Note: This the seventh video in the Git for beginners series. Watch the first video here.
Imagine there are parallel worlds. We have:
- a world where I have created this video, and you’re watching it
- a world where I have created this video, but you’re not watching it
- a world where I did not create this video.
In this parallel world concept, a Git branch is a parallel world.
You can have a branch that stays the same in one world. Then you branch off into a different world. Once you finish your code, you can complete the initial world by merging the changes into it.
How to create a branch
Open up your Git client. Look for the branch you want to branch from. Right click on it and select create new branch.
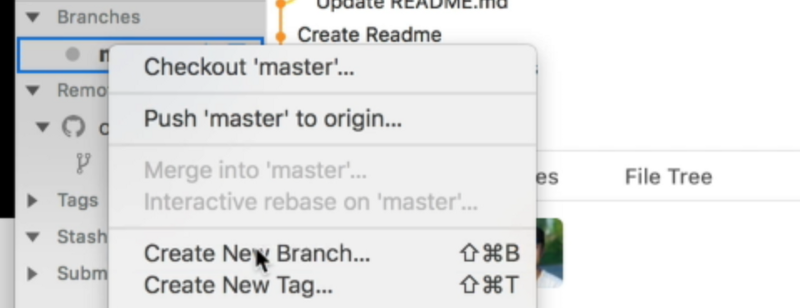
You can name your branch anything you want.
Usually the first branch we developers use is the development branch.
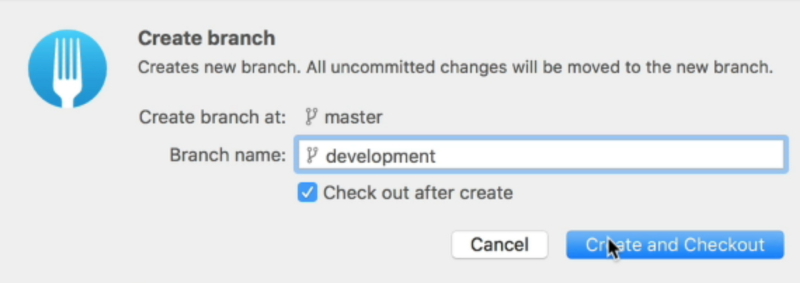
Once you name your branch, click on “Create and Checkout”. Checkout, in this case, means to move to the development branch.
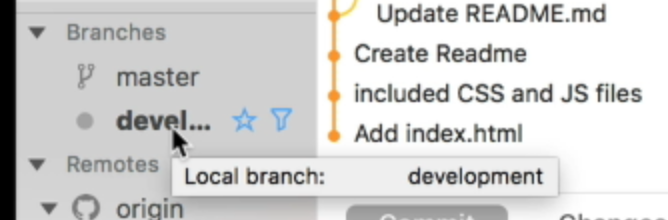
Once you create the development branch, you can see two branches in your branches section — master and development.
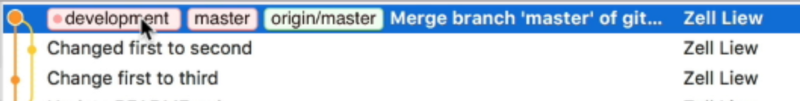
In the Git history, you can also see a new tag called development. This development tag is on the same commit as master and origin/master.
Why create a development branch?
Let’s say you have a website that’s ready for people to see. This website is on the master branch.
If you commit code to the master branch, it means you change the website directly. If you introduce any bugs, other people can see your bug immediately.
We’re humans. We make mistakes. We don’t want to show our mistakes to people.
So we create a new branch and work off it. When we’re done, and when we’re sure that there are no more bugs — at least we try to make sure! — we push the changes back to the master branch to update the website.
That’s why we use a development branch.
In this case, the master branch can also be called a production branch.
How to code on a new branch
When you create a new branch, you can code directly on the branch itself. Any code you change will be reflected only on that branch.
Let’s say we want to create a new file called development.md. In this file, we say “Hello! This is committed from the development branch!”.
# development.md Hello! This is committed from the development branch!If you go back to your Git client, you can commit this change to the development branch.
Make sure you’re on the development branch when you create the commit. In Fork, you can tell the branch you’re on by looking at the bolded branch.

Commit your code to the development branch.
Now, if you look at the Git history, you can see that the development branch is one commit ahead of the origin/master branch and the local master branch.
This shows we can code as much as we like on the development branch without affecting other branches.
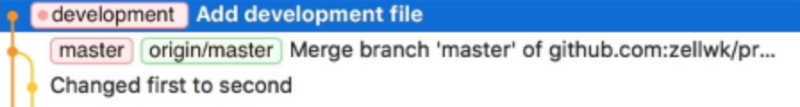
Pushing the development branch into the Git remote
You can push the development branch into the Git remote by clicking the push button. The steps will be similar to the steps when you pushed the master branch for the first time.
Once the push is completed, you can see the origin/development tag on the same commit as the development tag.
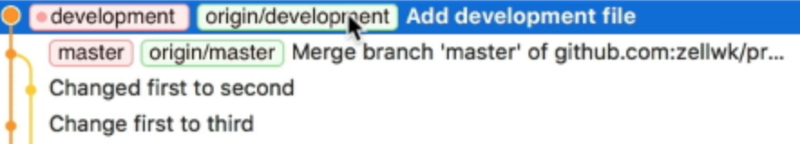
Switching between branches
To switch between branches, you can double-click the branch you want, on the sidebar. If you double-click on master, you will checkout master.
Checkout means to switch to the branch you chose.
If you look at your project now, you will realize that the development.md file is missing. This proves, again, that you can make as many commits as you need on your development branch without affecting other branches.
Merging branches
You’re done with the development process, and you’re ready to merge the branch back into master.
To merge, you first checkout the branch you want to merge to. This should be master.
Then, to merge the development branch into the master branch, you right-click the development branch in your Git client and select “Merge into ‘master’”.
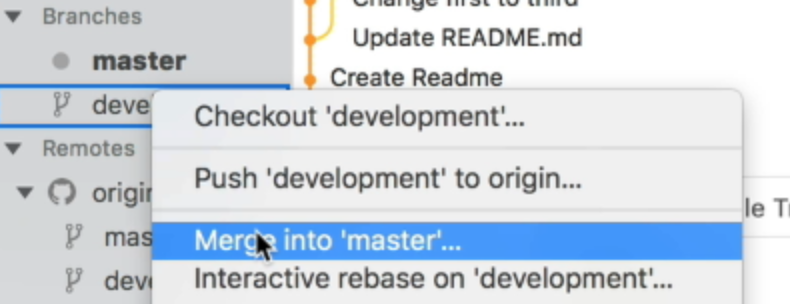
Fork will ask you whether you want to create a merge commit. Some clients do this for you automatically.
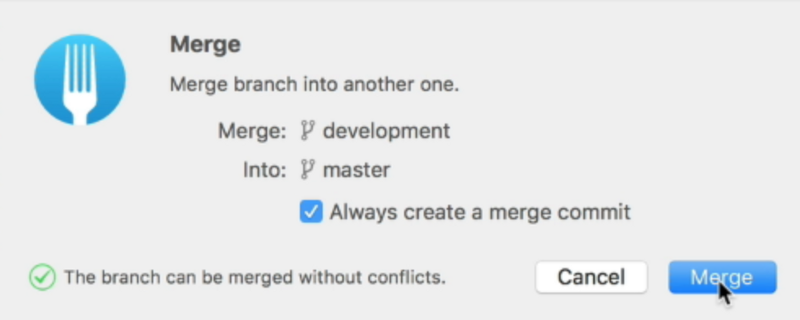
Select “Merge” and the merge will be completed.
If you look at the Git history now, you’ll see the master branch is ahead of the development and origin/development branches.
This is because we have done a merge commit.

At the same time, master is two commits ahead of the origin/master branch. That’s why we see 2 up in the sidebar.

When you’re done merging, you can update the Git remote by clicking on the Push button.

Deleting a branch
To delete a branch, you right-click the branch you want to delete and select “Delete ‘[branch-name]’”.
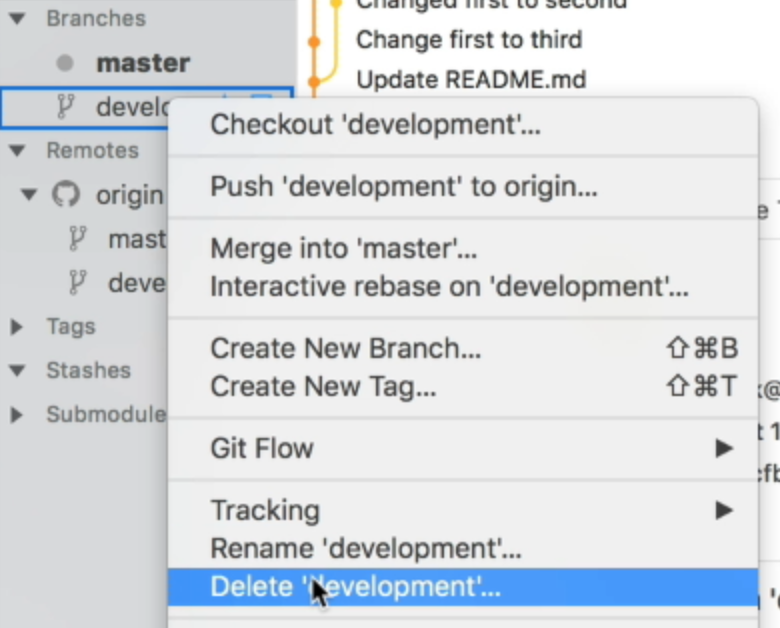
In Fork, you can also choose to remove the branch from the remote.
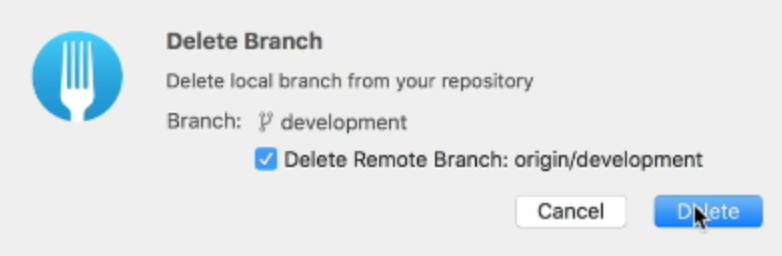
Click on “Delete” and Fork will delete both branches.
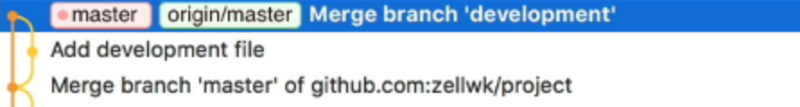
Once the delete is done, you can take a look at the Git history. You’ll notice that both the origin/development and development tags have both disappeared from the history.
Wrapping up
A branch is like a parallel world where you can create commit without introducing bugs into production code. You can always fix the bugs before merging your branch into the production code.
Thanks for reading. Did this article help you in any way? If you did, I hope you consider sharing it. You might help someone out. Thank you!
This article was originally posted at my blog.
Sign up for my newsletter if you want more articles to help you become a better frontend developer.