When developers and operations teams work together, they can identify and solve problems more quickly. This helps them deliver software to users faster and with fewer errors.
This general practice is called DevOps. It involves using tools and techniques to automate tasks and make software development and deployment more efficient.
In this tutorial, we will explore what DevOps is and why organizations should have DevOps specialists. We'll also discuss the DevOps lifecycle and compare it with the Agile methodology.
What is DevOps?
DevOps, at its core, focuses on implementing automation at each and every stage of the software development lifecycle.
The term DevOps is a combination of two terms: Development and Operations. DevOps aims to simplify and reduce the development life cycle of a system.
The DevOps Team is a combination of the Development Team and the Operations Team.
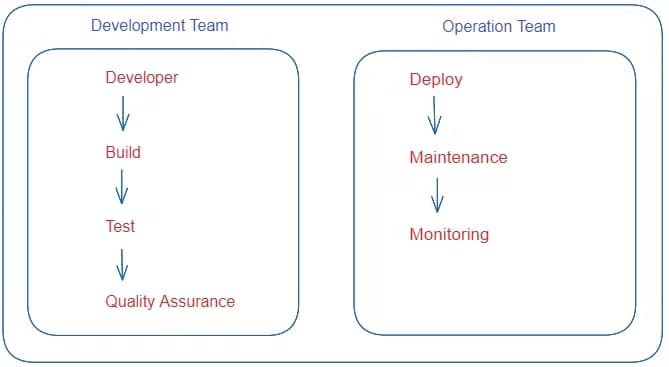
DevOps is a methodology that allows a single team to manage the entire application development life cycle – that is development, testing, deployment, and operations.
This approach can help your team produce superior quality software quickly and with more reliability.
How Does DevOps Work?
Before DevOps, the development team and the operations team worked separately. This often created a lot of issues in production because both teams were working separately without consulting each other and integrating best practices.
Suppose the operations team has an issue during deployment and they want to communicate with the deployment team. But the deployment team isn't available at that time, so they have to wait a while. Not only that, but the entire process was manual.
Because of all of these issues, the DevOps team got created. Again, it combines the Development Team and the Operations Team and automates every step of the process.
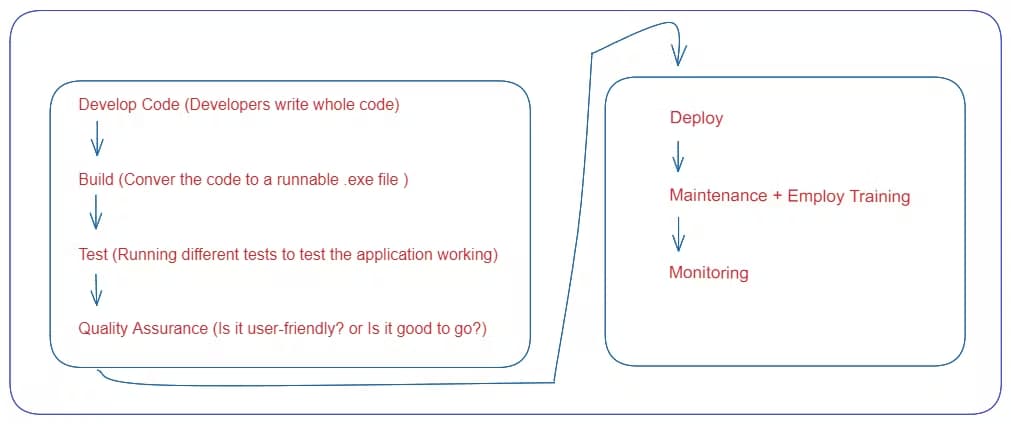
Let's look at a sample workflow a DevOps team might follow:

In general, developers use version control systems like Git to manage changes in their codebase, and they can use platforms like GitHub to collaborate with others and share their work.
Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) tools like Jenkins can be used to automate software building, testing, and deployment, and they often work together with build automation tools like Maven.
Browser automation tools like Selenium can be used to automate web application testing, and deployment automation tools like Chef, Ansible, Docker, and Kubernetes can be used to automate the process of deploying software to different environments.
Finally, monitoring tools like AWS CloudWatch can be used to monitor software applications and infrastructure performance and health.
Why Do You Need a DevOps Specialist?
A DevOps specialist plays an important role in achieving the goals of fast delivery, high quality, reduced costs, and improved reliability of software releases.
Fast delivery:
DevOps specialists help streamline the development process by automating build, test, and deployment pipelines, allowing the company to release software more quickly. They also help identify and resolve bottlenecks in the development process, improving efficiency, and reducing delays.
High quality:
DevOps specialists work closely with development and operations teams to ensure that software releases meet the necessary quality standards. They also make sure that customer feedback is incorporated into future releases, allowing the company to continually improve the quality of its software.
Less Capex (Capital Expenditure) + Opex (Operational Expenditure):
DevOps specialists help identify and implement tools and processes that reduce the time and resources required for software releases. By automating manual tasks and reducing the need for manual intervention, organizations can save time and money, and improve overall efficiency.
Reduce outages:
DevOps specialists help reduce outages and improve reliability by implementing monitoring and alerting systems that proactively identify and address issues before they become major problems.
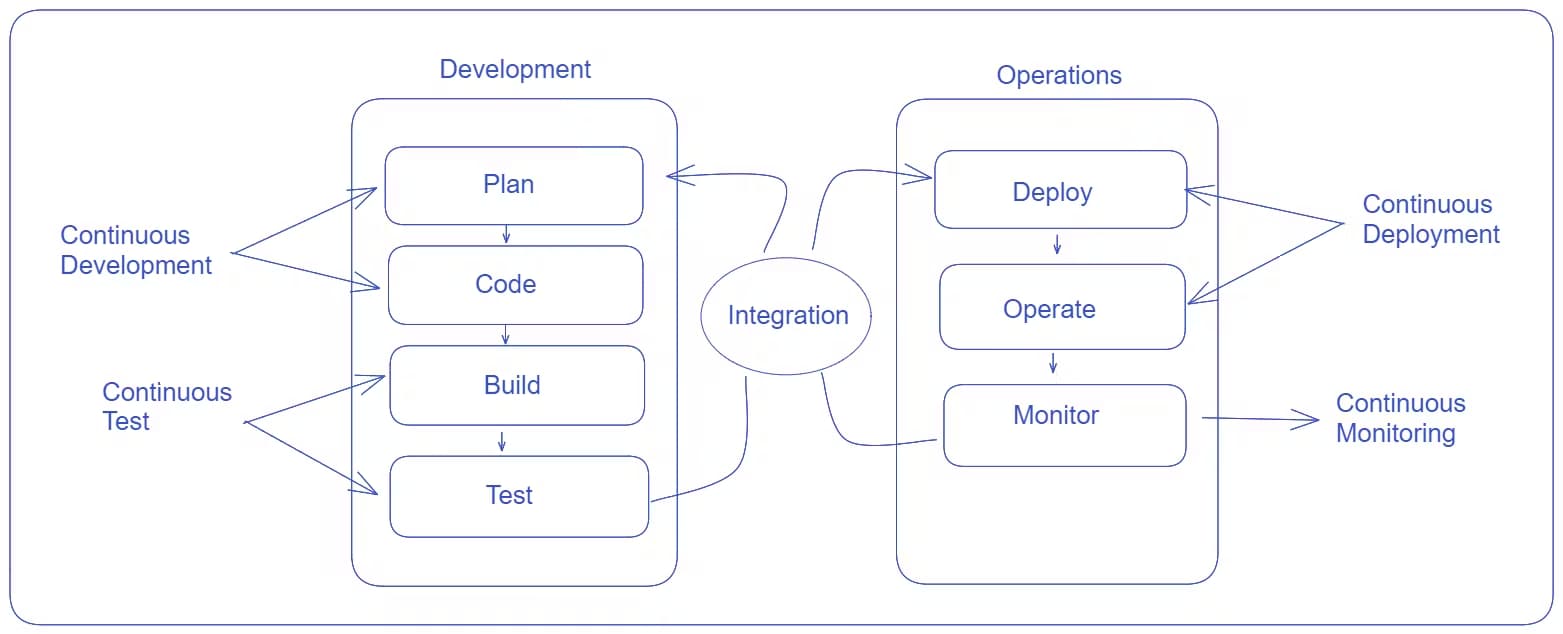
DevOps Life Cycle
When building a product, teams go through what is known as the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It's a process used by software development teams to design, develop, test, and deploy software applications.
It is helps to ensure that software is delivered on time, within budget, and meets the requirements of stakeholders.
Before DevOps, we used to follow the waterfall or step-by-step model.
The Waterfall methodology has been largely replaced by Agile methodology. The main difference between Agile and Waterfall is that Waterfall is a linear system of working that requires the team to complete each project phase before moving on to the next one. Agile, on the other hand, encourages the team to work simultaneously on different phases of the project and allows them to iterate, make changes, and check in along the way.
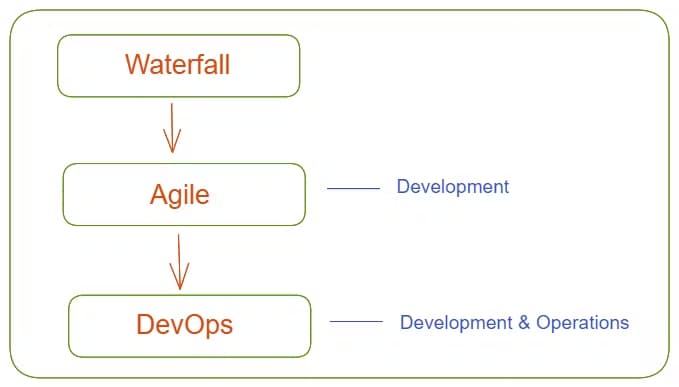
DevOps is an extension of Agile practices. DevOps builds on the principles of Agile, which emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development.
Agile phases are comprised of scrums, sprint planning, sprint review, and so on. DevOps, on the other hand, includes planning, building, continuous delivery, testing, and feedback.
Example:
Suppose a customer wants to build an e-commerce app. Let's have a look at the workflow:
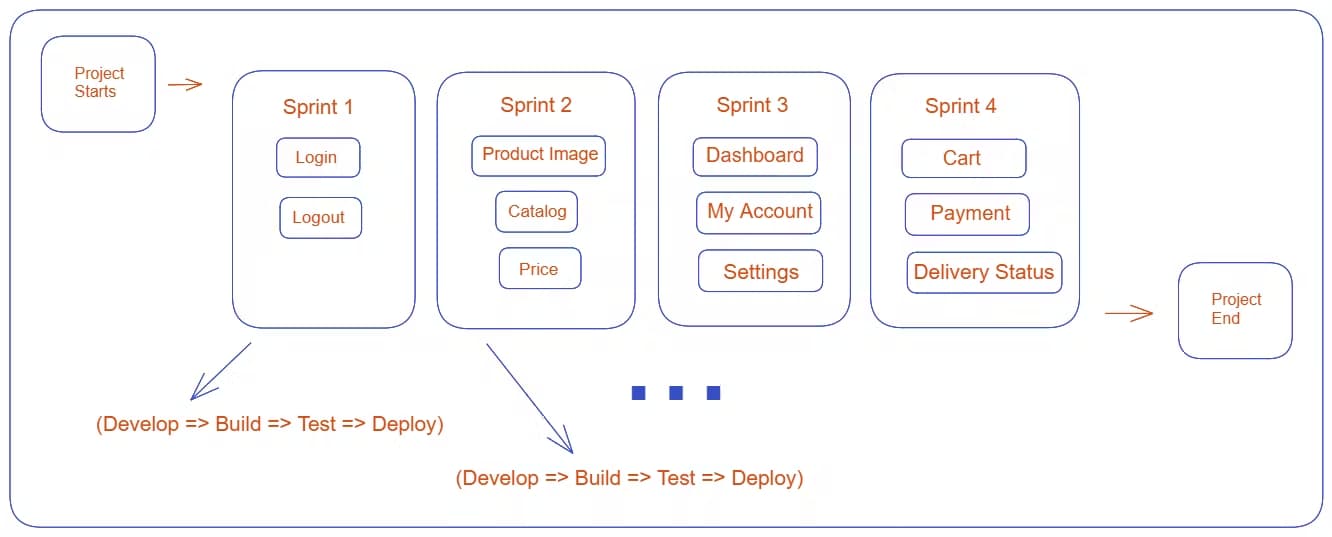
The sprints shown in the figure represent the steps in the project. Each sprint includes Develop, Build, Test, and Deploy phases.
After completing a sprint, the team contacts the client to check in. If the client wants any changes, the team can easily make them. Once a sprint finishes, the team move on to the next one.
This process may take several days or weeks, which is where DevOps comes in. By implementing DevOps practices like continuous integration and continuous delivery, you can automate the process of building, testing, and deploying the app.
If any issues arise, the team can quickly fix them without causing any downtime for the users.
Myths about DevOps:
- Deep Knowledge of a programming language is required: You only need to have a basic understanding of programming concepts to be able to work with code and automate processes.
- Linux experience is a must: You don't need to be an expert in it. Knowing some basic commands and navigating the file system is enough to get started.
- Prior IT experience is required: DevOps is about collaboration between development and operations teams to improve software delivery. You don't need prior IT experience to be part of a DevOps team.
- Non-technical background people can't be a DevOps engineer: Anyone can become a DevOps engineer, regardless of their technical background. While technical skills are important, soft skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving are equally valuable in DevOps.
Wrapping Up
In this article, we discussed how to get started with DevOps, why companies need a DevOps specialist, how DevOps works, and the DevOps life cycle.
You can feel confident learning about DevOps as DevOps isn't going anywhere. DevOps is a methodology that is becoming increasingly popular among organizations that are looking for ways to improve their software development process.
I hope that I have added some value 🚀

