The term cloud computing refers to software and services that run on the internet instead of locally on your on-site server or computer.
Adopting the cloud can help you and your team cut costs and ensure that your data and systems are available to your customers anywhere and at any time.
Cloud technology has a lot of potential for many different businesses and it continues to expand as well.
Many cloud providers are available around the world such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google GCP. So you should be able to find an option that's right for you to migrate from on-site servers to cloud servers.
In this article, you are going to learn why so many companies are moving to the cloud and top 5 cloud migration strategies that can be applied when smoothly moving your data and system to the cloud.
Let’s get started. 🚀
Why Move to the Cloud?
There are a number of reasons why companies make the move to the cloud. You can get these advantages without the cloud like you’ve been doing for years – but the cloud has made many of them easier and more affordable.
1. Fault Tolerance
A common reason companies many companies first get interested in the cloud is fault tolerance.
By definition, fault tolerance is the ability of a system to continue operating without interruption when one or more of its components fail. Here, a system can be a computer, network, or cloud cluster.
If you’re a company that values uptime and consistency, you'll likely have a disaster recovery plan. These plans usually involve some alternate place where you can store data or your systems if your primary data center has some sort of catastrophic problem.
Traditionally, companies do this by contracting with a provider to keep a physical second copy of their hardware. This way it's ready to go when the primary hardware fails to operate.
The only problem is that when everything’s up and running fine, that backup physical hardware is just sitting around collecting dust and becoming obsolete. And it will cost you more because you’re still paying for it even if you don’t use it at that moment.
Additionally, what if something happens to that physical copy? It's gone forever.
But what if there was a better way rather than buying all your backup equipment? Why not just rent it only when you need it?
Cloud providers can have massive amounts of system capacity available to you in seconds, and you only have to pay for what you use.
Also, you don't have to worry about managing those resources yourself. This almost always results in huge cost (and time) savings. Then when the crisis is over, you can just shut those things down and stop paying.
2. Cost Savings
Moving to cloud technology enables you to save both space and costs. Before the cloud, you had to pay for on-site servers (sometimes even off-site data centers). With the cloud, you pay cloud providers to handle the data centers and other resources rather than hosting the servers in-house on your own.
For example, Oracle reports that their cloud customers save approximately 30% to 50% by switching to the cloud.
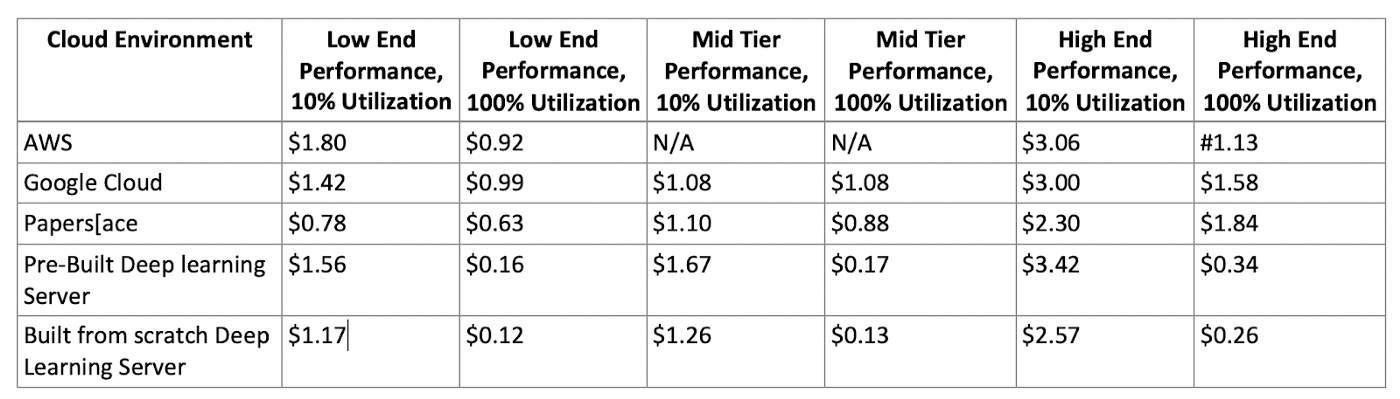
But if you misuse your cloud resources, they can easily cost dramatically more than any sort of on-site server. And this is why it’s so important to train your staff and involve experienced cloud architects.
So you can have great cost savings, but you have to be careful about the expectations you set, especially in the early days.
3. Globalisation
This is another common reason companies move to the cloud. As your business grows and expands beyond your home country, it makes sense to have resources and services close to those new markets that you want to reach. This can be for regulatory reasons or maybe performance reasons.
Cloud providers already have data centers and resources in various geographical locations around the world, and you can use those with little more than a click of a button.
This can save a lot of cost, since you don’t have to create data centers on your own. And customers always appreciate performance gains.
4. Agility
Another reason why companies move to the cloud is agility. In a simple definition, agility is the ability to respond to changing needs.
In many companies, if you want to run an experiment that requires IT equipment, you would likely have to endure a requisition and procurement process and secure resources from the IT group to set up and maintain that equipment. These steps could take weeks or months.
But by adopting cloud services from different providers, you can get access to that equipment in a matter of minutes and you can try your experiment and then shut down the equipment when you need to do so.
Another advantage is that you can get your results in days instead of a month and the cost will be low compared to other ways.
5. Scalability
Another reason companies adopt the cloud is scalability. Scalability in cloud computing refers to the ability to increase or decrease IT resources as needed to meet changing business demands. Your goal is to have your capacity as close to your needs as possible, but that’s a pretty tricky thing to forecast.
The pay-as-you-go model of cloud providers lets you have the flexibility and the ability to scale up or scale down depending on your business needs
How is Cloud Computing Implemented in the AI Space?
Cloud Computing helps companies work on big data and develop Artificial Intelligence solutions to solve their business problems.
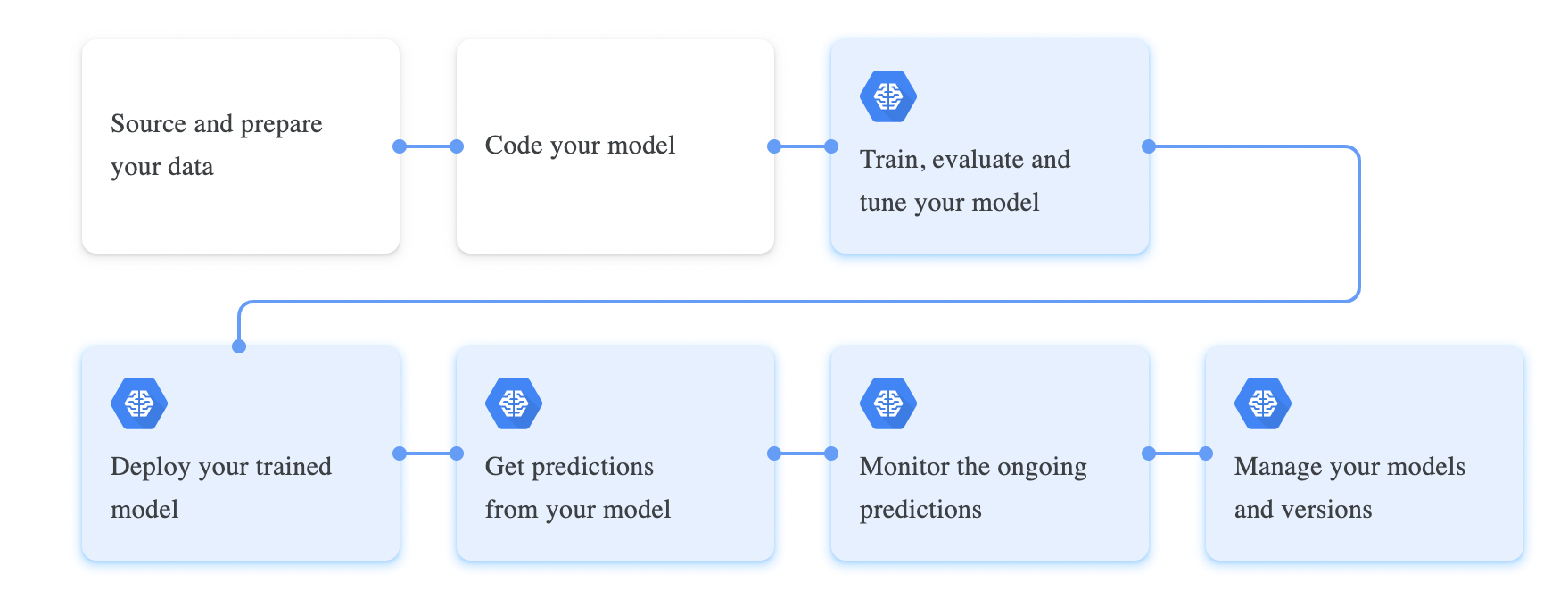
For example, Google Cloud ML Engine is a general-purpose service provided by Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It requires you to write code using Python and the TensorFlow libraries to train and evaluate machine learning models for different use cases such as image recognition.
You can also deploy and run your Artificial Intelligence solutions on the cloud platform so that they're accessible via APIs to your web applications.
What are the Top 5 Cloud Migration Strategies?
A cloud migration strategy is a plan a company can adopt to move some or all of its data and systems into the cloud. Having a good strategy is crucial because it can help a company to identify and validate the most efficient way to migrate its data and systems.
There are several migration strategies you can apply when moving to the cloud. The right strategy to apply will depend on the system’s requirements and your long-term plans.
1. Rehosting
The first migration strategy is just simply moving your existing data and systems to the cloud with no changes. This means you will move the same software, same operating system, and the same data that run on the old environment (on-site server) to the cloud provider.
Sometimes this strategy is called “Lift and Shift” as you just move from point a to point b without making any changes. The advantage of this strategy is that it has a lower risk when migrating to the cloud. But the downside is that it may not typically offer very much benefit in the long run.
“Cordant Group rehosted its IT operations on AWS and saved up to 50% infrastructure costs.”- simform.com
Note: This is a very common first step for many companies migrating to the cloud.
2. Replatform
This strategy gives you the advantage of using some of the cloud services provided by the cloud provider. Instead of just lifting your data and system over to the cloud, you can start to use existing cloud services offered by the cloud vendor.
For example, the cloud provider can offer a fully-managed database service that allows a company to manage its database and can potentially save costs on fault-tolerant and maintenance.
3. Repurchase
This strategy gives you an option to purchase something that is already in the cloud instead of moving your system to the cloud.
You can abandon an existing system and shop for new cloud services from a cloud vendor. Sometimes, this migration strategy is called “Drop and Shop”.
For example, a company can decide to license some user accounts or a new customer relationship management system that is already in the cloud. Salesforce is an example of these types of systems.
4. Rearchitect
If you wanted to get really ambitious, you can totally rearchitect by redesigning and rebuilding your systems on the cloud. You can use all of the various services that a cloud provider has to create what some people call a cloud-native version.
This just means that you are using methods that best take advantage of what a cloud provider has to offer. This process takes a lot of time and is only considered when you decide that your existing systems don’t meet current business needs.
This method tends to yield the best return in the long run. For example, a company can leverage cloud capabilities that are not available in existing environments such as serverless computing and cloud auto-scaling.
Note: This migration strategy is also the most complex and risky.
5. Retire
The last migration strategy is called Retire. Here a company can evaluate their systems to figure out which parts of the system are not being used at all.
And if this is the case, a company can simply turn them off since there’s a cost to keeping that system running. Sometimes this is called sunsetting a system or an application.
Final Thoughts
Cloud technology has a lot of benefits from both a business and operations perspective. In this article I have explained a few of them that can help you make a decision to adopt cloud technology in your company or for your personal projects.
Besides the benefits to adopting cloud technology, there are still potential risks that you have to take into consideration. Some of these risks are:
- Migration to the cloud can be time-consuming.
- You don't have as much control over your data because you're using a third party.
- Cloud technologies require more skill to manage.
- There's the potential for existing data loss.
You also have to know that cloud migration can be complex and risky. Implementing a cloud migration strategy can come up with its own challenges, such as cost management, vendor lock-in, data security and compliance.
These challenges can be handled if you select the right migration strategy based on your data and systems.
If you learned something new or enjoyed reading this article, please share it so that others can see it. Until then, see you in the next post!
You can also find me on Twitter @Davis_McDavid.

