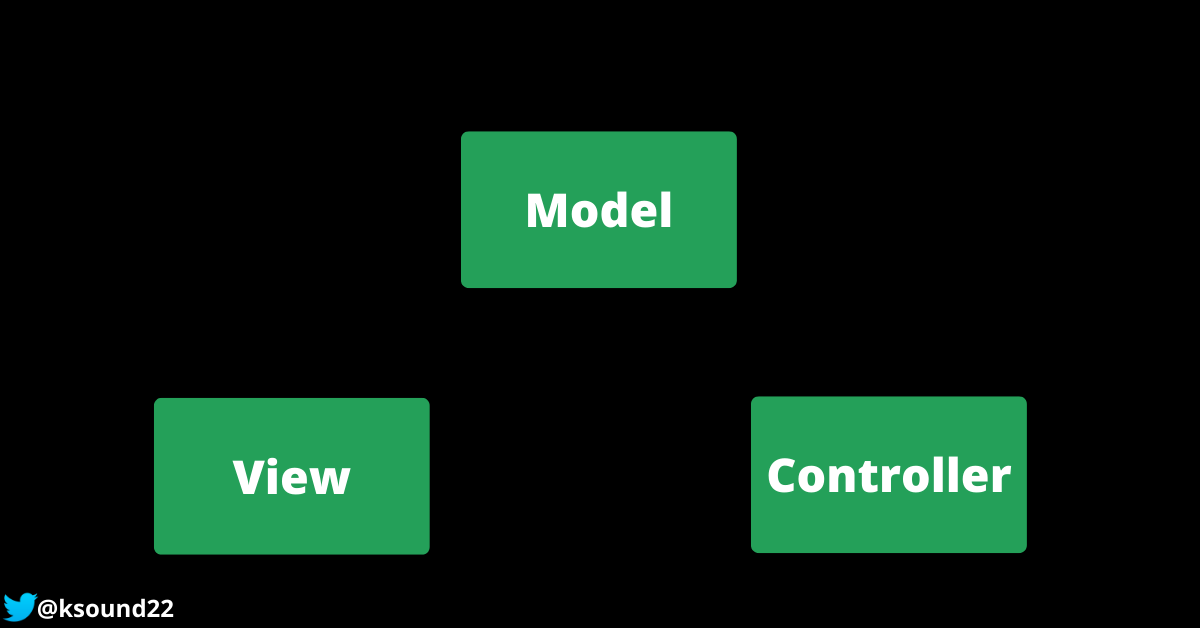
MVC is an abbreviation that stands for Model, View, and Controller. This architectural pattern was created in the late 1970s for making desktop apps, but it is now widely used in web application development.
In this article, I will dive deep into what MVC means alongside its 3 components, so you can understand it.
I have also prepared an infographic that can help you understand MVC better, but you have to read the article first. :)
What We'll Cover
- What is MVC and why is it Used
- Which Languages and Frameworks Use MVC?
- What is the Model in MVC?
- What is the View in MVC?
- What is the Controller in MVC?
- Conclusion
What is MVC and why is it Used?
In Computer science, MVC is a software design pattern for organizing application code into three interwoven parts – a model, view, and controller.
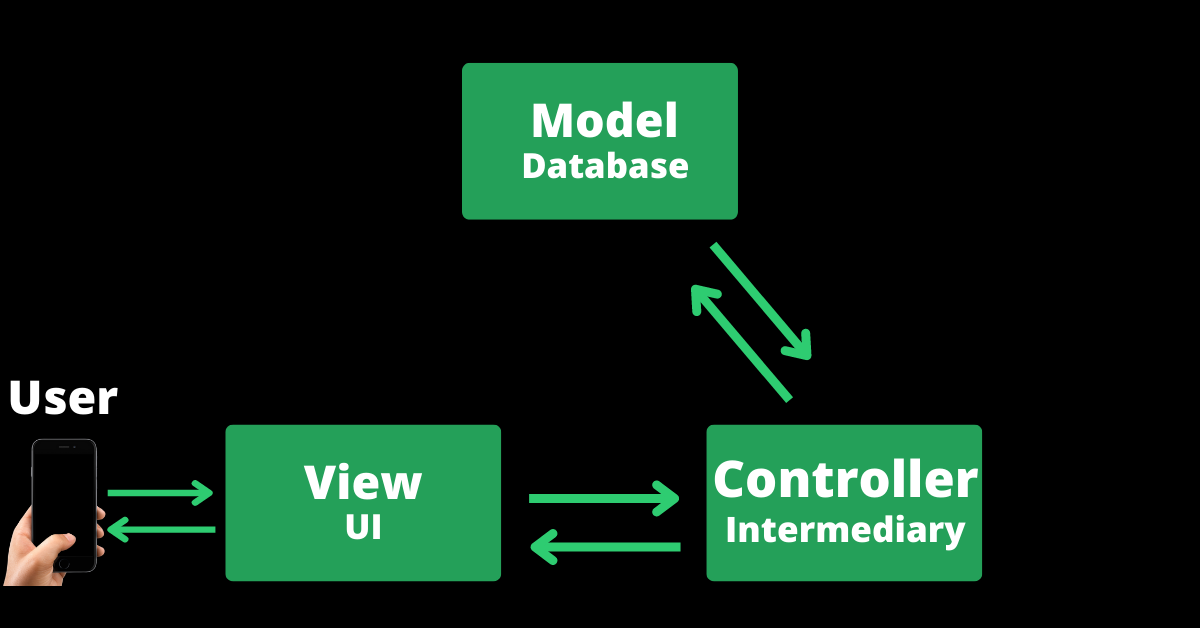
The model is the logic for interacting with the database, the view is the user interface the user interacts, and the controller is the intermediary between the view and model.
In many cases, the view never interacts directly with the model – the controller performs that function.
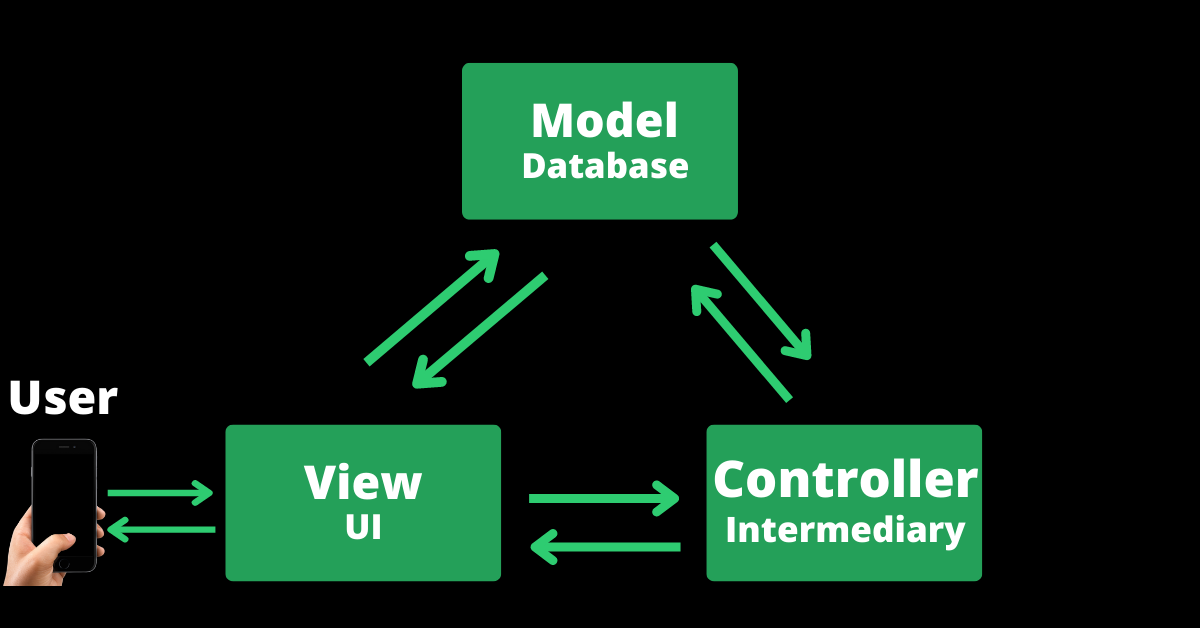
In some other frameworks, the model can interact with the view directly
The MVC design pattern aims to divide the application code into units of their own, so maintenance and optimization won’t be a hassle. This is popularly called “separation of concerns”.
Which Languages and Frameworks Use MVC?
In the past, MVC was used solely for making desktop GUIs. Today, many programming languages and frameworks implement MVC for web app development.
Some frameworks even force you to use MVC, so you might have been using MVC without realizing you’re using it.
In a full stack Express app, for example, developers would often divide the code into a model, controller, and client (view) folder.
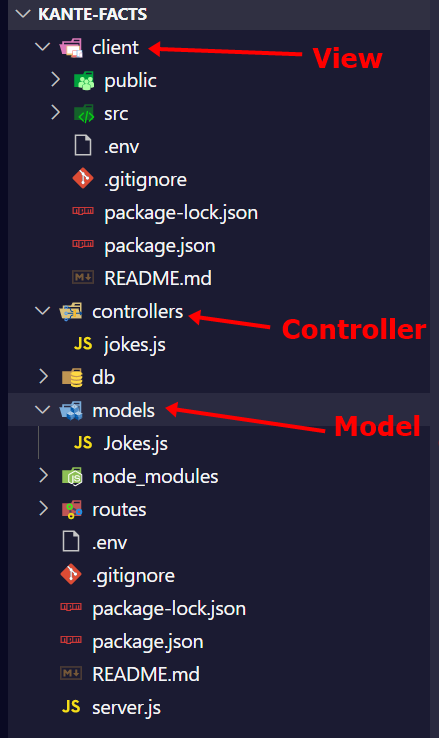
That is the folder structure of a joke generator I built for my favorite footballer.
Examples of programming languages that use MVC are C, C++, C#, Java, Ruby, Smalltalk, and many more.
The frameworks that use MVC are Angular, Express, Django, Flask, Laravel, Ruby on rails, and others.
What is the Model in MVC?
The model component contains the logic responsible for retrieving data from the database. For this, you can also use a JSON file in place of a database.
For instance, in the SQL database of an eCommerce application, this could be something like product-data = db.get(SELECT * FROM products;).
In many cases, the model communicates with the controller to send data to the view (user interface). In other cases, the model can send data directly to the view.
What is the View in MVC?
The view component is the part the user directly interacts with. It communicates with the controller to show what the user has requested with mouse and keyboard actions.
Languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are often used to implement this part. You can use frameworks like React, Vue, and Svelte, too.
Some developers also use template engines like Handlebars, ejs, and liquidjs to implement the view.
In an eCormerce application, the code could contain something like this:
<h1>{{product.name}}</h2>
<ul>
<p>{{product.description}}</p>
<p>{{product.delivery-modes}}</p>
What is the Controller in MVC?
The controller component is the intermediary between the model and the view. It is neither model nor view – it is the part that links them.
What the controller does with the view is receive and process the user requests and actions performed with the view (user interface). So, it processes requests like GET, POST, PUT or PATCH, and DELETE.
When the controller receives the user requests, it then communicates with the model to get what the user wants, then sends it back to the view (user interface) for the user to see.
Some pseudocode for what the controller does is in the snippet below:
if (success) {
show products;
} else {
show error;
}
Conclusion
The model-view-controller pattern has become a widely used architecture pattern for making web applications and other software products.
It might be confusing at first, but persistent learning and practice should help you clear up your confusion.
If you are still confused about what MVC is, look at it this way:
- you call a restaurant to order pizza – you are the
view - you give your order to a waiter – the waiter is the
controller - the waiter gets your pizza from the store and gives it to you – the store is the
model
You can see that you, the view, never have to go to the store for your pizza, just like the view never retrieves data directly from the model on many occasions.
Thanks for reading.