by Vince Tabora
How to run GETH from a Docker container
Installing the Ethereum node client on a machine can be a tedious process. There is a simpler way this can be done using a Docker client. This is a guide for running the GETH (Ethereum-Go) node client from inside a Docker container. GETH is the GoLang implementation of the Ethereum protocol. There is an image available to pull from the Docker hub repository that can run the environment.
The GoEthereum website lists the following available images with descriptions.
ethereum/client-go:latestis the latest develop version of Gethethereum/client-go:stableis the latest stable version of Gethethereum/client-go:{version}is the stable version of Geth at a specific version numberethereum/client-go:release-{version}is the latest stable version of Geth at a specific version family
The following ports are opened by default when running from the container.
8545TCP, used by the HTTP based JSON RPC API8546TCP, used by the WebSocket based JSON RPC API30303TCP and UDP, used by the P2P protocol running the network30304UDP, used by the P2P protocol's new peer discovery overlay
The Docker client software must be installed on the machine you are going to run the container from. Containers can only run if you have the Docker client installed. Depending on your operating system, the correct version of the client will be needed.
There are separate versions for Windows, Linux and the MacOS. The container can even be run on a Linux instance running on AWS, like a typical Linux installation. Once the Docker client is installed, the underlying platform doesn’t matter. The commands will be the same for all.
Getting The Image
Open a terminal on Linux or MacOS, or PowerShell command prompt from Windows. In the CLI prompt, type the following command:
docker pull ethereum/client-go
This pulls the Docker image from the hub repository where it was uploaded by the Ethereum developers. Once you have issued this command, the following verbose or similar should be displayed:

I have already pulled the image, so the verbose may look different. When you issue the pull command it will always download the latest image available, which is good practice.
Running The Node
Now you can start the node by issuing the following command:

We want to run the node with the flag options -i and -t to display information from our container. The -p indicates the use of a port number, in this case 30303. Likewise, the command can be run without the flags and it will simply use the default ports and settings from inside the container.
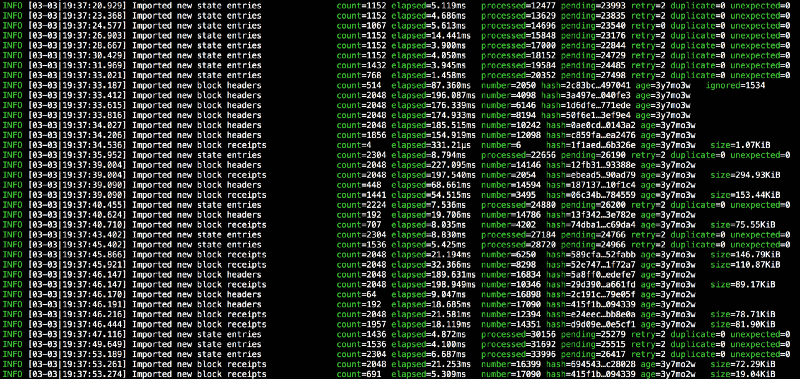
The following information should appear from the terminal.

The INFO line that shows the config reveals what the node client software has installed. The node client is running the latest (as of this posting) version of the Ethereum software which is Constantinople that is a user activated hard fork at block height 7280000.
When running in JSON-RPC API:

Take note that running the option rpcaddr “0.0.0.0” is not secure, since you are opening up your node to all traffic. If your ETH wallet were unlocked, a hacker can get to your node in this way and take your coins. I don’t cover security in this article, but you can read more about that here (securing your GETH node’s RPC ports). Always abide to safe and best practices.
If the node displays the following in the INFO line, there will be a problem:
config=”{ChainID: 1 Homestead: 1150000 DAO: 1920000 DAOSupport: true EIP150: 2463000 EIP155: 2675000 EIP158: 2675000 Byzantium: 4370000 Constantinople: <nil> Engine: ethash}”
The Constantinople: <nil> indicates the software was not updated. There is also no line for ConstantinopleFix, which appears in the correct configuration.
Persistent Data
For persistent blockchain data, Docker data volumes should be used with the option -v. The /path/on/host should be replaced with the location you specify. For this the following command must be used:

Checking Node Status
You can check the container’s status using the following command:
docker ps

This will display the Container ID with the image name, status and ports used.
#These are the commands to run from the Docker CLI to run the Ethereum Go node client
#GETTING THE IMAGE
docker pull ethereum/client-go
#RUNNING THE NODE
docker run -it -p 30303:30303 ethereum/client-go
#RUNNING NODE USING API
docker run -it -p 8545:8545 -p 30303:30303 ethereum/client-go --rpc --rpcaddr "0.0.0.0"
#Note, warning about using --rpcaddr "0.0.0.0" in a live environment. It is an insecure way of opening your node.
#There are different ways to secure your ports, but this is one thing to take note of if you plan to use the API.
#PERSISTENT DATA
docker run -it -p 30303:30303 -v /path/on/host:/root/.ethereum ethereum/client-go
Take note that this does not automatically mine ETH. That is a different process. For getting quick access to the Ethereum blockchain, this is the purpose for running GETH.
For full code source, visit: https://github.com/Play3rZer0/GETHDocker.git