You can now solve the classic Project Euler programming problems using the Rust language. Each of these problems comes with a user-friendly test suite.
Here's the full Project Euler Rust GitHub repository.
If you do not know Rust, and want to learn it, you can start with freeCodeCamp's interactive Rust course.
All right. Let's see how to get started working through Project Euler in Rust.
How to Run the Project Euler Problems Locally in VSCode
First, you'll need to download and install the freeCodeCamp Courses VSCode extension.
Also, ensure you have the Microsoft Dev Containers VSCode extension.
Then, in an empty workspace, open the VSCode command palette with Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + P.
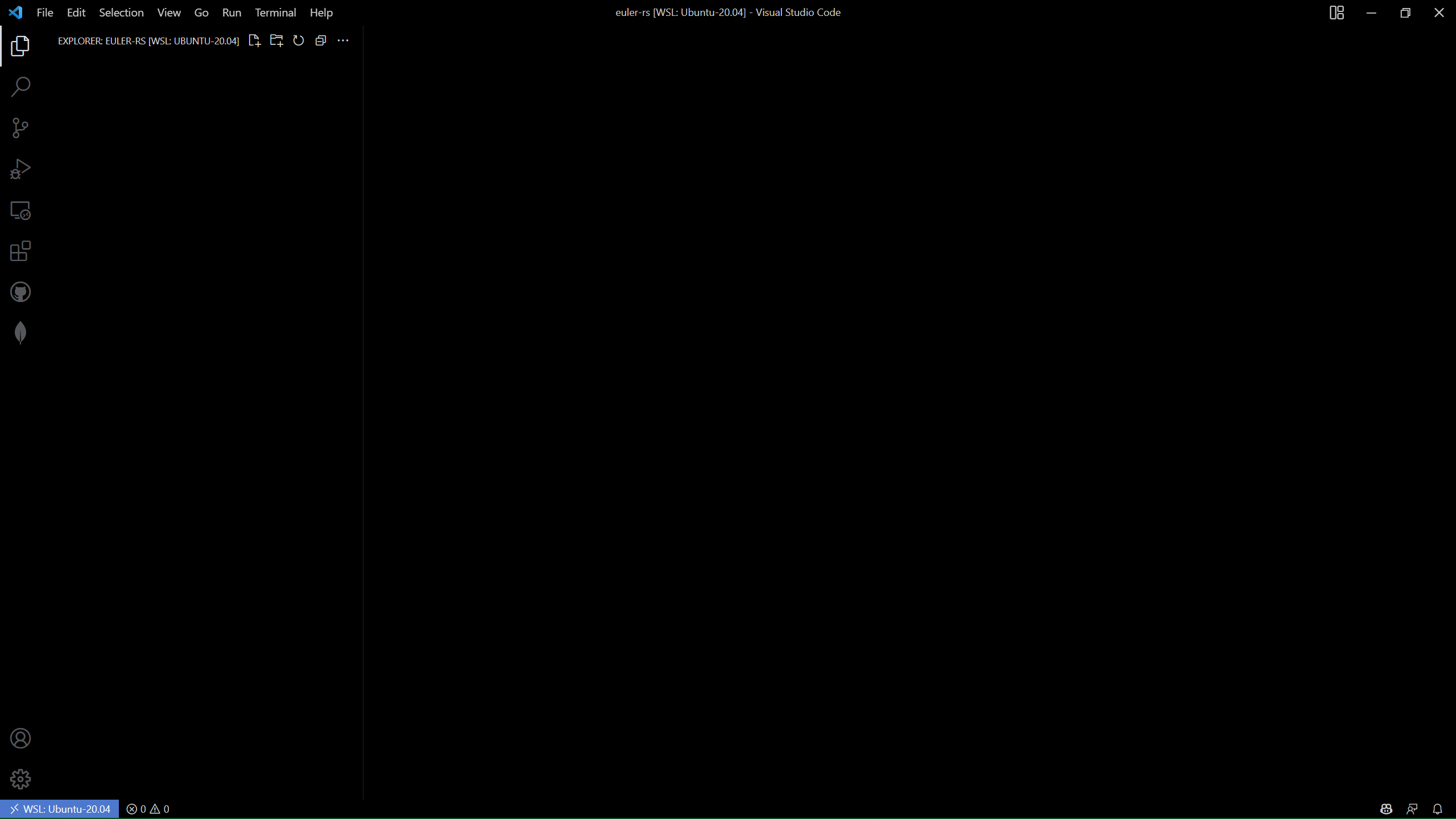
Select the command freeCodeCamp: Open Course.
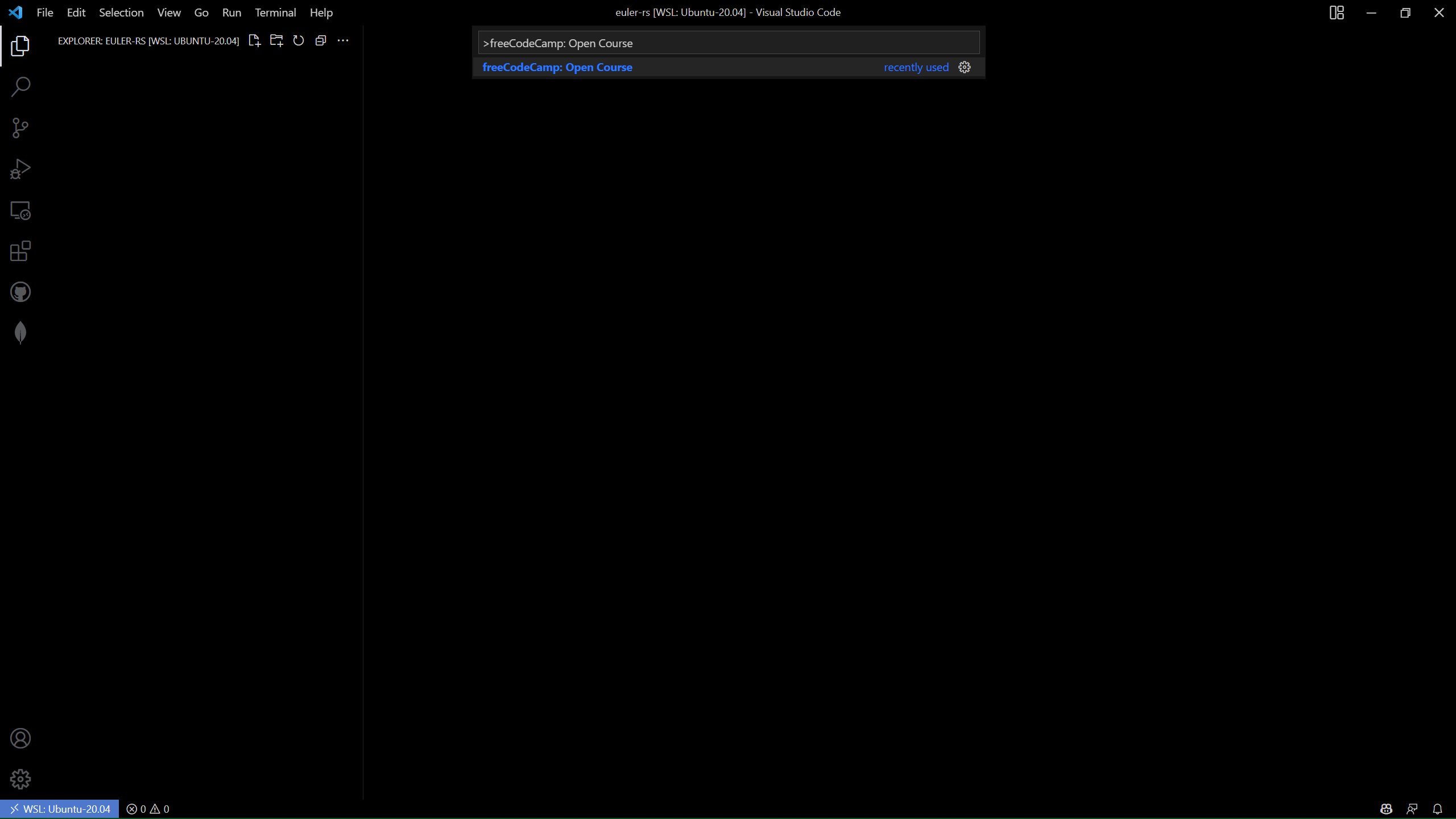
Next, choose the Project Euler: Rust option.
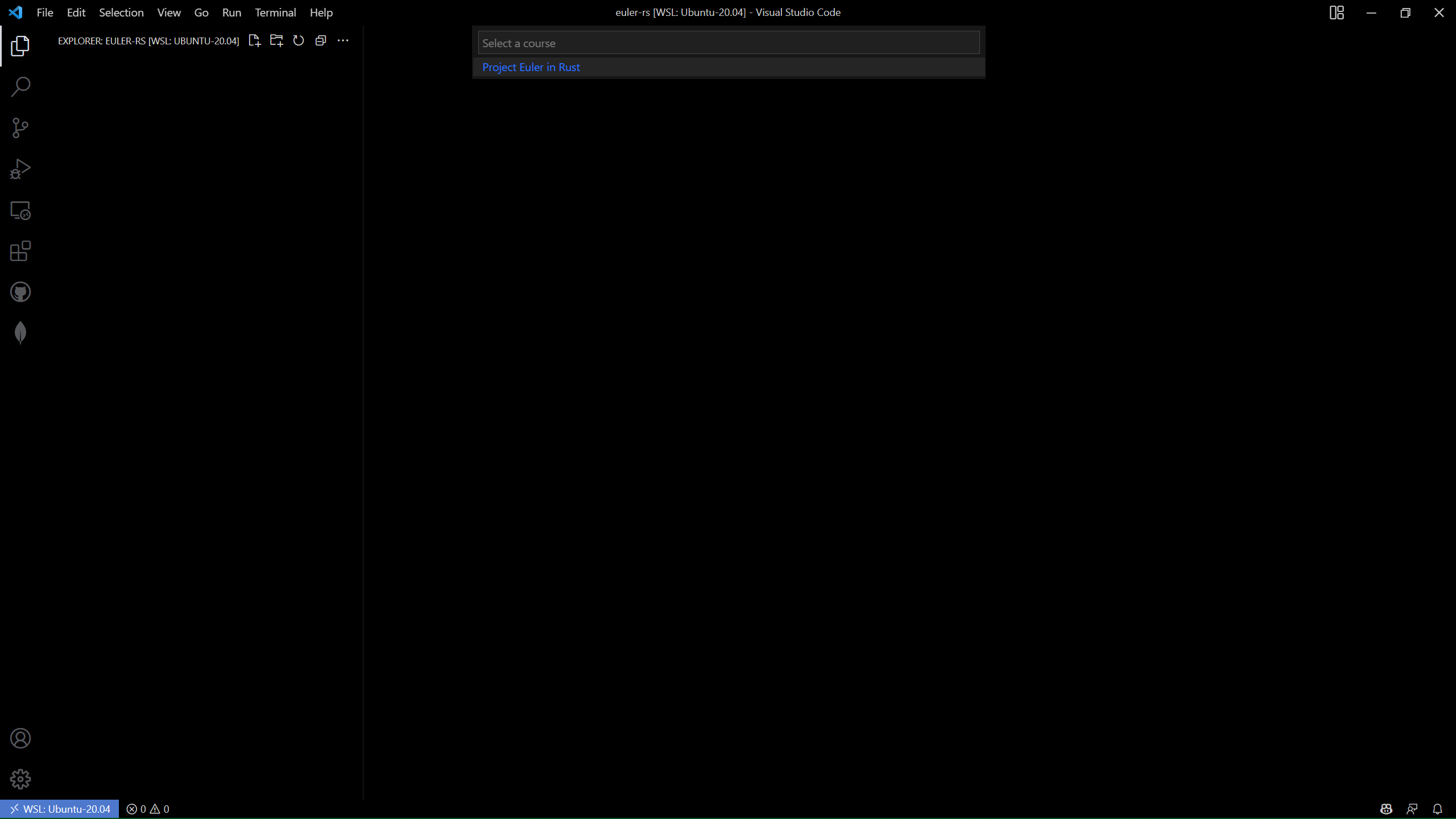
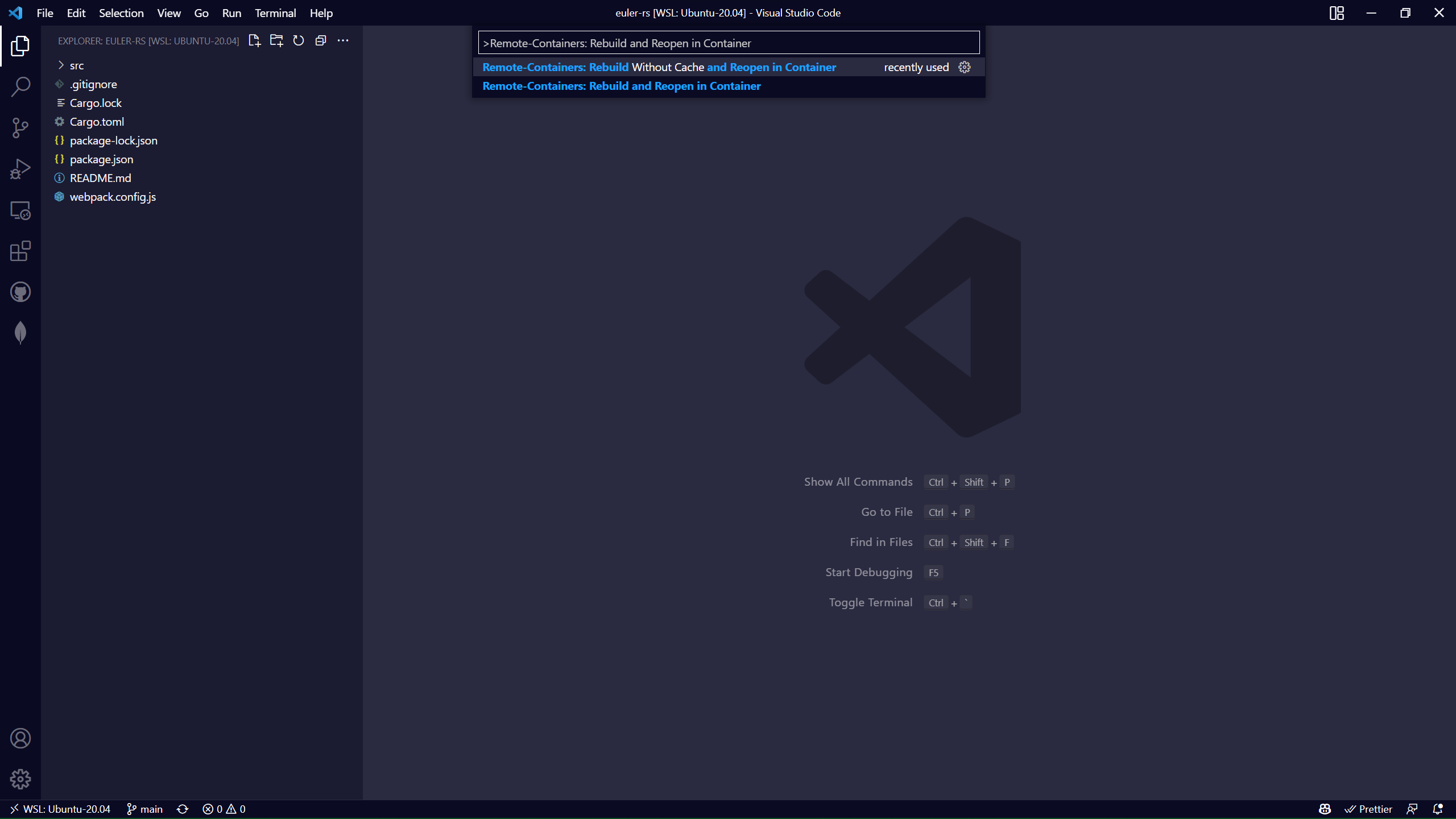
Once the course is cloned, open the command palette again and select Dev Containers: Rebuild and Reopen in Container.
How to Run the Project Euler Problems Locally without the Extension
If you would prefer to run these without the VS Code extension, you'll need to fork the repository:
Then clone your fork to your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/<your_username>/euler-rust.git
cd euler-rust
Build and open the Docker container like this:
docker build -f Dockerfile -t euler-rust .
And then start the course:
npm i && npm run start
Optionally, you can also clone and build the container with Docker like this:
docker build github.com/<your_username>/euler-rust
How to Run the Project Euler Problems Using Gitpod
GitPod is a popular tool for running a VM in your browser, and is yet another way you can solve these Project Euler problems. First, fork the repository:

Then open your fork in Gitpod: https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/<your_user_name>/euler-rust
Optionally, if you have the Gitpod browser extension installed, you can click the Gitpod button it adds to GitHub:

Useful Information
NOTE: If you are using any of the above methods with Docker, you will need to have Docker installed on your machine, and have the Daemon running.
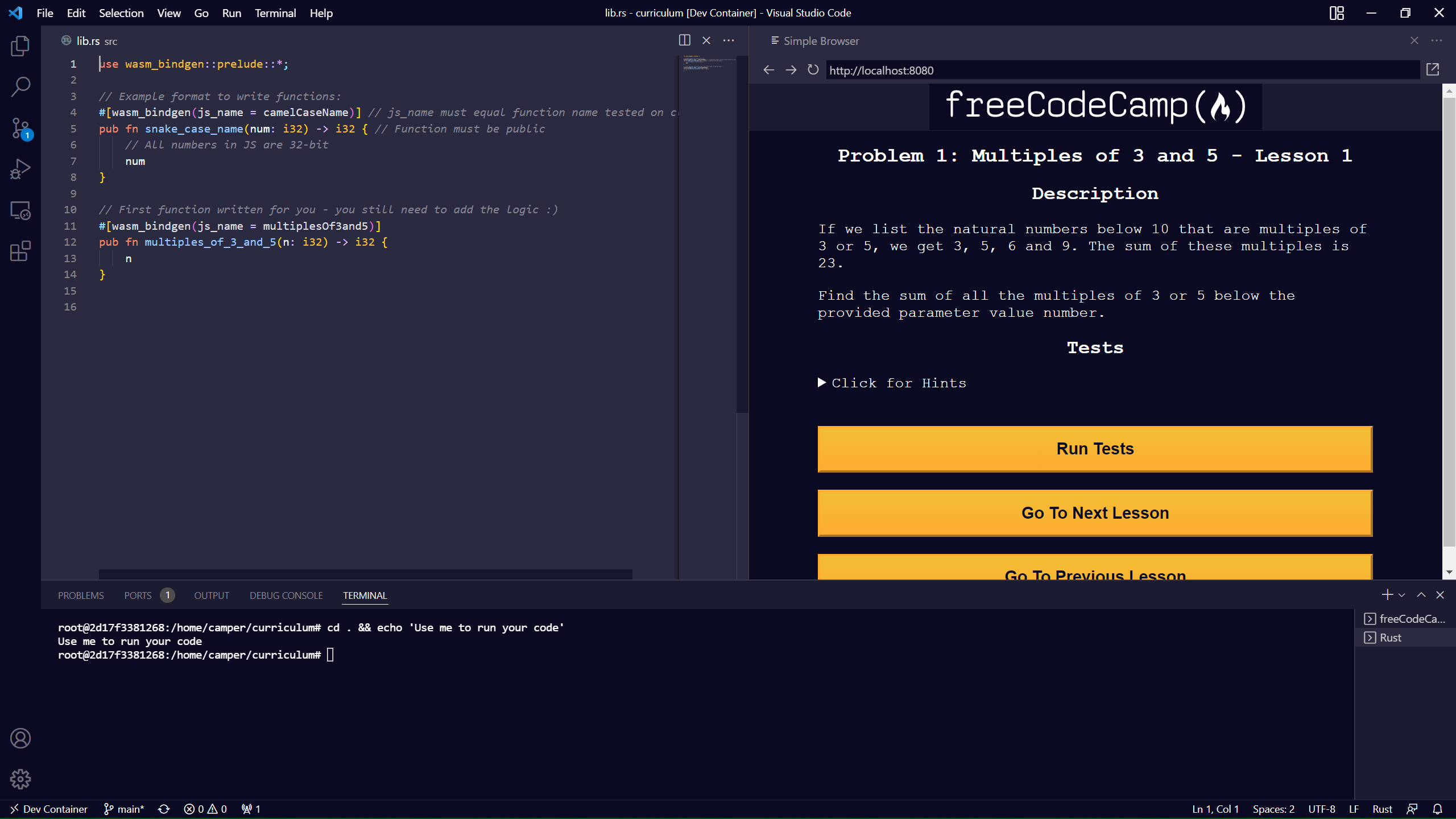
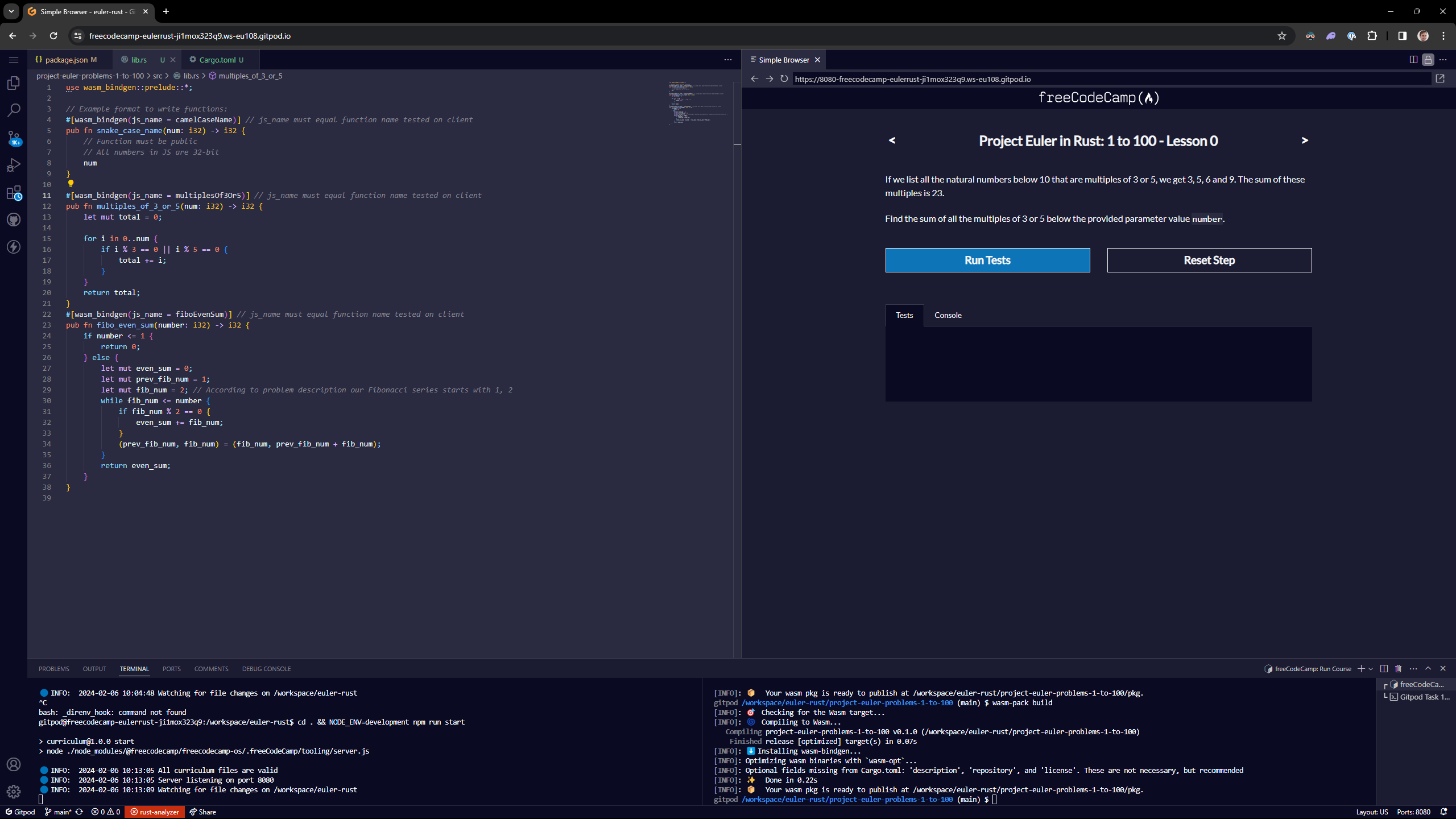
You should need to only edit the src/lib.rs file within each project-euler-problems-... directory, and you can follow the example code there to get started.
To compile your code, before running the tests, run:
wasm-pack build
If at any point you get stuck, I recommend that you check out more information about Rust with WASM. Otherwise, feel free to open a new topic on the freeCodeCamp forum.
How the Project Works
First, taking your Rust code in src/lib.rs:
use wasm_bindgen::prelude::*;
// Example format to write functions:
#[wasm_bindgen(js_name = camelCaseName)] // js_name must equal function name tested on client
pub fn snake_case_name(num: i32) -> i32 { // Function must be public
// All numbers in JS are 32-bit
num
}
The Rust is transpiled into JavaScript code using wasm-pack:
import * as wasm from "./curriculum_bg.wasm";
/**
* @param {number} n
* @returns {number}
*/
export function camelCaseName(num) {
var ret = wasm.camelCaseName(num);
return ret;
}
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Will these Project Euler problems be made available in other programming languages?
We welcome any and all well-intended contributions to the freeCodeCamp community. So, if you are interested in developing on a fork of the repository, please do so!
Can I save my progress on my freeCodeCamp.org account?
Not yet, but it is something that we can look into further.
The Docker step takes such a long time. Is there a quicker way to get started?
Well, provided you have the tenacity to install all the necessary tooling on your local machine, you can simple run the following commands within the project:
npm ci
npm run start
cd project-euler-problems-1-to-100
wasm-pack build
Now, you should be able to open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080/, and begin.