An AVL tree is an improved version of the binary search tree (BST) that is self-balancing. It was named after its inventors Adelson-Velsky and Landis, and was first introduced in 1962, just two years after the design of the binary search tree in 1960. The AVL tree is considered to be the first data structure of its type.
A BST is a data structure composed of nodes. It has the following guarantees:
- Each tree has a root node (at the top).
- The root node has zero or more child nodes.
- Each child node has zero or more child nodes, and so on.
- Each node has up to two children.
- For each node, its left descendants are less than the current node, which is less than the right descendants.
AVL trees have an additional guarantee:
- The difference between the depth of right and left subtrees cannot be more than one.
In order to maintain this guarantee, implementations of AVL trees include an algorithm to rebalance the tree when adding an additional element would cause the difference in depth between the right and left trees to be greater than one.
AVL trees have a worst case lookup, insert and delete time of O(log n).
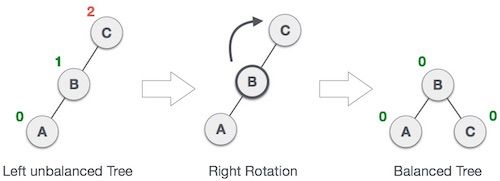
Right Rotation
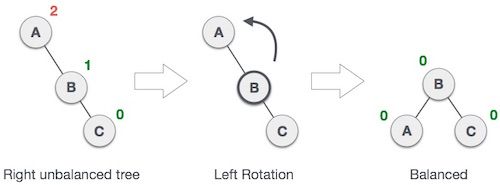
Left Rotation
AVL Insertion Process
This works similarly to a normal binary search tree insertion. After the insertion, you fix the AVL property by using left or right rotations.
- If there is an imbalance in left child of right subtree, then you perform a left-right rotation.
- If there is an imbalance in left child of left subtree, then you perform a right rotation.
- If there is an imbalance in right child of right subtree, then you perform a left rotation.
- If there is an imbalance in right child of left subtree, then you perform a right-left rotation.
Example
Here's an example of an AVL tree in Python:
class node:
def __init__(self,value=None):
self.value=value
self.left_child=None
self.right_child=None
self.parent=None # pointer to parent node in tree
self.height=1 # height of node in tree (max dist. to leaf) NEW FOR AVL
class AVLTree:
def __init__(self):
self.root=None
def __repr__(self):
if self.root==None: return ''
content='\n' # to hold final string
cur_nodes=[self.root] # all nodes at current level
cur_height=self.root.height # height of nodes at current level
sep=' '*(2**(cur_height-1)) # variable sized separator between elements
while True:
cur_height+=-1 # decrement current height
if len(cur_nodes)==0: break
cur_row=' '
next_row=''
next_nodes=[]
if all(n is None for n in cur_nodes):
break
for n in cur_nodes:
if n==None:
cur_row+=' '+sep
next_row+=' '+sep
next_nodes.extend([None,None])
continue
if n.value!=None:
buf=' '*int((5-len(str(n.value)))/2)
cur_row+='%s%s%s'%(buf,str(n.value),buf)+sep
else:
cur_row+=' '*5+sep
if n.left_child!=None:
next_nodes.append(n.left_child)
next_row+=' /'+sep
else:
next_row+=' '+sep
next_nodes.append(None)
if n.right_child!=None:
next_nodes.append(n.right_child)
next_row+='\ '+sep
else:
next_row+=' '+sep
next_nodes.append(None)
content+=(cur_height*' '+cur_row+'\n'+cur_height*' '+next_row+'\n')
cur_nodes=next_nodes
sep=' '*int(len(sep)/2) # cut separator size in half
return content
def insert(self,value):
if self.root==None:
self.root=node(value)
else:
self._insert(value,self.root)
def _insert(self,value,cur_node):
if value<cur_node.value:
if cur_node.left_child==None:
cur_node.left_child=node(value)
cur_node.left_child.parent=cur_node # set parent
self._inspect_insertion(cur_node.left_child)
else:
self._insert(value,cur_node.left_child)
elif value>cur_node.value:
if cur_node.right_child==None:
cur_node.right_child=node(value)
cur_node.right_child.parent=cur_node # set parent
self._inspect_insertion(cur_node.right_child)
else:
self._insert(value,cur_node.right_child)
else:
print("Value already in tree!")
def print_tree(self):
if self.root!=None:
self._print_tree(self.root)
def _print_tree(self,cur_node):
if cur_node!=None:
self._print_tree(cur_node.left_child)
print ('%s, h=%d'%(str(cur_node.value),cur_node.height))
self._print_tree(cur_node.right_child)
def height(self):
if self.root!=None:
return self._height(self.root,0)
else:
return 0
def _height(self,cur_node,cur_height):
if cur_node==None: return cur_height
left_height=self._height(cur_node.left_child,cur_height+1)
right_height=self._height(cur_node.right_child,cur_height+1)
return max(left_height,right_height)
def find(self,value):
if self.root!=None:
return self._find(value,self.root)
else:
return None
def _find(self,value,cur_node):
if value==cur_node.value:
return cur_node
elif value<cur_node.value and cur_node.left_child!=None:
return self._find(value,cur_node.left_child)
elif value>cur_node.value and cur_node.right_child!=None:
return self._find(value,cur_node.right_child)
def delete_value(self,value):
return self.delete_node(self.find(value))
def delete_node(self,node):
## -----
# Improvements since prior lesson
# Protect against deleting a node not found in the tree
if node==None or self.find(node.value)==None:
print("Node to be deleted not found in the tree!")
return None
## -----
# returns the node with min value in tree rooted at input node
def min_value_node(n):
current=n
while current.left_child!=None:
current=current.left_child
return current
# returns the number of children for the specified node
def num_children(n):
num_children=0
if n.left_child!=None: num_children+=1
if n.right_child!=None: num_children+=1
return num_children
# get the parent of the node to be deleted
node_parent=node.parent
# get the number of children of the node to be deleted
node_children=num_children(node)
# break operation into different cases based on the
# structure of the tree & node to be deleted
# CASE 1 (node has no children)
if node_children==0:
if node_parent!=None:
# remove reference to the node from the parent
if node_parent.left_child==node:
node_parent.left_child=None
else:
node_parent.right_child=None
else:
self.root=None
# CASE 2 (node has a single child)
if node_children==1:
# get the single child node
if node.left_child!=None:
child=node.left_child
else:
child=node.right_child
if node_parent!=None:
# replace the node to be deleted with its child
if node_parent.left_child==node:
node_parent.left_child=child
else:
node_parent.right_child=child
else:
self.root=child
# correct the parent pointer in node
child.parent=node_parent
# CASE 3 (node has two children)
if node_children==2:
# get the inorder successor of the deleted node
successor=min_value_node(node.right_child)
# copy the inorder successor's value to the node formerly
# holding the value we wished to delete
node.value=successor.value
# delete the inorder successor now that it's value was
# copied into the other node
self.delete_node(successor)
# exit function so we don't call the _inspect_deletion twice
return
if node_parent!=None:
# fix the height of the parent of current node
node_parent.height=1+max(self.get_height(node_parent.left_child),self.get_height(node_parent.right_child))
# begin to traverse back up the tree checking if there are
# any sections which now invalidate the AVL balance rules
self._inspect_deletion(node_parent)
def search(self,value):
if self.root!=None:
return self._search(value,self.root)
else:
return False
def _search(self,value,cur_node):
if value==cur_node.value:
return True
elif value<cur_node.value and cur_node.left_child!=None:
return self._search(value,cur_node.left_child)
elif value>cur_node.value and cur_node.right_child!=None:
return self._search(value,cur_node.right_child)
return False
# Functions added for AVL...
def _inspect_insertion(self,cur_node,path=[]):
if cur_node.parent==None: return
path=[cur_node]+path
left_height =self.get_height(cur_node.parent.left_child)
right_height=self.get_height(cur_node.parent.right_child)
if abs(left_height-right_height)>1:
path=[cur_node.parent]+path
self._rebalance_node(path[0],path[1],path[2])
return
new_height=1+cur_node.height
if new_height>cur_node.parent.height:
cur_node.parent.height=new_height
self._inspect_insertion(cur_node.parent,path)
def _inspect_deletion(self,cur_node):
if cur_node==None: return
left_height =self.get_height(cur_node.left_child)
right_height=self.get_height(cur_node.right_child)
if abs(left_height-right_height)>1:
y=self.taller_child(cur_node)
x=self.taller_child(y)
self._rebalance_node(cur_node,y,x)
self._inspect_deletion(cur_node.parent)
def _rebalance_node(self,z,y,x):
if y==z.left_child and x==y.left_child:
self._right_rotate(z)
elif y==z.left_child and x==y.right_child:
self._left_rotate(y)
self._right_rotate(z)
elif y==z.right_child and x==y.right_child:
self._left_rotate(z)
elif y==z.right_child and x==y.left_child:
self._right_rotate(y)
self._left_rotate(z)
else:
raise Exception('_rebalance_node: z,y,x node configuration not recognized!')
def _right_rotate(self,z):
sub_root=z.parent
y=z.left_child
t3=y.right_child
y.right_child=z
z.parent=y
z.left_child=t3
if t3!=None: t3.parent=z
y.parent=sub_root
if y.parent==None:
self.root=y
else:
if y.parent.left_child==z:
y.parent.left_child=y
else:
y.parent.right_child=y
z.height=1+max(self.get_height(z.left_child),
self.get_height(z.right_child))
y.height=1+max(self.get_height(y.left_child),
self.get_height(y.right_child))
def _left_rotate(self,z):
sub_root=z.parent
y=z.right_child
t2=y.left_child
y.left_child=z
z.parent=y
z.right_child=t2
if t2!=None: t2.parent=z
y.parent=sub_root
if y.parent==None:
self.root=y
else:
if y.parent.left_child==z:
y.parent.left_child=y
else:
y.parent.right_child=y
z.height=1+max(self.get_height(z.left_child),
self.get_height(z.right_child))
y.height=1+max(self.get_height(y.left_child),
self.get_height(y.right_child))
def get_height(self,cur_node):
if cur_node==None: return 0
return cur_node.height
def taller_child(self,cur_node):
left=self.get_height(cur_node.left_child)
right=self.get_height(cur_node.right_child)
return cur_node.left_child if left>=right else cur_node.right_child