In this article, I want my readers to get a picture of a very basic concept of the web world. Previously, I've written articles on the fancy stuff of today’s market, i.e. Angular journey, basics of react, etc. But, today, I want my readers to get into the journey which they encounter at first when they hit any URL.
As the topic is self explanatory - when we hit any URL then what happens? - let’s start!
Before discussing what happens after hitting the URL, we must go through what a URL actually is, and what different parts of the URL mean - right? Without wasting any time, let’s understand more about URLs.
URL – Uniform Resource Locator
If you look into its full form, then it is self explanatory: it has the location of the resources which we want to access. It is an address of the place where we want to go to interact with or find information.
Let's look into your daily life. If you want to visit your friend’s house for some work or to get information, you need their address. The same thing goes here in this big web world: we have to give an address of the website which we want to access. The web site is like the house and the URL is the address.
Anatomy of a URL
Now, we know what a URL is but we still don’t know about the parts of a URL. Let’s go!
Let’s take an example:
Here, the first part is ‘https’. This basically tells the browser which protocol it should use. It can be http, https, ftp, etc. A protocol is a set of rules that browser use for communication over the network. 'https' is basically a secure version, i.e. information is exchanged in a secure way.
The second part www.example.com is a domain name. You can relate it to your friend’s house. It is an address of website. We use it to reach to the server (trained computer) that is responsible for serving the information for that website. Wait! You might think, a seconds before I mentioned URL is the address whereas I also mentioned domain name is also address. You may have been confused. Don’t be confused!
Difference between URL and Domain Name
The major difference between both is that the URL is a complete address. URL tells about the method through which information should exchange, the path after reaching that website. Whereas the domain name is part of a URL.
Let’s take our previous example to better understand. You can say that your friend’s house address is a domain name, whereas the URL not only tells the friend’s house address (domain name) but also how you are going to communicate like talking in a separate room (secure) or in front of everyone (info can get leak). It also tells the path, i.e. at which part of the house you will go after entering into the house. Hence, the domain name is part of the URL. A domain name with more information is a URL.
I hope now you are clear with the URL. Let’s get into the next part.
Domain Name
In the previous part, I explained about domain names, but not in depth. I want you to go into it more. As I told you, the Domain name is the address of the website. It gives a unique identity to your website in such a huge web world. No two domain names can be the same BUT - Yes! There is ‘but’. This is not the only definition of a domain name. There is another story behind it. Let’s get into that story.
As we know, when we hit any URL or you can say domain name, then that website gets opened with its content. A server (a trained computer) serves it. We also know that every computer has an IP address which is used for communication over the internet. It is an address as its self explaining ‘IP address’. When we hit any URL, then we are actually hitting the IP address of the computer which is responsible for serving the website content (hosting).
But, now, you might think what the hell...is everything an address? Why does this domain name exist if the IP address is there? Why can’t we use IP address to get content of the website?
Yes! You can use IP addresses to get content of the website but really!.. Would you be able to remember each website’s associated IP address? Obviously not! It’s hard to remember the IP address of every website. That’s why domain names came into the market.
You can relate it to your contact list. You can’t remember every person’s number, but you can remember their name. Same concept applies here as well. You can’t remember those scary IP addresses, but you can easily remember domain names.
This huge amount of data is maintained in a database where the domain name with its IP address is stored. A system that stores domain names with its corresponding IP address is known as DNS (Domain name system) (I believe you must have heard about it).
I think I have discussed enough basics. Now, get a deep dive into the process of when we hit any URL.
DNS lookup to find IP address
After hitting the URL, the first thing that needs to happen is to resolve IP address associated with the domain name. DNS helps in resolving this. DNS is like a phone book and helps us to provide the IP address that is associated with the domain name just like our phone book gives a mobile number which is associated with the person’s name.
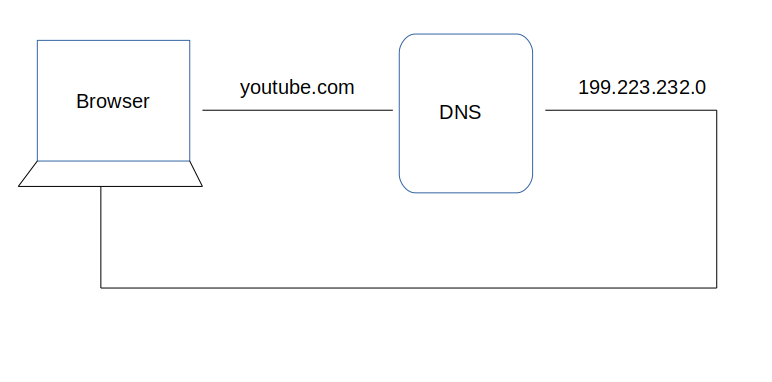
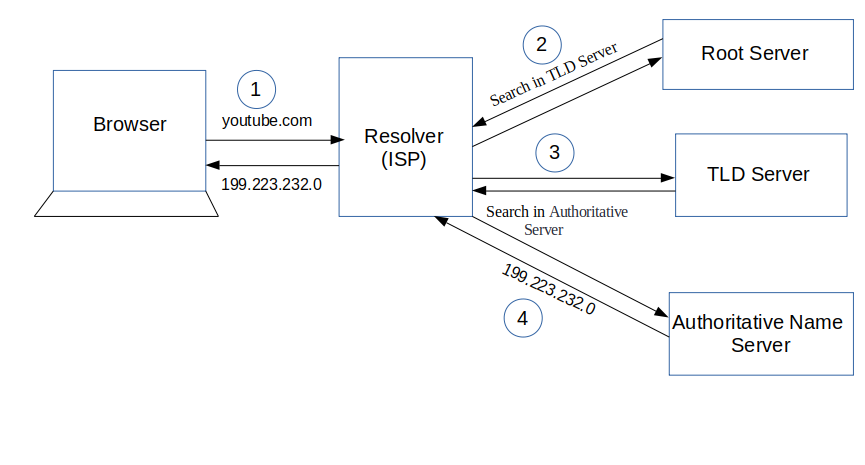
This is the overview, but there are four layers through which this domain name query goes through. Let’s understand the steps:
1. After hitting the URL, the browser cache is checked. As browser maintains its DNS records for some amount of time for the websites you have visited earlier. Hence, firstly, DNS query runs here to find the IP address associated with the domain name.
2. The second place where DNS query runs in OS cache followed by router cache.
3. If in the above steps, a DNS query does not get resolved, then it takes the help of resolver server. Resolver server is nothing but your ISP (Internet service provider). The query is sent to ISP where DNS query runs in ISP cache.
4. If in 3rd steps as well, no results found, then request sends to top or root server of the DNS hierarchy. There it never happens that it says no results found, but actually it tells, from where this information you can get. If you are searching IP address of the top level domain (.com,.net,.Gov,. org). It tells the resolver server to search TLD server (Top level domain).
5. Now, resolver asks TLD server to give IP address of our domain name. TLD stores address information of domain name. It tells the resolver to ask it to Authoritative Name server.
6. The authoritative name server is responsible for knowing everything about the domain name. Finally, resolver (ISP) gets the IP address associated with the domain name and sends it back to the browser.
After getting an IP address, resolver stores it in its cache so that next time, if the same query comes then it does not have to go to all these steps again. It can now provide IP address from their cache.
This is all about the steps that is followed to resolve IP address that is associated with the domain name. Have a look below to better understand:
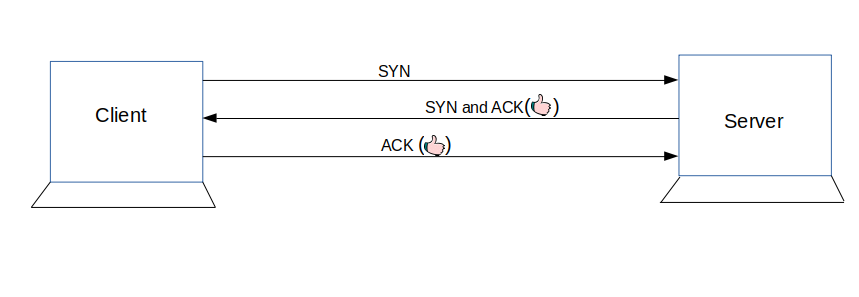
TCP connection initiates with the server by Browser
Once the IP address of the computer (where your website information is there) is found, it initiates connection with it. To communicate over the network, internet protocol is followed. TCP/IP is most common protocol. A connection is built between two using a process called ‘TCP 3-way handshake’. Let’s understand the process in brief:
1. A client computer sends a SYN message means, whether second computer is open for new connection or not.
2. Then another computer, if open for new connection, it sends acknowledge message with SYN message as well.
3. After this, first computer receives its message and acknowledge by sending an ACK message.
To better understand, look below diagram.
Communication Starts (Request Response Process)
Finally, the connection is built between client and server. Now, they both can communicate with each other and share information. After successful connection, browser (client) sends a request to a server that I want this content. The server knows everything of what response it should send for every request. Hence, the server responds back. This response contains every information that you requested like web page, status-code, cache-control, etc. Now, the browser renders the content that has been requested.
That’s it! All the above process happens when we hit any URL. Although this lengthy process takes less than seconds to complete. This is the answer to your question ‘what happens when we hit any URL in a browser?’
Thanks for reading!
