Say you're working on your code in Git and something didn't go as planned. So now you need to revert your last commit. How do you do it? Let's find out!
There are two possible ways to undo your last commit. We'll look at both of them in this article.
The revert command
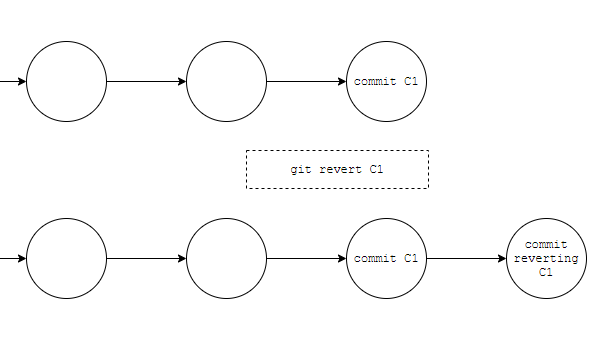
The revert command will create a commit that reverts the changes of the commit being targeted. You can use it to revert the last commit like this:
git revert <commit to revert>You can find the name of the commit you want to revert using git log. The first commit that's described there is the last commit created. Then you can copy from there the alphanumerical name and use that in the revert command.
The reset command
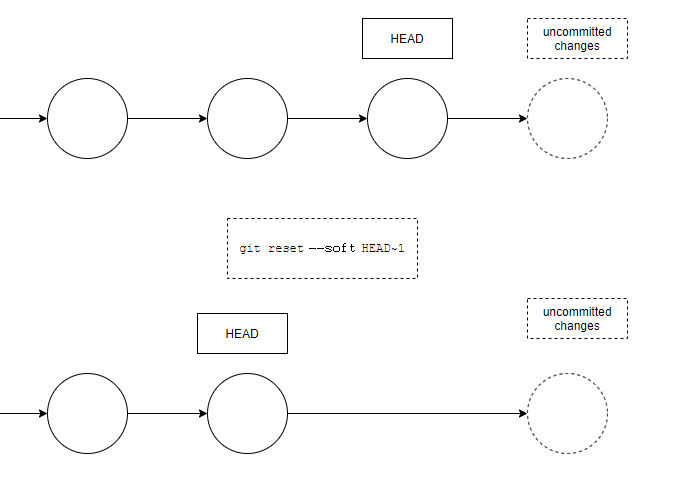
You can also use the reset command to undo your last commit. But be careful – it will change the commit history, so you should use it rarely. It will move the HEAD, the working branch, to the indicated commit, and discard anything after:
git reset --soft HEAD~1The --soft option means that you will not lose the uncommitted changes you may have.
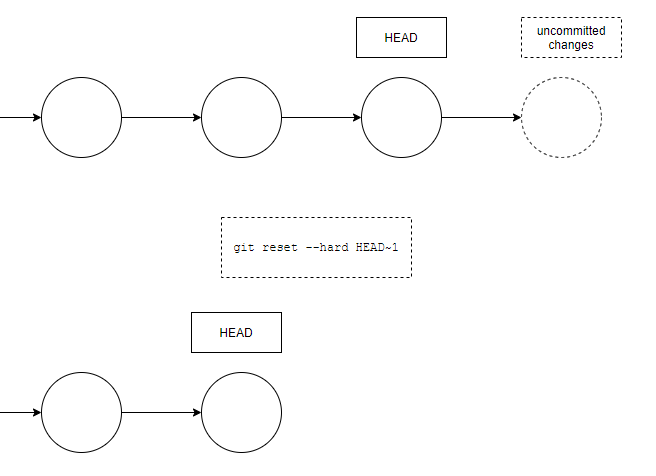
If you want to reset to the last commit and also remove all unstaged changes, you can use the --hard option:
git reset --hard HEAD~1This will undo the latest commit, but also any uncommitted changes.
Should You Use reset or revert in Git?
You should really only use reset if the commit being reset only exists locally. This command changes the commit history and it might overwrite history that remote team members depend on.
revert instead creates a new commit that undoes the changes, so if the commit to revert has already been pushed to a shared repository, it is best to use revert as it doesn't overwrite commit history.
Conclusion
You have learned two ways to undo the last commit and also when it's best to use one over the other.
Now if you notice that your last commit introduces a bug or should have not been committed you know how to fix that!

