Data is a powerful tool that drives everything you see and interact with on the internet.
It facilitates research and powers today's technology. It is the driving force behind today's artificial intelligence and robotics. And so much more.
Previously, these data were stored on paper, in physical files within cabinets. But now they are stored online in what is known as a database.
In this article, you will learn about what a database is, the two major types of databases, and then what SQL is and why it is important.
What is a Database?
A database is a structured collection of electronically stored data. These data can be accessed, managed, modified, updated, controlled, and organized with the help of a database management system (DBMS).
Data and DBMS are generally linked and referred to as a database system, frequently shortened to just a database.
There are several types of databases, depending on how data is stored, retrieved, and modified. But there are two major types, which are relational and non-relational databases.
What is a Relational Database?
A relational database, also known as a SQL database, is used to store data in tables. This means that the data is organized into rows and columns.
This type of database organizes data in predefined relationships and stores that data in one or more tables of columns and rows. This makes it easy to see and understand how different data structures relate to one another.

This type of database is referred to as “relational” because two or more tables may be related to each other.
For example, when you have a table of users with a unique id, you can use that id to store each user's order in a different order table and request them using the user's unique id.

Popular examples of relational database management systems are MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL, and Oracle. To access data from relational databases, you will use SQL (Structured Query Language).
What is a Non-Relational Database?
Non-Relational Databases, also known as NoSQL Databases, are databases that store data in a non-tabular format.
This means that data is not modelled in rows and columns but rather in key-value pairs. For example, in key-value pairs, you can have objects representing each user:

Examples of non-relational databases are MongoDB, Amazon DynamoDB, Redis, and lots more.
What is SQL?
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a query language used with relational databases such as MySQL, Oracle, MSSQL, PostgreSQL, and many others.
It is a query language that you can use to create and delete databases and tables, insert and read data into tables, delete data from tables, and much more.

For example, let's say that you have a table of users, as seen above, that holds the unique id, first name, last name, and age. You can use SQL to read or get specific data from the table, such as the first and last names only:
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM Users;
This will return a table with only the queried data:
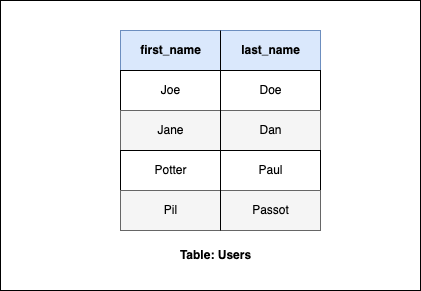
You can do a lot more with SQL, but this was just an introduction. If you want to learn more, I've linked a couple great resources below.
That's it!
In this article, you have learned the fundamental and major differences between relational and non-relational databases. You also learned that SQL is a query language used with relational databases to interact with the database.
There is more to what you can do with SQL and databases. You can learn more about SQL and databases by watching one of the best videos on the internet, with over 14 million views. You can also check out over 120 articles on SQL published on the freeCodeCamp publication.
Have fun coding!
You can access over 150 of my articles by visiting my website. You can also use the search field to see if I've written a specific article.

