Imagine for a moment that you been working hard to setup a website, protected with SSL, and then your hardware fails. This means that unless you have a perfect backup of your machine, you will need to install all the software and configuration files by hand.
What if it's not just one server but many? The amount of time you will need to fix all of them will grow exponentially – and because is a manual process it will be more error-prone.
And then the nightmare scenario: You don't have an up-to-date backup, or you have incomplete backups. Or the worst – there are no backups at all. This last case is more common than you think, especially in home labs where you are tinkering and playing around with stuff by yourself.
In this tutorial, I'll show you how you can do a full infrastructure provisioning of a pair of web servers on a Cloud provider, with SSL certificates and monitoring metrics with Prometheus.
What You Need for This Setup
The first thing you need is a cloud provider. Oracle Cloud offers a Free Tier version of their cloud services, which allows you to setup virtual machines for free. This is great for a home lab with lots of rich features that you can use to try new tools and techniques.
You'll also need an automation tool. I used Ansible because its doesn't have many requirements (you only need an SSH daemon and public key authentication to get things going). I also like it because it works equally well regardless of the cloud environment you are trying to provision.
In this tutorial we will use the Open Source version of this tool, as it is more than sufficient for our purposes.
What's included in the Ansible playbook
An Ansible playbook is nothing more than a set of instructions you define to execute tasks that will change the status of a host. These actions are carried out on an inventory of hosts you define.
Here, you are going to learn about the following:
How to clean inventory sources by using the proper layout in your playbooks.
How to provision two NGINX instances, with the request of their proper free SSL certificates using Certbot.
How to set up the local Linux firewalls and add a Prometheus node_exporter agent and one scraper to collect that data.
Concepts like variables, roles (with task inclusion), and conditional execution.
Important techniques like task tagging, debug messages, and static validation with ansible-lint.
All the code can be found in this GitHub repository.
What You Should Know Before Trying This
Because we will cover several tasks here, you will probably need to be familiar with several things (I'll provide links as we go along):
This is not an introductory course on Ansible but more of a "how all things fit together" with a more detailed, but not too complex, playbook.
An OCI Cloud Free Tier account
Privileged account, most likely SUDO
Basic knowledge of TCP/IP and firewalls with firewalld
How to use RPM and how to package applications (we will not do that here, but it helps to understand when an RPM is better than a complex task in Ansible)
What is not included here
OCI Cloud has a complete REST API to manage a lot of aspects of their cloud environment. Their setup page (specifically the SDK) is also very detailed.
You'll Probably Do Things Differently in Production.
Installing the OCI-Metrics-datasource instead of Prometheus agents on a virtual machine
You can go to this page to install it on your Grafana instance (Bare metal or Cloud). Also you need to setup your credentials and permissions as explained here.
This is probably the most efficient way to monitor your resources as you do not need to run agents on your virtual machines. But I will install instead a Prometheus node_exporter agent and scraper that will be visible from a Grafana Cloud instance.
An exposed Prometheus on the Internet endpoint is not a good idea
It is very clear, I'm exposing my Prometheus scraper to the Internet so Grafana cloud can reach it. On an Intranet with a private cloud and your local Grafana, this is not an issue – but here, a Prometheus agent pushing data to Grafana would be a better option.
Still, Grafana provides a list of public IP addresses that you can use to setup your allow list.
So the following will work:
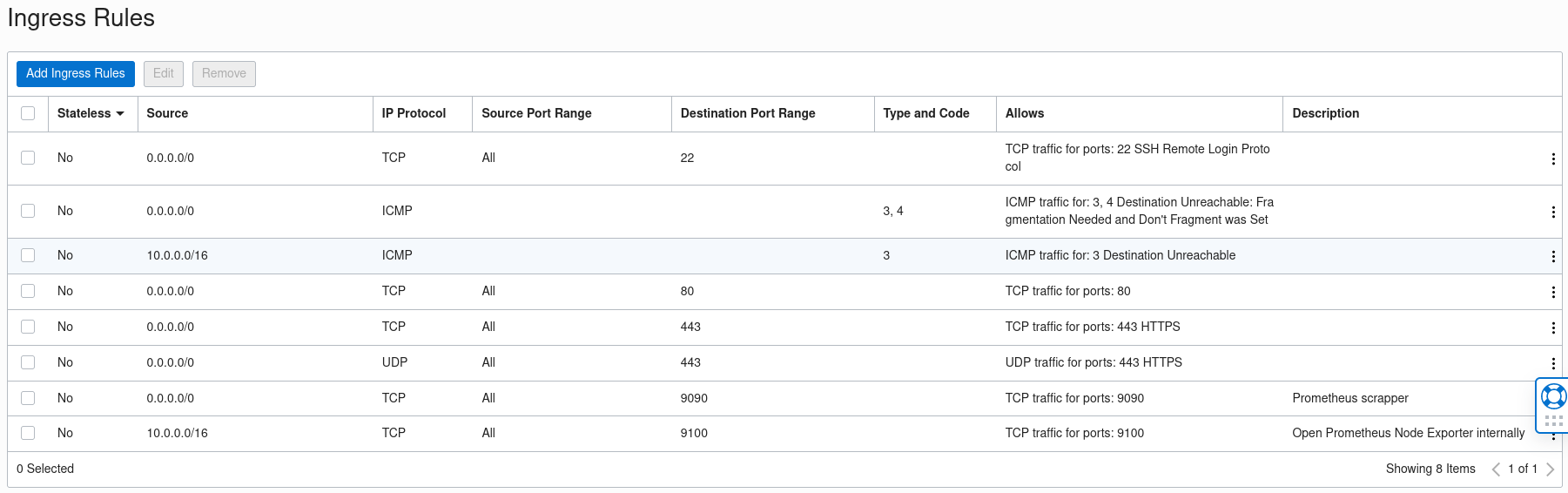
Oracle Cloud Ingress Rules
But it is not the best. Instead, you want to restrict the specific IP addresses that can pull data from your exposed services. The prometheus exporter can be completely hidden from Grafana on port 9100. Instead we only need to expose the Prometheus scraper that listens on port 9000.
For this home lab, it is not a big deal having such services fully exposed. But if you have a server with sensitive data, you must restrict who can reach the service!
An alternative to the Prometheus endpoint is to push the data to Grafana by using a Grafana agent but I will not cover that option here.
Playbook Analysis
Ansible lets you have a single file with the playbook instructions, but eventually you will find that such a structure is difficult to maintain.
For my playbook I decided to keep the suggested structure:
tree -A
.
├── inventory
│ └── cloud.yaml
├── oracle.yaml
├── roles
│ └── oracle
│ ├── files
│ │ ├── logrotate_prometheus-node-exporter
│ │ ├── prometheus-node-exporter
│ │ └── requirements_certboot.txt
│ ├── handlers
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── meta
│ ├── tasks
│ │ ├── controller.yaml
│ │ ├── main.yaml
│ │ ├── metrics.yaml
│ │ └── nginx.yaml
│ ├── templates
│ │ ├── prometheus-node-exporter.service
│ │ ├── prometheus.service
│ │ └── prometheus.yaml
│ └── vars
│ └── main.yaml
└── site.yaml
Below is a brief description of how the content is organized:
You can have more than one site. You control that inside the [site.yaml](file:///home/josevnz/OracleCloudHomeLab/site.yaml) file.
The host list is inside the inventory directory. You can have more than one inventory file or scripts to generate the hostlist, or a combination of both.
The roles/oracle group the tasks. We only have one role called 'oracle' because that's the cloud provider I'm focusing on here.
Our playbook uses metadata in the form of variables, with each one defined on the 'vars' directory. That way we can customize the behaviour of the playbook in multiple places:
---
# Common variables for my Oracle Cloud environments
controller_host: XXXX.com
ssl_maintainer_email: YYYYYY@ZZZZ.com
architecture: arm64
prometheus_version: 2.38.0
prometheus_port: 9090
prometheus_node_exporter_nodes: "['X-server1:{{ node_exporter_port }}', 'Y-server2:{{ node_exporter_port }}' ]"
node_exporter_version: 1.4.0
node_exporter_port: 9100
internal_network: QQ.0.0.0/24
The roles/oracle files directory contains files that can be copied as is to the remote directory. The templates' directory is similar, but the files in there can be customized for each host by using the Jinja templating language.
# A template for the prometheus scraper configuration file
---
global:
scrape_interval: 30s
evaluation_interval: 30s
scrape_timeout: 10s
external_labels:
monitor: 'oracle-cloud-metrics'
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'node-exporter'
static_configs:
- targets: {{ prometheus_node_exporter_nodes }}
tls_config:
insecure_skip_verify: true
The 'tasks' directory is where we store our tasks, that is the actions that will modify the server state. Note that Ansible will not execute tasks if it's not necessary. The idea is that you can re-run a playbook as many times as needed and the final state will be the same.
# Fragment of the nginx tasks file. See how we notify a handler to restart nginx after the SSL certificate is renewed.
---
- name: Copy requirements file
ansible.builtin.copy:
src: requirements_certboot.txt
dest: /opt/requirements_certboot.txt
tags: certbot_requirements
- name: Setup Certbot
pip:
requirements: /opt/requirements_certboot.txt
virtualenv: /opt/certbot/
virtualenv_site_packages: true
virtualenv_command: /usr/bin/python3 -m venv
tags: certbot_env
- name: Get SSL certificate
command:
argv:
- /opt/certbot/bin/certbot
- --nginx
- --agree-tos
- -m {{ ssl_maintainer_email }}
- -d {{ inventory_hostname }}
- --non-interactive
notify:
- Restart Nginx
tags: certbot_install
There is one special directory called 'handlers'. There we define actions that must happen if a task changes the state of our host.
We now have a picture of how all the pieces work together, so let's talk about some specific details.
Firewall provisioning
With Ansible, you can replace a sequence of commands like this:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
With a firewalld module:
---
- name: Enable HTTP at the Linux firewall
firewalld:
zone: public
service: http
permanent: true
state: enabled
immediate: yes
notify:
- Reload firewall
tags: firewalld_https
- name: Enable HTTPS at the Linux firewall
firewalld:
zone: public
service: https
permanent: true
state: enabled
immediate: yes
notify:
- Reload firewall
tags: firewalld_https
Common tasks have nice replacements
So instead of running SUDO with a privileged command:
sudo dnf install -y nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx.service --now
You can have something like this:
# oracle.yaml file, which tells which roles to call, included from site.yaml
---
- hosts: oracle
serial: 2
remote_user: opc
become: true
become_user: root
roles:
- oracle
# NGINX task (roles/oracle/tasks/nginx.yaml)
- name: Ensure nginx is at the latest version
dnf:
name: nginx >= 1.14.1
state: present
update_cache: true
tags: install_nginx
# And a handler that will restart NGINX after it gets modified (handlers/main.yaml)
---
- name: Restart Nginx
ansible.builtin.service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
- name: Reload firewall
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: firewalld.service
state: reloaded
How to Run the Playbooks
Normally you don't wait to have the whole playbook written, but you run the pieces you need in the proper order. At some point you will have your whole playbook finished and ready to go.
Make sure the playbook behaves properly with --check before making any changes
The very first step is to check your playbook file for errors. For that you can use yamllint:
yamllint roles/oracle/tasks/main.yaml
But doing this for every yaml file in your playbook can be tedious an error-prone. As an alternative, you can run the playbook in a 'dry-run' mode, to see what will happen without actually making any changes:
Another way to gradually test a complex playbook is by executing a specific task by using a tag or group of tags. That way you can do controlled execution of your playbook:
Keep in mind that this will not execute any dependencies that you may have defined on you playbook, tough:
Use Ansible-lint when ansible-playbook --check is not good enough
Some errors are more subtle and will not get caught with ansible-playbook --check. To get a more complete check on your playbooks before minor issues become a headache you can use ansible-lint. So let's get it installed:
python3 -m venv ~/virtualenv/ansiblelint && . ~/virtualenv/ansiblelint/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install --upgrade wheel
pip install ansible-lint
Now we can check the playbook:
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ ansible-lint site.yaml
WARNING Overriding detected file kind 'yaml' with 'playbook' for given positional argument: site.yaml
WARNING Listing 1 violation(s) that are fatal
syntax-check[specific]: couldn't resolve module/action 'firewalld'. This often indicates a misspelling, missing collection, or incorrect module path.
roles/oracle/tasks/nginx.yaml:2:3
Strange, firewalld is available on our Ansible installation. What else was installed by ansible-lint?
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ ansible --version
ansible [core 2.14.0]
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/home/josevnz/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /home/josevnz/virtualenv/ansiblelint/lib64/python3.9/site-packages/ansible
ansible collection location = /home/josevnz/.ansible/collections:/usr/share/ansible/collections
executable location = /home/josevnz/virtualenv/ansiblelint/bin/ansible
python version = 3.9.9 (main, Nov 19 2021, 00:00:00) [GCC 10.3.1 20210422 (Red Hat 10.3.1-1)] (/home/josevnz/virtualenv/ansiblelint/bin/python3)
jinja version = 3.1.2
libyaml = True
Ansible-lint installed its own ansible [core], and firewalld is part of ansible.posix collection. We will use Ansible Galaxy to install it:
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ which ansible-galaxy
~/virtualenv/ansiblelint/bin/ansible-galaxy
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ ansible-galaxy collection install ansible.posix
Starting galaxy collection install process
Process install dependency map
Starting collection install process
Downloading https://galaxy.ansible.com/download/ansible-posix-1.4.0.tar.gz to /home/josevnz/.ansible/tmp/ansible-local-18099xpw_8usc/tmp8msc9uf5/ansible-posix-1.4.0-_f17f525
Installing 'ansible.posix:1.4.0' to '/home/josevnz/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/ansible/posix'
ansible.posix:1.4.0 was installed successfully
Running it again:
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ ansible-lint site.yaml
WARNING Overriding detected file kind 'yaml' with 'playbook' for given positional argument: site.yaml
WARNING Listing 50 violation(s) that are fatal
name[play]: All plays should be named. (warning)
oracle.yaml:2
fqcn[action-core]: Use FQCN for builtin module actions (service).
roles/oracle/handlers/main.yaml:2 Use `ansible.builtin.service` or `ansible.legacy.service` instead.
fqcn[action-core]: Use FQCN for builtin module actions (command).
roles/oracle/handlers/main.yaml:6 Use `ansible.builtin.command` or `ansible.legacy.command` instead.
Some warnings are pedantic ('Use FQCN for builtin module actions (command)') and others require attention (Commands should not change things if nothing needs doing.).
Ansible-lint found many smells on the playbook, there is one option to re-write the files and correct some of these errors automatically:
There are some guidelines you can follow to correct these issues. Below are some that can be directly applied to the warnings we got earlier:
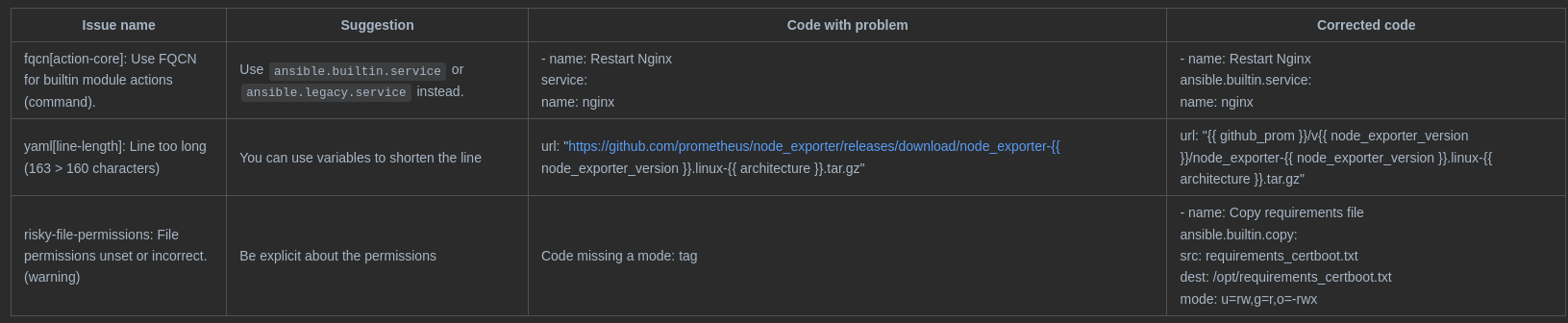
Note that all the errors are easy to solve. Some commands decide on their own if they should make changes or not but have a hard time communicating back to Ansible:
- name: Get SSL certificate
ansible.builtin.shell:
argv:
- /opt/certbot/bin/certbot
- --nginx
- --agree-tos
- -m "{{ ssl_maintainer_email }}"
- -d "{{ inventory_hostname }}"
- --non-interactive
notify:
- Restart Nginx
tags: certbot_install
In our case, certboot prints a message if the certificate is not yet due for renewal. If that output is missing then we trigger the Nginx restart (see defining changed):
- name: Get SSL certificate
ansible.builtin.shell:
argv:
- /opt/certbot/bin/certbot
- --nginx
- --agree-tos
- -m {{ ssl_maintainer_email }}
- -d {{ inventory_hostname }}
- --non-interactive
register: certbot_output # Registers the certbot output.
changed_when:
- '"Certificate not yet due for renewal" not in certbot_output.stdout'
notify:
- Restart Nginx
tags: certbot_install
I do want to use shell, as I need to expand the variable for certbot, but ansible-lint is still not happy:
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ ansible-lint site.yaml
WARNING Overriding detected file kind 'yaml' with 'playbook' for given positional argument: site.yaml
WARNING Listing 1 violation(s) that are fatal
command-instead-of-shell: Use shell only when shell functionality is required.
roles/oracle/tasks/nginx.yaml:47 Task/Handler: Get SSL certificate
You can skip specific rules or tags by adding them to your configuration file:
# .config/ansible-lint.yml
warn_list: # or 'skip_list' to silence them completely
- command-instead-of-shell # Use shell only when shell functionality is required.
Rule Violation Summary
count tag profile rule associated tags
1 command-instead-of-shell basic command-shell, idiom
Failed after min profile: 1 failure(s), 0 warning(s) on 8 files.
Time to treat this error as a warning, as I know they are not issues, by creating a .config/ansible-lint.yml:
(ansiblelint) [josevnz@dmaf5 OracleCloudHomeLab]$ ansible-lint site.yaml
WARNING Overriding detected file kind 'yaml' with 'playbook' for given positional argument: site.yaml
WARNING Listing 1 violation(s) that are fatal
command-instead-of-shell: Use shell only when shell functionality is required. (warning)
roles/oracle/tasks/nginx.yaml:47 Task/Handler: Get SSL certificate
Rule Violation Summary
count tag profile rule associated tags
1 command-instead-of-shell basic command-shell, idiom (warning)
Passed with min profile: 0 failure(s), 1 warning(s) on 8 files.
Much better now, the warning is not treated as an error.
Jinja best practices
If you plan to use variables and Jinja templates, make sure you quote them (example: "dest: /opt/prometheus-{{ prometheus_version }}.linux-{{ architecture }}.tar.gz")
Constrain where the playbook runs with --limit and --tags
Say that you are only interested in running your playbook on a certain host. In that case, you can also do that by using the --limit flag:
ansible-playbook --inventory inventory --limit fido.yourcompany.com --tags certbot_renew site.yaml
Here we did run only a task tagged certbot_renew on the host fido.yourcompany.com.
How to deal with a real issue
Let's make this interesting: say that I was eager to update one of my requirements for certboot, and I changed versions if pip to '22.3.1':
pip==22.3.1
wheel==0.38.4
certbot==1.32.0
certbot-nginx==1.32.0
When I run the playbook we have a failure:
This is an issue with the versions if specified on the requirements_certboot.txt file. When you install a Python library using a virtual environment you can specify versions like this:
pip==22.3.1 wheel==0.38.1 certbot==1.23.0 certbot-nginx==1.23.0
To fix the issue, we will revert the versions used on the file and then re-run the requirements file and Certbot installation task:
- name: Setup Certbot
pip:
requirements: /opt/requirements_certboot.txt
virtualenv: /opt/certbot/
virtualenv_site_packages: true
virtualenv_command: /usr/bin/python3 -m venv
state: forcereinstall
tags: certbot_env
ansible-playbook --inventory inventory --tags certbot_env site.yaml
See it in action:
How to run the whole playbook
ansible-playbook --inventory inventory site.yaml
It is time to run the whole playbook:
Wrapping up
This tutorial only touches the surface of what you can do with Ansible. So below are a few more resources you should explore to learn more:
Improving inventories: How to create dynamic inventory files in Ansible, How to write a Python script to create dynamic Ansible inventories, How to write an Ansible plugin to create inventory files
Sometimes your playbooks will run slow, and you may need to Assess resource consumption with Ansible callback plugins.
And there will be a time when deeper debugging is needed.

