Object Oriented Programming is one of the most widely used programming paradigms. The name itself defines how it works. “Object Oriented” - the Object plays an important role. Manipulating objects and getting the results is the ultimate goal of Object Oriented Programming.
The languages that use Object Oriented Programming paradigms are known as Object Oriented Programming Languages. They are mostly high level languages such as
- Java
- C#
- Python - Python is both a Scripted/Structured & Object Oriented Language
To program in Object Oriented Programming, concepts called “Object Oriented Concepts” are used. These concepts simplify & add more value to Object Oriented Programming.
Those concepts are
- Encapsulation
- Abstraction
- Polymorphism
- Inheritance
Before moving into these concepts, we need to know about Class & Objects.
An Object is the basic run-time entity in OOP. In our day-today life we see a lot of objects like a television, mobile phone, dog, humans, cars & other living and non-living objects. These can be portrayed as objects in OOP.
A Class is a blueprint or prototype that defines variables/properties and methods/functions common to all objects of a certain kind. It's a logical component.
Simply said, Class is a user-defined data type. Objects are variables of a Class. Once the Class has been created we can create as many Objects as we want.
For example, take a class named Tree. State/properties of the Tree class are:
- Name of the tree
- Age of the tree
- Type of the tree
- Height of the tree
State/properties are used to define the attributes of an object.
That is, State/properties/attributes all represents the same thing.
Behaviors of the Tree can be:
- Giving fruit
- Falling of leaves
- Absorbing water from roots to the upper parts
- Creating shadows
Then, Mango is a variable of Class Tree. We can store and retrieve all the properties & behaviors we defined for the class Tree by creating an object of Mango.
Syntax for Creating an object of Mango from class Tree:
Tree Mango;
Encapsulation
Have you ever used a tablet/medicine which encapsulated by a colored cover?
 Medicines are encapsulated & placed inside the tablet
Medicines are encapsulated & placed inside the tablet
Inside that medicine is kept safely. We can't find anything with our naked eye. To see what's inside we need to open up that cover....
Similarly, all the data members (variables,attributes/properties) & behaviors(functions/methods) are gathered together and closed. Class is a best example for Encapsulation.
For an instance,
You are going to the pharmacy to buy prescribed medicines for you. You handover the prescription to the pharmacist and then he/she will take the medicine from the store & give you the bill.
In this scenario,
Medicines - act as variables or properties or attributes
Pharmacist - act as member function/method where he/she helps in giving you the medicine
You - external application or another software code
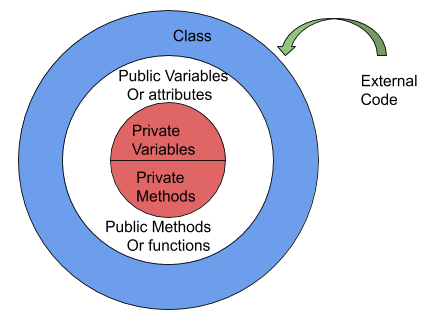
By using Encapsulation, data can be restricted from the usage of the outside world. The function defined in the class only can access the properties. This can be defined at the implementation stage. Programmers can define and specify the accessibility of the member variables while under development rather than making all the variables global like in procedural languages. This controlling of accessibility is also known as Information hiding.
Encapsulation allows to expose the necessary things and hiding the important things from the outside world. So, the hidden parts of a class acts like Encapsulation & the exposed parts acts like Abstraction.
Abstraction
Exposing necessary features of a class without explaining much or details is done by Abstraction.
Today morning I wanted to make a hot tea and I used a water kettle to boil the water. I just turned on the On button to start boil water. I don’t want to know the inner workflow of the kettle where it has high resistance and that resistance produces heat and boils the water. Instead, I have to fulfill my work easily. Therefore, having this On button to boil the water is known as Abstraction.
Similarly, we can take a remote controller which helps in manipulating TV operation using simple keys in the remote.
Data abstraction is a programming technique that depends on the separation of interface and implementation.
This data abstraction can be archived from using 2 different classes while coding using OOP
- Abstraction class: (0-100)% abstraction
- Interface class: 100% abstraction
Inheritance
The word itself describe what its functionality. Everyone has their inheritance qualities from their birth. You could have your grandparents/ your parents qualities from your birth. This is what Inheritance does in OOP.
A class can have properties & methods of its parent class. Additionally the class can have its own properties and methods too. The parent class is called as base class. The class that inherits base class is called as derived class. Inheritance is the most powerful feature of OOP.
By using Inheritance effectively we could save a lot of time and reduce the errors in our program. This causes us to increase the quality of work and productivity.
There are different types of Inheritance
- Single Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multi Level Inheritance
Polymorphism
Polymorphism is a Greek term which refers to the ability of taking more than one form / overloading.
Say for example we all know about functions in programming. They take different arguments inside parenthesis. Polymorphism is nothing but with the same function name, different arguments passed to get the result.
For e.g :- function called sum can take 2 arguments or 3 arguments.
sum(3,4) sum(10,23,56)
Calling these functions by providing suitable number of parameters will give the result according to how the called function has designed.
How the program distinguish which function need to be executed at the above scenario?
There is a feature called Dynamic binding in OOP. This will call the actual function according to the program execution. When the program runs the function with 2 arguments compiler takes the two argument functions to execute the program similarly for 3 arguments too.
Until the run-time, compiler won’t know exactly which function need to be invoked. It depends on the way the program calls the function name. This is also be known as Late binding.
Uses of Object Oriented Concepts
- Data can be hidden from outside using Encapsulation (Information hiding)
- Code can be reused by using Inheritance
- Operators/methods.functions can be overloaded by using Polymorphism. I.e: same function or operator name can be used for multi-tasking
- Data abstraction can be archived from Abstraction.
- Project migrations are easy (can be converted to larger size from smaller size)
- Partitioning the works for same project
- Manageable software complexity
Areas of application of OOP
- AI and expert systems
- Enterprise applications
- Neural Network and parallel programming
- Office automation systems
Hope you enjoyed a brief introduction to Object Oriented Concepts by reading. I hope to write how can we program Object Oriented Programming in my upcoming posts too.
Please send you feedback about my article to parathan19@gmail.com

