You may already know that Git is like a save point system. What you generally learn with Git initially is to learn to save your changes and commit them to a remote repository. But how do you undo a change, and go back to a previous state?
That’s what we’re going to cover within this article.
I’ve covered the contents in this article in a video if you like learning by watching instead of reading.
Local vs Remote
It’s more complicated to undo something that’s already on the remote. This is why you want to keep things on your local until they’re kind of confirmed.
Four common scenarios
We’ll be covering the following four common scenarios
- Discarding local changes
- Amending the previous commit
- Rolling back to a previous commit
- Reverting a commit that has been pushed to the remote
Note: In the screen shots below, I’ve used the Fork for Mac OS Git Client. You can do the same in other similar Git clients.
Scenario 1: Discarding local changes
The first scenario is when you’ve created some changes. They’re not committed yet. And you want to delete these changes.
Let’s say we want to create a new feature. We’re going to add some HTML and CSS into the project:
<!--In index.html-->
<div class="feature"></div>
```
```css
/* In CSS file */
.feature {
font-size: 2em;
/* Other styles */
}To discard these changes:
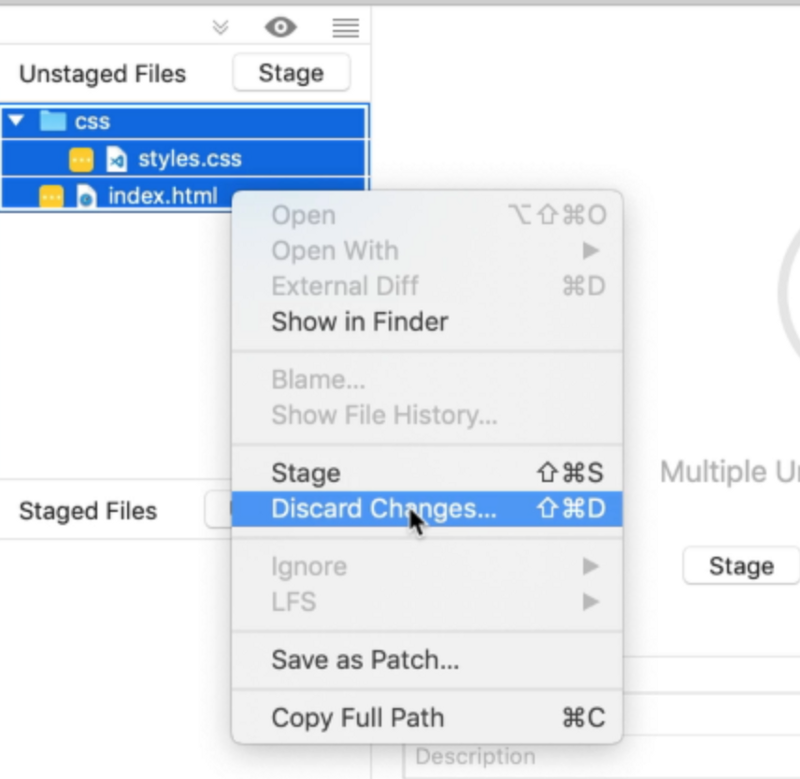
- Go to the staging area
- Select the files where you want to discard changes
- Right click on the files
- Select discard changes
Scenario 2: Amending the previous commit
When you have created a commit and you missed out some changes and you want to add these changes in the previous commit message.
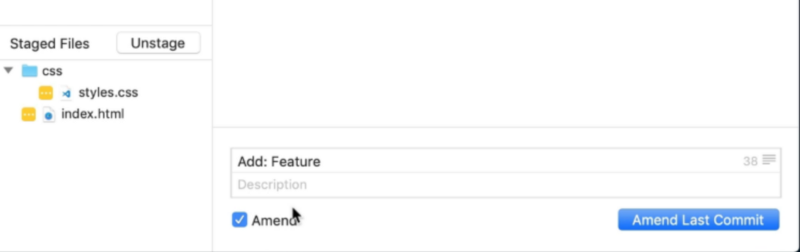
- Go to the staging area
- Stage the files to commit
- Click on the amend checkbox
- Edit your commit message
- Commit
Scenario 3: Rolling back to a previous commit
You already have a few commits in your local repository. You decide that you don’t want these commits anymore and you want to “load” your files from a previous state.
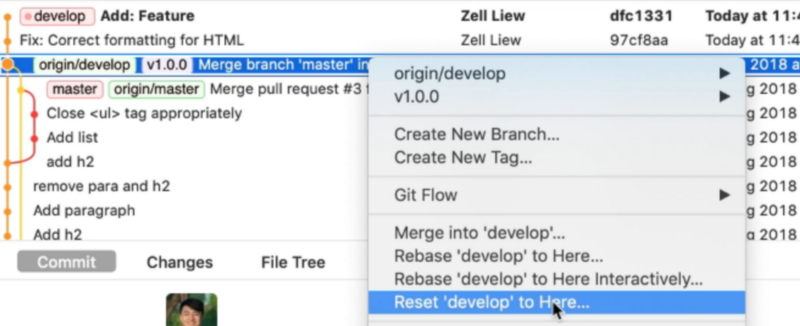
- Go into the Git History
- Right click the commit you want to roll back to
- Select reset
branchto here
Note: You can only reset to a commit that hasn’t been pushed into the remote.
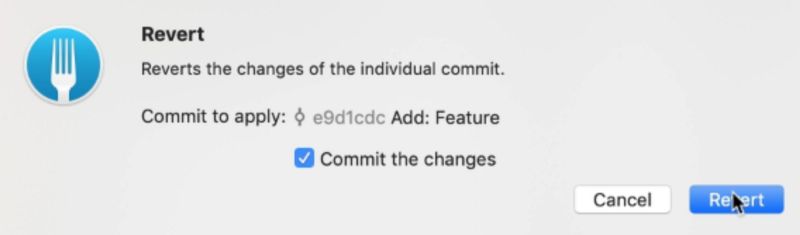
Scenario 4: Reverting a commit that has been pushed to the remote
If you have a commit that has been pushed into the remote branch, you need to revert it.
Reverting means undoing the changes by creating a new commit. If you added a line, this revert commit will remove the line. If you removed a line, this revert commit will add the line back.
To revert, you can:
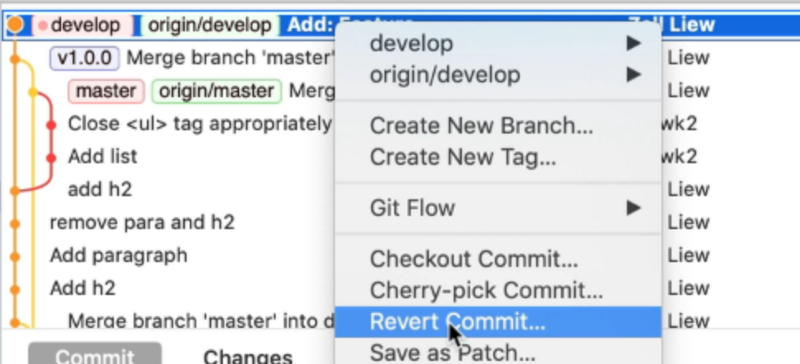
- Go to the Git history
- Right click on the commit you want to revert
- Select revert commit
- Make sure
commit the changesis checked. - Click revert
Other scenarios
GitHub has a useful article that shows you how to undo almost everything with Git. It will be helpful if you face other scenarios. Read it here.
Thanks for reading. Did this article help you in any way? If it did, I hope you consider sharing it. You might help someone out. Thank you!
This article was originally posted at my blog.
Sign up for my newsletter if you want more articles to help you become a better frontend developer.