A virtual machine is a program you run on a computer that acts like it is a separate computer. It is basically a way to create a computer within a computer.
A virtual machine runs in a window on the host computer and gives a user the same experience they would have if they were using a completely different computer. Virtual machines are sandboxed from the host computer. This means that nothing that runs on the virtual machine can impact the host computer.
Virtual machines are often used for running software on operating systems that software wasn't originally intended for. For instance, if you are using a Mac computer you can run Windows programs inside a Windows virtual machine on the Mac computer. Virtual machines are also used to quickly set up software with an image, access virus-infected data, and test other operating systems.
A single physical computer can run multiple virtual machines at the same time. Often a server will use a program called a hypervisor to manage multiple virtual machines that are running at the same time. Virtual machines have virtual hardware, including CPUs, memory, hard drives, and more. Each piece of virtual hardware is mapped to real hardware on the host computer.
There are a few drawbacks with virtual machines. Since hardware resources are indirect, they are not as efficient as a physical computer. Also, when many virtual machines are running at the same time on a single computer, performance can become unstable.
Virtual Machine Programs
There are many different virtual machine programs you can use. Some options are VirtualBox (Windows, Linux, Mac OS X), VMware Player (Windows, Linux), VMware Fusion (Mac OS X) and Parallels Desktop (Mac OS X).
VirtualBox is one of the most popular virtual machine programs since it is free, open source, and available on all the popular operating systems. We'll show you how to set up a virtual machine using VirtualBox.
Setting up a Virtual Machine (VirtualBox)

VirtualBox is an open source Virtual Machine program from Oracle. It allows users to virtually install many operating systems on virtual drives, including Windows, BSD, Linux, Solaris, and more.
Since VirtualBox runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac, the process for setting up a virtual machine is pretty much the same in each operating system.
Start with downloading and installing VirtualBox. You can download it at this link: VirtualBox Downloads
You will also need to download an .iso file for the operating system that you want to run in your virtual machine. For instance, you can download a Windows 10 .iso file here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/software-download/windows10ISO
Once you have VirtualBox running, click the "New" button
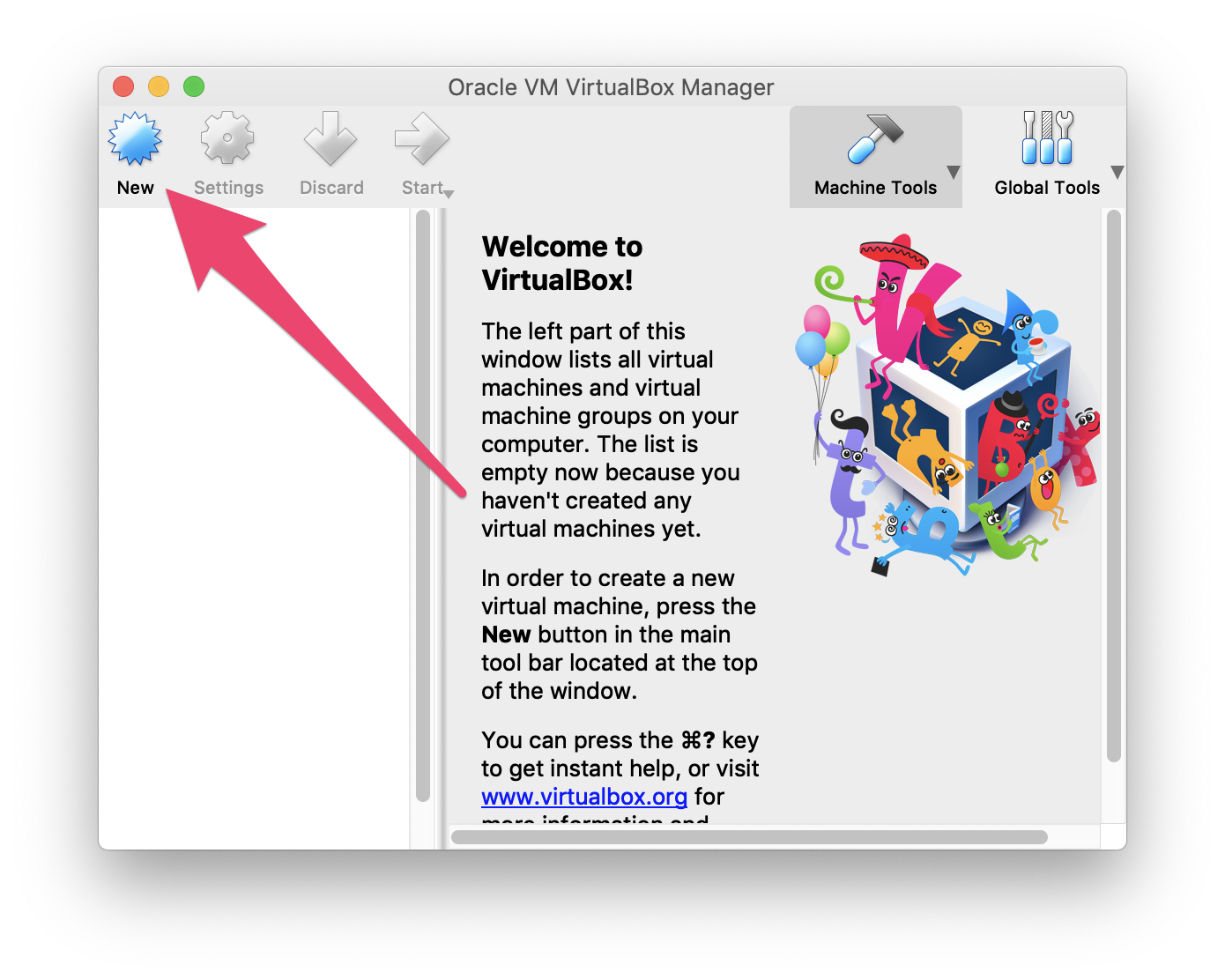
Next you will have to choose which OS you plan on installing. In the "Name" box, type the name of the OS you want to install. VirtualBox will guess the type and version based on the name you type in, but you can change these settings if you need to.
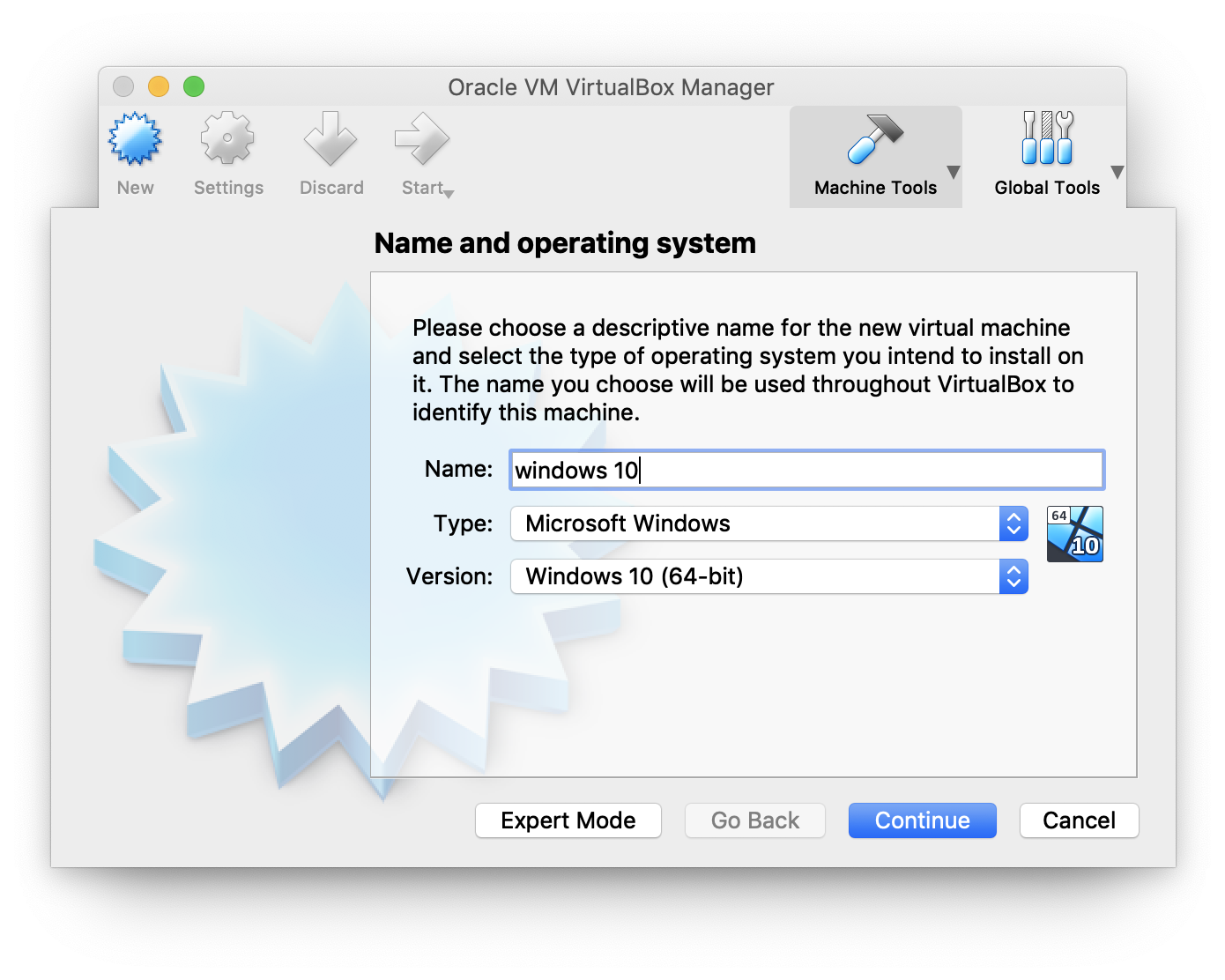
The wizard will automatically select default settings based on the OS type and version you selected. You can always change the settings as you go through the wizard. Just keep clicking "Continue" and "Create" until you get through the wizard. It's usually fine to use the defaults.
Next, start the virtual machine you just created by clicking "Start".
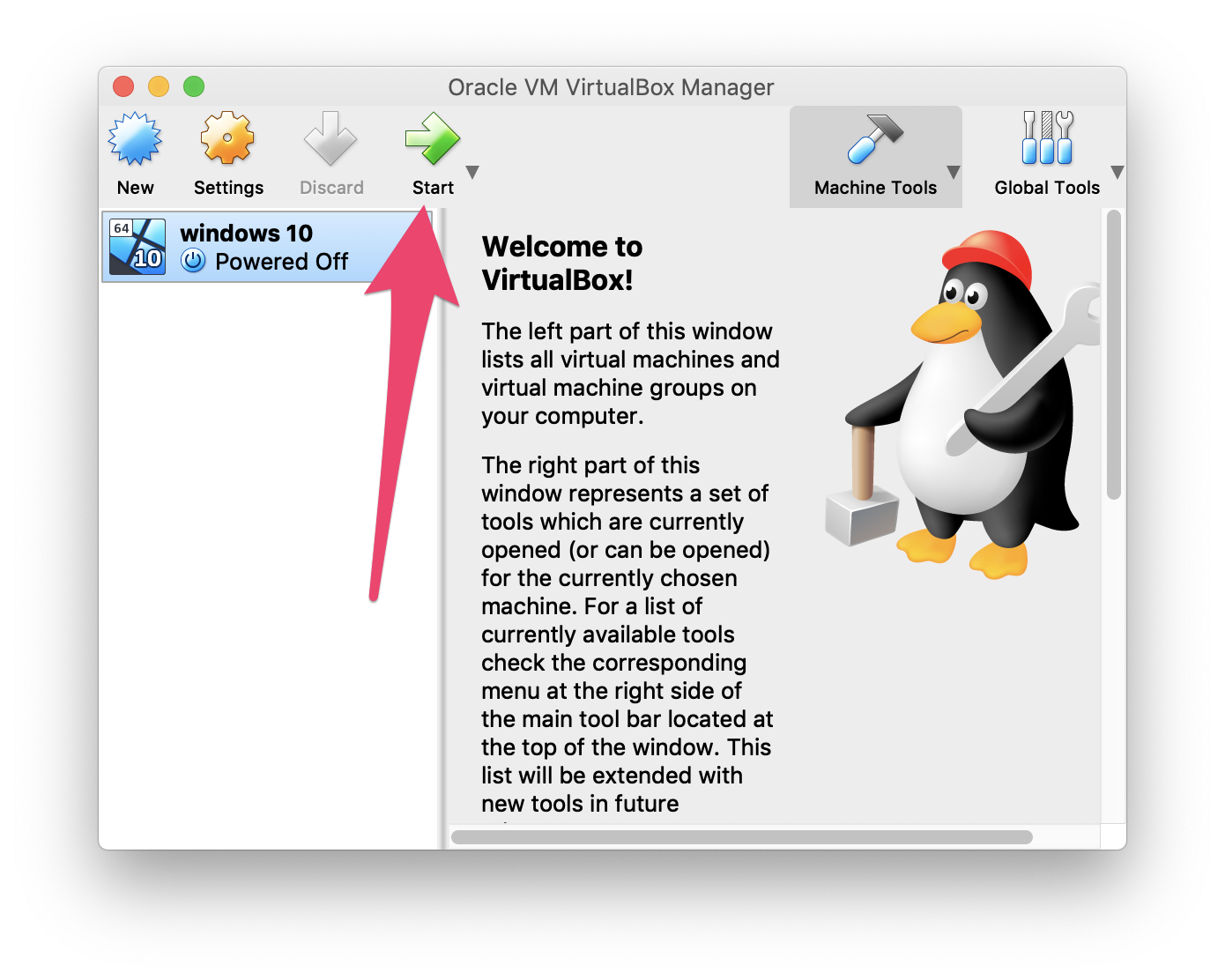
Once the virtual machine starts up, select the .iso image file you want to use.
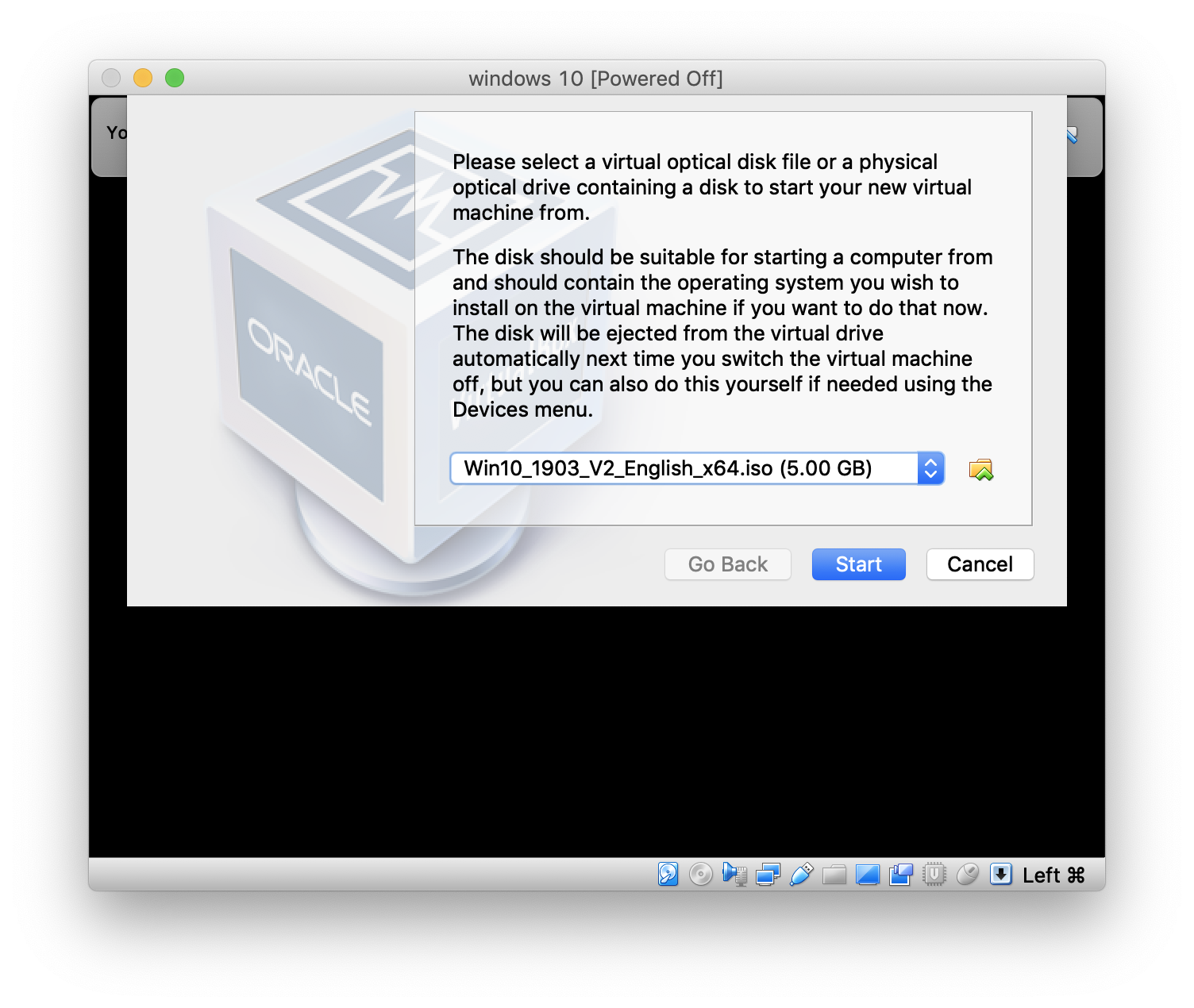
Your virtual machine will now load your selected operating system. The operating system may require some setup, but it will be the same setup that would be required if you had installed it on a standard computer.
Congratulations! You’ve run your first Virtual Machine in VirtualBox.
