to deliver both pre-customized and fully customizable solutions. In this way, Azure is able to provide solutions for both beginners and experts in IoT. Microsoft Azure enables to easily scale IoT systems to include devices from different manufacturers and also provides analytics and Machine Learning services support.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is one of the most popular solution for cloud based services. AWS can enable to perform IoT projects from end to end and making use of the four following packages:
- AWS IoT Core: is the basic package which can be used to set up IoT devices. Using IoT Core we can integrate different devices to communicate each other over a secured connection making possible to exchange data through cloud storage.
- AWS IoT Analytics: is used to process and analyse all the data produced by IoT devices. Once all the data is stored using a semi-structured format (eg. JSON, CSV) it can be then used for Machine Learning purposes (eg. monitor and optimise the interaction between IoT devices).
- AWS IoT Device Defender: is used to construct and personalise the security mechanisms of IoT devices (such as choosing device authentication and data encryption).
- AWS IoT Device Management: enables to easily integrate new IoT devices to an environment and monitor/update their functionalities.
Conclusion
Internet of Things devices are definitely going to play a really important role in future technology advancements. Although there are still the same issues that have to be addressed. In fact, one of the main concerns about IoT devices can be cyber-security.
Because most IoT devices make use of a cloud centre to store their data and to collect useful information from the internet, that makes them vulnerable from Hackers attacks (creating a single point of failure).
In order to resolve this problem, could be either possible to increase the encryption standards (slowing down the transfer of data) or makes use of Artificial Intelligence security powered techniques such as Differential Privacy and Federated Learning.
In case a Hacker would be able to access control of an IoT device (or an entire group) there would be two main risks associated with it:
- The Hacker would be able to access and steal sensitive data of the IoT device users.
- The Hacker could be able to take remote control of the device itself.
In addition to the cloud services provided before, also the following ones can be considered a valid alternative: SAP, Oracle Internet of Things, Cisco IoT Cloud Connect, IBM Watson Internet of Things, etc...
Contacts
If you want to keep updated with my latest articles and projects follow me and subscribe to my mailing list. These are some of my contacts details:
Cover photo from this article.
Bibliography
[1] Wikipedia, Internet of Things. Accessed at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things
[2] Global IoT market to reach $318 billion by 2023, says GlobalData. Michelle Froese, Windpower Engineering & Development. Accessed at: https://www.windpowerengineering.com/business-news-projects/global-iot-market-to-reach-318-billion-by-2023-says-globaldata/
[3] Anni Junnila, HOW IOT WORKS – SUMMARY – TRACKINNO BLOG. Accessed at: https://trackinno.com/2018/08/09/how-iot-works-part-4-user-interface/how-iot-works-summary-001/
[4] Overview of the best IOT platforms. Tips for selecting the right cloud solution in 2019. Anna Davydova, Edsson. Accessed at: https://www.edsson.com/en/blog/article?id=iot-platforms