WordPress is a free and open-source content management system based on PHP and MySQL. Features include a plugin architecture and a template system. It is most associated with blogging, but supports other types of web content including more traditional mailing lists and forums, media galleries, and online stores.
WordPress is powering almost 27% of all websites and currently is dominating the CMS market share. Backed up by a huge community, this Open Source platform powers a multi-billion dollar economy with themes/plugins and custom software.
We recommend you start learning with freeCodeCamp's 4-hour WordPress tutorial on YouTube. This will help you build a WordPress website from scratch.

Then, we encourage you to learn PHP - the programming language that powers WordPress. freeCodeCamp has a 4-hour tutorial on PHP and WordPress on YouTube.

What is PHP?
PHP is a server-side scripting language created in 1995 by Rasmus Lerdorf.
PHP is a widely-used open source general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and can be embedded into HTML.
What does the acronym PHP stand for?
Originally PHP stood for ‘Personal Home Page’, as Rasmus Lerdorf created it for use on his own website. Then in 1997 more developers expanded the language and the acronym also changed to what it stands for today: ‘PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor’. As the first ‘P’ in PHP also stands for ‘PHP’, it is known as a ‘recursive acronym’.
What is PHP used for?
As of October 2017, PHP is used on 82% of websites whose server-side language is known. It is typically used on websites to generate web page content dynamically. Use-cases include:
- Websites and web applications (server-side scripting)
- Command line scripting
- Desktop (GUI) applications
Typically, it is used in the first form to generate web page content dynamically. For example, if you have a blog website, you might write some PHP scripts to retrieve your blog posts from a database and display them. Other uses for PHP scripts include:
- Processing and saving user input from form data
- Setting and working with website cookies
- Restricting access to certain pages of your website
How does PHP work?
All PHP code is executed on a web server only, not on your local computer. For example, if you complete a form on a website and submit it, or click a link to a web page written in PHP, no actual PHP code runs on your computer.
Instead, the form data or request for the web page gets sent to a web server to be processed by the PHP scripts. The web server then sends the processed HTML back to you (which is where ‘Hypertext Preprocessor’ in the name comes from), and your web browser displays the results.
For this reason, you cannot see the PHP code of a website, only the resulting HTML that the PHP scripts have produced.
This is illustrated below:
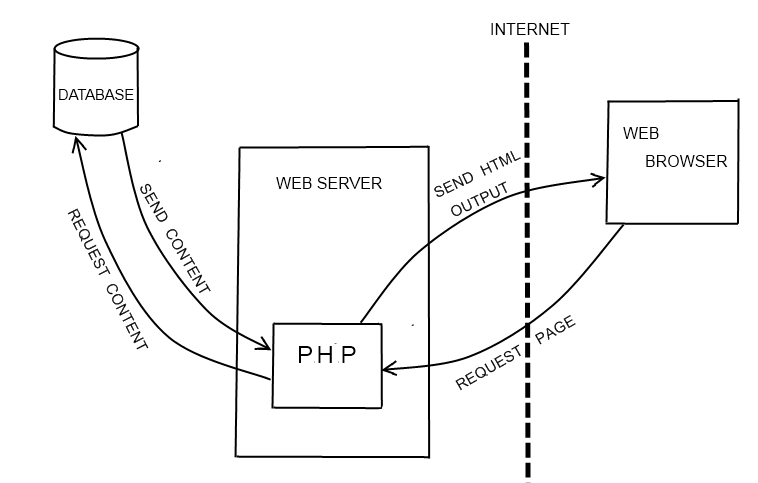
PHP is an interpreted language. This means that when you make changes to your source code you can immediately test these changes, without first needing to compile your source code into binary form. Skipping the compilation step makes the development process much faster.
PHP code is enclosed between the <?php and ?> tags and can then be embedded into HTML.
Installation
PHP can be installed with or without a web server.
GNU/Linux
On Debian based GNU/Linux distros, you can install by:
sudo apt install phpAfter installing you can run any PHP files by simply doing this in your terminal:
php file.phpYou can also install a localhost server to run PHP websites. For installing Apache Web Server:
sudo apt install apache2 libapache2-mod-phpWhat Can PHP Do?
- PHP can generate dynamic page content
- PHP can create, open, read, write, delete, and close files on the server
- PHP can collect form data
- PHP can send and receive cookies
- PHP can add, delete, modify data in your database
- PHP can be used to control user-access
- PHP can encrypt data
Why PHP?
- PHP runs on various platforms (Windows, Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, etc.)
- PHP is compatible with almost all servers used today (Apache, IIS, etc.)
- PHP supports a wide range of databases
- PHP is free. Download it from the official PHP resource: secure.php.net
- PHP is easy to learn and runs efficiently on the server side
PHP Frameworks
Since writing the whole code for a website is not really practical/feasible for most projects, most developers tend to use frameworks for the web development. The advantage of using a framework is that
- You don’t have to reinvent the wheel every time you create a project; a lot of the nuances are already taken care of for you
- They are usually well-structured so that it helps in the separation of concerns
- Most frameworks tend the follow the best practices of the language
- A lot of them follow the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern so that it separates the presentation layer from logic
Popular frameworks
Documentation
PHP is well documented. The official docs include examples on almost every function reference guide, as well as user comments.
Other Resources
- Tizag.com PHP Tutorial: still-relevant tutorials for getting started with PHP
- Awesome PHP: a curated list of PHP libraries, resources, and “shiny things”
- Laracasts.com: a membership website to learn web application development with PHP
