The Node Package Manager (npm) provides various features to help you install and maintain your project's dependencies.
Dependencies can become outdated over time due to bug fixes, new features, and other updates. The more project dependencies you have, the harder it is to keep up with these updates.
Outdated packages can pose a threat to security and can have negative effects on performance. Up-to-date packages prevent vulnerabilities. This means that periodic dependency checks and updates are important.
How to Keep Dependencies Up-To-Date
Now, you could go through each individual package in package.json one by one to change the version and run npm install <package>@latest to get the latest version. But this isn't going to be the most efficient method.
Imagine if you had 20 or more packages that could use a version bump. Instead, you should develop a workflow to periodically check for new versions before the number of outdated dependencies grows and it becomes increasingly harder to upgrade.
Here's a workflow that helps me stay on top of updates: first, discover which packages need to be updated and how far behind the versions are. Next, choose to update packages individually or together in a batch. Always test out the updates to ensure breaking changes haven't occurred.
I prefer to perform major version updates individually. With major updates, you're likely to encounter breaking changes. It's much easier to undo or address code changes in relation to one package compared to many.
In this article, I will go over methods to inspect and upgrade dependencies in detail.
How to Use the npm outdated Command
npm outdatedThis command will check every installed dependency and compare the current version with the latest version in the npm registry. It is printed out into a table outlining available versions.
It is built into npm so there are no additional packages required to download. npm outdated is a good place to start for an overview of the number of dependency updates required.

- Current is the current version installed.
- Wanted is the max version of the package according the semver range.
- Latest is the version of the package tagged as latest in the npm registry.
With this method, to install updates for every package, you just need to run:
npm updateKeep in mind that with npm update it will never update to a major breaking-changes version. It updates the dependencies in package.json and package-lock.json. It will use the "wanted" version.
To obtain the "latest" version append @latestto individual installs, for example npm install react@latest.
How to Use npm-check-updates
For an advanced and customizable upgrading experience, I'd recommend npm-check-updates. This package can do everything npm outdated and npm upgrade can do with some added customization options. It does require a package installation, however.
To get started, install the npm-check-updates package globally:
npm install -g npm-check-updatesThen, run ncu to display packages to upgrade. Similar to npm outdated it will not apply any changes.
ncu
Checking package.json
[====================] 12/12 100%
@testing-library/user-event ^13.5.0 → ^14.2.1
@types/jest ^27.5.2 → ^28.1.4
@types/node ^16.11.42 → ^18.0.1
Run ncu -u to upgrade package.jsonTo upgrade dependencies, you just need to run:
ncu --upgrade
// or
ncu -u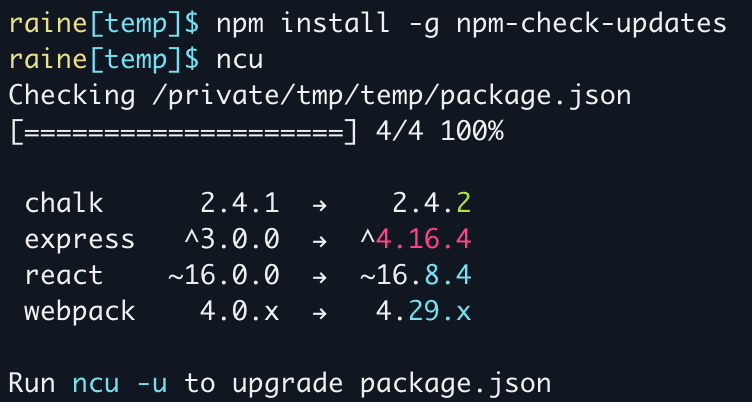
- Red = major
- Cyan = minor
- Green = patch
This updates dependencies in only the package.json file and will select the latest version even if it includes a breaking change. With this method, npm install is not run automatically so be sure to run that afterward to update package-lock.json.
To choose your preferred version type, run ncu --target [patch, minor, latest, newest, greatest].
How to Use Interactive Mode with npm-check-updates
ncu --interactive
// or
ncu -iInteractive mode allows you to select specific packages to update. By default, all packages are selected.
Navigate down through each package and use space to deselect, and enter when you are ready to upgrade all of the selected packages.
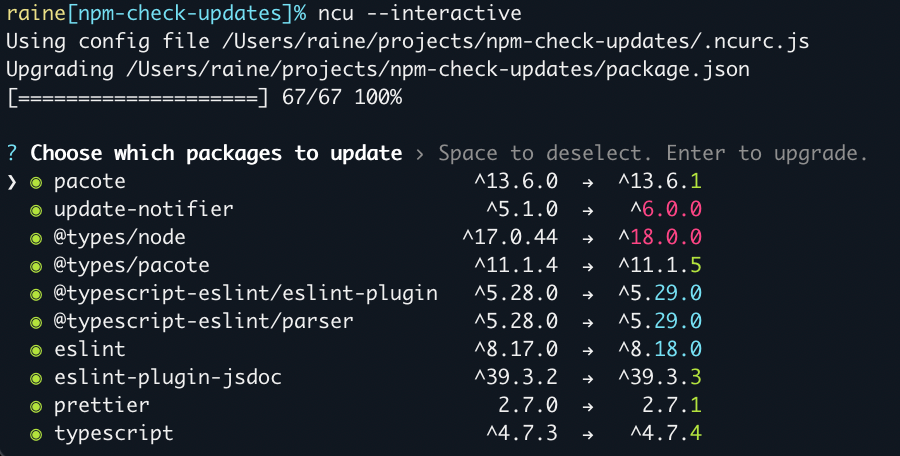
There are several ways to elevate the interactive npm-check-updates experience.
ncu --interactive --format groupThis command groups and organizes packages into major, minor and patch releases.

npm-check-updates provides other useful tools such as doctor mode which installs upgrades and runs tests to check for breaking changes.
I highly suggest taking a look at the documentation overall to learn more about all this package has to offer. The project is well-maintained along with a climbing weekly download rate of ~294,467 at the time of writing this article.
Summary
Getting in the habit of regularly updating your dependencies will help your apps' security and performance.
Both npm outdated and npm-check-updates are useful tools to check for packages that could use a version bump.
I suggest trying both of these out to see which provides a better developer experience.
I hope these methods help along the path of updating!