In this article, I will show you how I quickly set up and ran a Docker container for free on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
In short, I used a VM in the Always Free Tier of OCI, and for a side project I set up a dockerised Postgres database.
Let's get into the details a bit more now.
Why Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Oracle offers an Always Free cloud services option. You can see the details below:

Note that the workload of a container has to fit in the shape of this always free VM: VM.Standard.E2.1.Micro, 1/8 OCPU, 1 GB RAM and up to 480 Mbps network bandwidth (see the docs). The boot volume offers just over 45GB of disk storage.
In order for the container to be accessible, the ports mapped on the VM to container also have to be configured in ingress rules in the security list. We need to install Docker ourselves in the VM – it's provisioned with just an Oracle Linux image.
Lets get started.
Step 1 – Get yourself a tenancy and create a virtual machine
The first thing we need to do is create a VM. If you've got a cloud tenancy then you probably already know how to create an instance. If you're new to Oracle Cloud, then watch the below video and create an "always free" VM by signing up at https://cloud.oracle.com/free:
Note: Most of the details like availability zone, image details, and networking options are already pre-filled by Oracle. But you can adjust them if you want something specific. I went ahead with the standard settings.
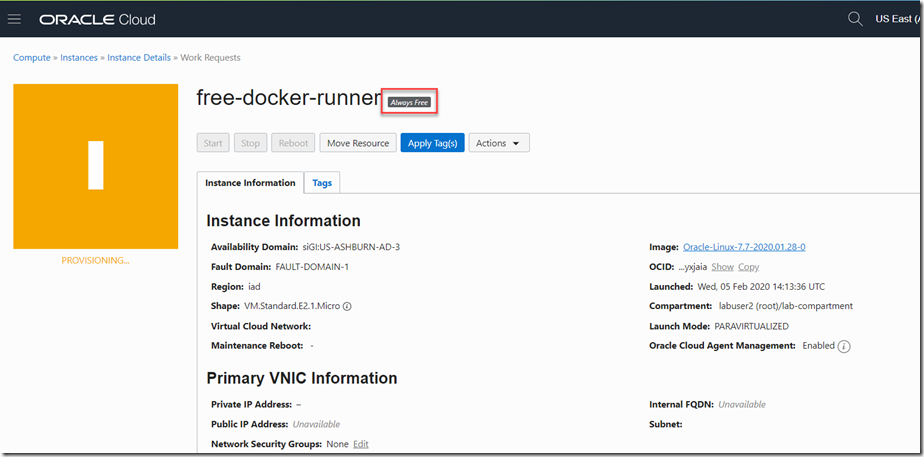
The VM will now be provisioned as is indicated here:
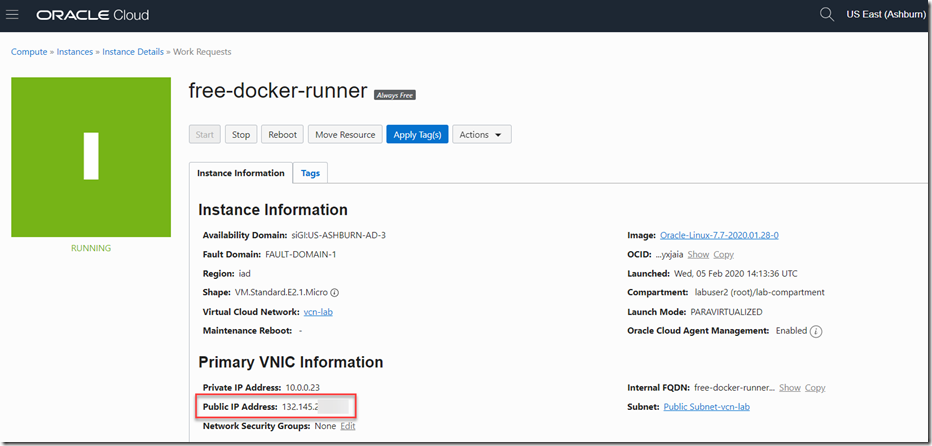
After a little while, the VM will be up and running — and has a public IP address assigned to it:
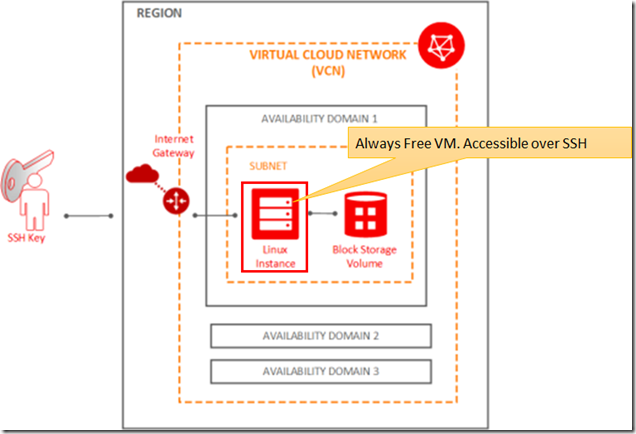
The situation at this point can be visualized as is shown in the below figure:
Step 2 – Setup the Ingress Rules in the Security List for your VM
This lets you open up the ports required for whatever container you want to run.
The VM is associated with a public subnet in a Virtual Cloud Network. The security list(s) for this subnet should be configured with ingress rules that make the required traffic possible to the port(s) that will be mapped to the container image.
Open the details page for the public subnet. Click on the security list (or create a new one):
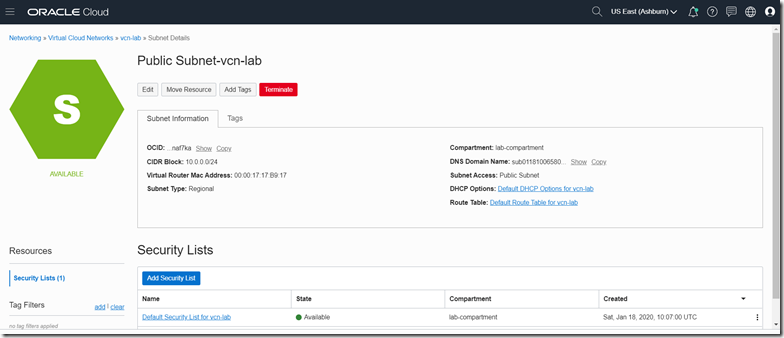
We will run the Postgres container image. The port we map in the VM to the Postgres container is one we can choose ourselves. Let’s pick 5432 which is the default port for Postgres.
We need to configure an ingress rule as below:
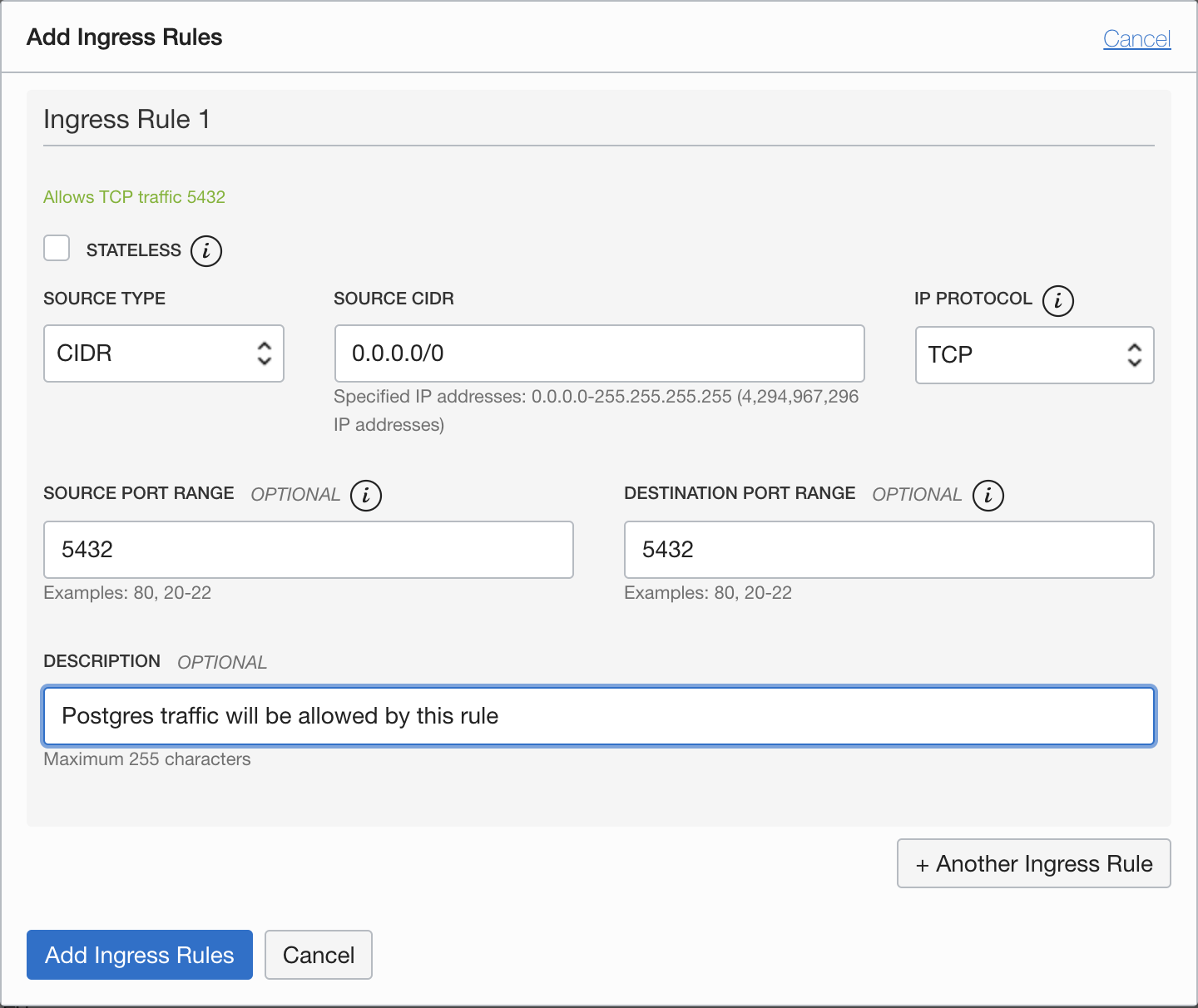
Source CIDR is set to 0.0.0.0/0, and Source Port Range is left blank (that is, All) which means that this rule applies to any client.
Step 3 – SSH into the VM and install Docker
At this point, we have a running VM instance with just a Linux Operating System but no Docker. Let’s SSH into the VM using this command:
ssh opc@public-id-address -i private-key-file
Replace the public-id-address with the public IP assigned to the VM. Replace private-key-file with a reference to the file that contains the SSH private key.
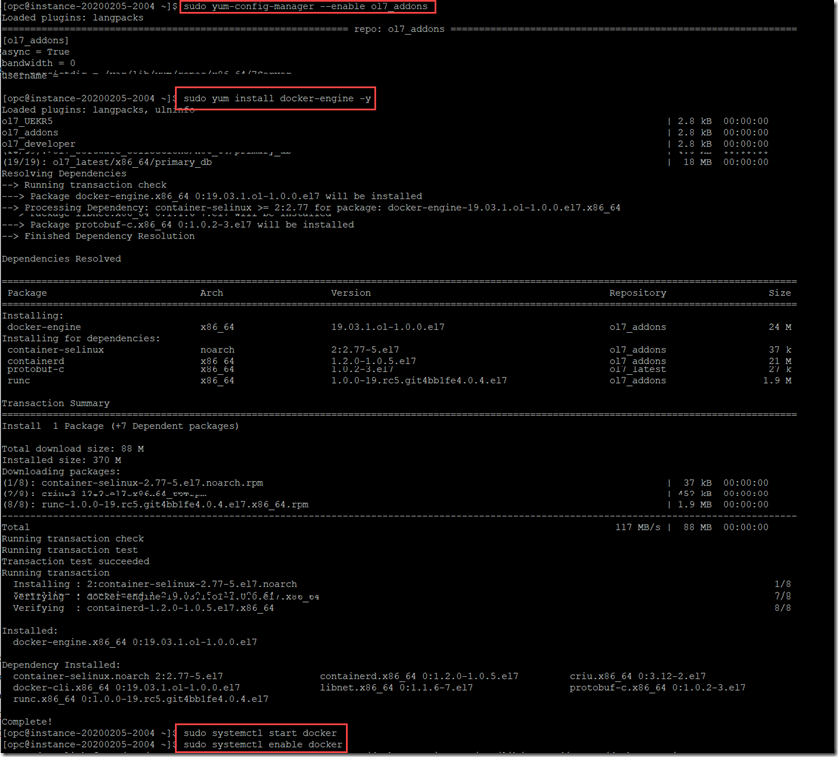
Now to install Docker, execute these commands:
sudo yum-config-manager --enable ol7_addons
sudo yum install docker-engine -y
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
To run Docker as a non-root user, read these instructions.
How to Run the Docker Container Image
With Docker installed, we can now run the Postgres container image.
Run the container image with this command. Don't forget to add a different password for POSTGRES_PASSWORD:
sudo docker run -d -p 5432:5432 --name postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword postgres
Use sudo docker ps to verify if the container is running. The above command will start a PostgreSQL database and map ports using the following pattern: -p <host_port>:<container_port>.
Port 5432 of our container will be mapped on port 5432 of our host or server.
Access the container on your host or server. We will create a database inside our Postgres container.
sudo docker exec -it postgres bash
Now you are ‘inside’ your container. We can access Postgres and create the database.
root@12d48fde2627:/# psql -U postgres
psql (13.3 (Debian 13.3-1.pgdg100+1))
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE testdb;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# \q
And with that we're done! You can exit your container (\q) and go to your local machine.
Here you need a PostgreSQL Client tool installed like DBeaver or pgAdmin. Connect to the DB server by using the public IP as the host, 5432 as the port, postgres as the username, the POSTGRES_PASSWORD as the password and connect to the testdb. Save the connect and you should now be able to access your DB.
Congrats, you have now run a Postgres Docker Container on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure!
Thanks for reading! I really hope that you find this article useful. I'm always interested to know your thoughts and happy to answer any questions you might have in your mind. If you think this post was useful, please share it to help promote this piece to others.
Thanks for reading! :)
P.S. Do feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn or Twitter.
Resources
This article leans heavily on the following material:
- Run Always Free Docker Container on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure - Lucas Jellema
- Connect From Your Local Machine to a PostgreSQL Database in Docker - Lorenz Vanthillo